Floor of the pharynx
- 1. Floor of the pharynx
- 2. Floor of the pharynx ŌĆó Development of the tongue. ŌĆó Development of thyroid gland.
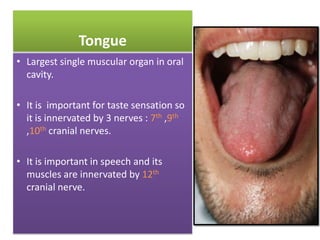
- 3. Tongue ŌĆó Largest single muscular organ in oral cavity. ŌĆó It is important for taste sensation so it is innervated by 3 nerves : 7th ,9th ,10th cranial nerves. ŌĆó It is important in speech and its muscles are innervated by 12th cranial nerve.
- 4. Development of tongue Muscles Mucosa Anterior 2/3 Of tongue Posterior 1/3 Of tongue
- 5. Mucosa : Anterior 2/3 of tongue: ŌĆó It developed from endodermal floor of the pharynx. ŌĆó In region of 1st pharyngeal arch. ŌĆó 3 Swellings appear: ’üČ Median swelling tuberculum imper ’üČ RT. and Lt. lateral swellings.
- 6. Mucosa ŌĆó Posterior 1/3 of tongue: ŌĆó It develops from endodermal floor of the pharynx. ŌĆó In regions of 2nd,3rd,4th pharyngeal arches. ŌĆó Only one swelling called hypo branchial eminence ŌĆó Anterior part ŌĆó Posterior part. post. Part of tongue. Epiglottis.
- 7. Stages of tongue development
- 8. Muscles ŌĆó All muscles of tongue except: palatoglossus m. are developed from 2nd,3rd,4th occipital myotomes.
- 9. Congenital anomalies Macro glossia Bifid tongue Tie tongue Aglossia Micro glossia
- 10. Thyroid gland ŌĆó 1st endocrine gland. ŌĆó Very important gland. thyroid H.is very important for development of neonatal brain. ŌĆó Its development starts ;24th day of gestation.
- 11. Development of thyroid gland ŌĆó It developed from endodermal floor of the pharynx. ŌĆó between 1st,2nd pharyngeal arches. ŌĆó Thyroid primordium thyroid diverticulum thyroglossal duct. ŌĆó Thyro glossal duct descends ant. To hyoid bone then ant. To larnyx. ŌĆó Its lower end proliferates to form thyroid lobes ithmus. ŌĆó Descent COMPLETE at 7th gestational week
- 13. Development of cells of thyroid gland: 1. Thyroid follicles diverticulum. endoderm of thyroid 2. Para follicular cells endoderm of ultimo branchial body[ from 6th pharyngeal pouch]. N.B : inner capsule ct. septa mesoderm.
- 14. Fate of thyroglossal duct ŌĆó Upper end foramen caecum. apex of sulcus terminalis . ŌĆó Intermediate part degenerates. ŌĆó Lower end pyramidal lobe glandulae thyroidae. levator
- 15. Pyramidal lobe ŌĆó In up to 50% of people. ŌĆó Persistance of the tower end of thyro glossal duct. ŌĆó Attached to hyoid bone by levator glandulae thyroidae.
- 16. Congenital anomalies ŌĆó thyro glossal duct if persists can form a sinus or fistulae or cyst. 1. Thyro glossal cyst: persistant of a part of this duct. ’ā╝ Many sites for thyro glossal cyst. Commonest site
- 17. 2. Thyroid agenesis: apsent gland >>>>>>> cause cretinism. 3.Ectopic thyroid: common in the back of tongue >>>>>>>> lingual thyroid .












![Development of cells of thyroid gland:
1. Thyroid follicles
diverticulum.
endoderm of thyroid
2. Para follicular cells
endoderm of ultimo
branchial body[ from 6th pharyngeal pouch].
N.B
: inner capsule ct. septa
mesoderm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floorofthepharynx-131109155038-phpapp02/85/Floor-of-the-pharynx-13-320.jpg)




