Introduction to Engineering (Beasiswa Indonesia Maju)
- 1. Introduction to Engineering Dr. Ir. Muhammad Amin Sulthoni
- 2. How lucky you are!!! 6-12 (SD) 13-15 (SMP) 16-18 (SMA) 19-24 (PT) Angka Partisipasi Sekolah 99,10% 95,92% 73,15% 25,99% Angka Partisipasi Murni 97,88% 80,89% 61,87% NA Angkatan Kerja 34,8 juta 26 juta 44,1 juta 18 juta 28,3% 21,15% 35,88% 14,65 ŌĆó Sumber: BPS ŌĆó Mahasiswa baru ITB 2022: 5100 (Total), 2085 (SNMPTN), 1716 (SBMPTN), 1269 (Mandiri) ŌĆó Penerima BIM 2022: 3755 (total), 220 (bergelar) jenjang S1 dan S2 di 14 PT 7 Negara
- 3. History of Engineering (1) ŌĆó The first engineer known by name and achievement is Imhotep, builder of the Step Pyramid at ß╣óaqq─ürah, Egypt, ~ 2550 BCE. ŌĆó Followed then... ŌĆó The Pharos (great lighthouse) of Alexandria (~250 BC) ŌĆó The Pont du Gard aqueduct (~60 AD) ŌĆó The Colosseum of Rome (~80 AD) ŌĆó The Borobudur (~825 AD)
- 4. History of Engineering (2) ŌĆó Civil Engineering first professional society: 18th century ŌĆó Mechanical Engineering: Improvements to the steam engine by James Watt in 1769 including the invention of the steam condenser ŌĆó Electrical Engineering: Electric cell invented in 1800 by Alessandro Volta ŌĆó In the late 20th century electrical and electronics engineers outnumbered all others in the world. ŌĆó Chemical engineering: 19th-century proliferation of industrial processes involving chemical reactions in metallurgy, food, textiles, and many other areas. By 1880 the use of chemicals in manufacturing had created an industry whose function was the mass production of chemicals.
- 5. Terminology ŌĆó The words engine and ingenious are derived from the same Latin root, ingenerare, which means ŌĆ£to create.ŌĆØ ŌĆó Engineering: the application of science to the optimum conversion of the resources of nature to the uses of humankind.
- 6. Principles ŌĆó Associated with engineering is a great body of (special) knowledge (BoK) ŌåÆ Electrical Engineering, Mechanical Engineering,ŌĆ”etc ŌĆó Preparation (Education) for professional (engineering) practice involves extensive training in the application of that knowledge. ŌĆó Standards of engineering practice are maintained through the efforts of professional societies.
- 7. Body of Knowledge of Electrical Engineering 7 BASIC SCIENCE AND MATHEMATICS CORE SUBJECTS Digital System, Electronics, Circuit and Signal, Discrete Mathematics, Statistics, Programming, Electromagnetics, Engineering Mathematics BREADTH SUBJECTS Advanced Electronics, Power System, Telecommunications, Computer Architecture, Signal Processing, Digital Control System, Microprocessors, System Engineering, Hardware Implementation ELECTIVE DEPTH SUBJECTS CAPSTONE PROJECTS
- 8. Scientist versus Engineer ŌĆó The function of the scientist is to know, while that of the engineer is to do. ŌĆó Scientist tool is the scientific method, while engineer tool is the engineering design method. ŌĆó Scientists add to the store of verified systematized knowledge of the physical world, and engineers bring this knowledge to bear on practical problems. ŌĆó Unlike scientists, engineers are not free to select the problems that interest them. They must solve problems as they arise, and their solutions must satisfy conflicting requirements.
- 9. Engineering Functions ŌĆó Problem solving is common to all engineering work. The problem may involve quantitative or qualitative factors; it may be physical or economic; it may require abstract mathematics or common sense. ŌĆó Of great importance is the process of creative synthesis or design, putting ideas together to create a new and optimum solution: Engineering design method. ŌĆó The engineering solution is the optimum solution that taking many factors into account. It may be the most reliable within a given weight limit, the simplest that will satisfy certain safety requirements, or the most efficient for a given cost. Usually, efficiency costs money, safety adds to complexity, and improved performance increases weight. In many engineering problems the social and environmental costs are significant. ŌĆó Engineering design is set of engineering decisions.
- 10. Major Function of Engineering (1) ŌĆó Research. Using mathematical and scientific concepts, experimental techniques, and inductive reasoning, the research engineer seeks new principles and processes. ŌĆó Development. Development engineers apply the results of research to useful purposes. Creative application of new knowledge may result in a working model of a new electrical circuit, a chemical process, or an industrial machine. ŌĆó Design. In designing a structure or a product, the engineer selects methods, specifies materials, and determines shapes to satisfy technical requirements and to meet performance specifications. ŌĆó Construction. The construction engineer is responsible for preparing the site, determining procedures that will economically and safely yield the desired quality, directing the placement of materials, and organizing the personnel and equipment.
- 11. Major Function of Engineering (2) ŌĆó Production. Plant layout and equipment selection are the responsibility of the production engineer, who chooses processes and tools, integrates the flow of materials and components, and provides for testing and inspection. ŌĆó Operation. The operating engineer controls machines, plants, and organizations providing power, transportation, and communication; determines procedures; and supervises personnel to obtain reliable and economic operation of complex equipment. ŌĆó Management. In some countries and industries, engineers analyze customersŌĆÖ requirements, recommend units to satisfy needs economically, and resolve related problems. ŌĆó Other functions: maintenance, troubleshooting, standardization, etc
- 12. The Engineering Design ŌĆó Problem formulation is key in engineering design ŌĆó Accurate problem formulation results optimum solution ŌĆó Accurate problem formulation requires comprehensive understanding on problemŌĆÖs background and situation ŌĆó Optimum solution must consider the constraints and chosen systematically among possible alternatives
- 13. Keywords in Engineering ŌĆó Knowledge of Math and Basic Sciences ŌĆó Specific Body of Knowledge ŌĆó Engineering Tools: SW, HW, Supportive tools ŌĆó Engineering Design Methodology ŌĆó Optimization of Conflicting Constraints
- 14. Engineering Professional Path (in Indonesia) Sarjana Teknik By PT Insinyur By PSPPI PT Insinyur Profesional By PII STRI By PII (International) Professional Engineer Example: Asian Eng by AFEO Reference: UU Keinsinyuran No. 11 / 2014
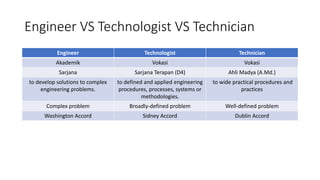
- 15. Engineer VS Technologist VS Technician Engineer Technologist Technician Akademik Vokasi Vokasi Sarjana Sarjana Terapan (D4) Ahli Madya (A.Md.) to develop solutions to complex engineering problems. to defined and applied engineering procedures, processes, systems or methodologies. to wide practical procedures and practices Complex problem Broadly-defined problem Well-defined problem Washington Accord Sidney Accord Dublin Accord
- 16. International Agreement on Engineering Education ŌĆó Washington Accord: a multi-lateral agreement between bodies responsible for accreditation or recognition of tertiary-level engineering qualifications within their jurisdictions who have chosen to work collectively to assist the mobility of professional engineers. ŌĆó ABET, IABEE ŌĆó On the basis of Outcome Based Education (OBE), mandatory competencies for future engineer are established: ŌĆó Mastery of Math and Basic Sciences for engineering activities ŌĆó Engineering design skill ŌĆó Communication, Ethics, and Team working ŌĆó Experimental skill ŌĆó Lifelong learning
- 17. Study Abroad
- 18. TokyoTech QNERC ŌĆó 2008-2012 ŌĆó Oda Laboratory, O-Okayama Campus ŌĆó Kodai, Miyamae-ku, Kawashaki-shi, Kanagawa-ken
- 19. Study abroad is not always better, butŌĆ” ŌĆó Chance to exposed to frontier science R & D ŌĆó Chance for better academic atmosphere ŌĆó Chance to exposed to other cultures
- 20. Tips for study abroad ŌĆó Gather all available information: ŌĆó Administrative matters ŌĆó Local daily live and culture ŌĆó Your program studyŌĆÖs curricula ŌĆó Local Indonesian students ŌĆó Learn and master the language ŌĆó BlendŌĆ” Join local Indonesian community ŌĆó Respect local culture and adapt ŌĆó Choose your friend carefully ŌĆó Save your money ŌĆó Focus, prioritize, focus
- 21. A sign of maturity is when you know your purpose in life, and are willing to live a life that fulfills that purpose