Presentation for Aircraft Stress Analysis Lections
1 like803 views
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°РөСӮ РҫСҒРҪРҫРІСӢ авиаСҶРёРҫРҪРҪРҫР№ РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮРё, РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҸ СҒРёР»СӢ, РҙРөР№СҒСӮРІСғСҺСүРёРө РҪР° СҒамРҫР»РөСӮ, Рё РҝСҖРёРҪСҶРёРҝСӢ СҖавРҪРҫРІРөСҒРёСҸ РІ РіРҫСҖРёР·РҫРҪСӮалСҢРҪРҫРј РҝРҫР»РөСӮРө. Р Р°СҒСҒРјР°СӮСҖРёРІР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ СҖазлиСҮРҪСӢРө СӮРёРҝСӢ СҒамРҫР»РөСӮРҫРІ РІ завиСҒРёРјРҫСҒСӮРё РҫСӮ РёС… РјР°РҪРөРІСҖРөРҪРҪРҫСҒСӮРё, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҫСҒРҪРҫРІРҪСӢРө СҖР°СҒСҮРөСӮРҪСӢРө СҒР»СғСҮаи РҙР»СҸ СҖР°СҒРҝСҖРөРҙРөР»РөРҪРёСҸ РҝРҫРҙСҠРөРјРҪРҫР№ СҒРёР»СӢ РәСҖСӢла. РўР°РәР¶Рө СҒРҫРҙРөСҖжаСӮСҒСҸ РҙР°РҪРҪСӢРө Рҫ СҒСӮР°СӮРёСҮРөСҒРәРёС… РёСҒРҝСӢСӮР°РҪРёСҸС… Рё РәРҫРҪСҒСӮСҖСғРәСӮРёРІРҪСӢС… СҒС…Рөмах РәСҖСӢР»СҢРөРІ.
1 of 45
Downloaded 34 times










Ad
Recommended
AVALIAГҮГғO PSICOMOTORA E DESENVOLVIMENTO MOTOR.pdfHELLEN CRISTINA
Мэ
O documento apresenta uma avaliação psicomotora para crianГ§as, utilizando a Escala de Desenvolvimento Motor (EDM) que abrange motricidade fina, global, equilГӯbrio, esquema corporal, organização espacial e temporal, e lateralidade. Гү descrito um mГ©todo para identificar atrasos no desenvolvimento motor por meio de atividades especГӯficas adequadas a diferentes idades. AlГ©m disso, inclui um questionГЎrio sobre transtornos de coordenação, enfatizando a impossibilidade de avaliar as dificuldades motoras sem considerar o contexto amplo da crianГ§a.Projeto 200 anossandrabio
Мэ
O documento descreve atividades e aprendizado sobre a vinda da famГӯlia real ao Brasil em 1808, incluindo a influГӘncia da missГЈo artГӯstica francesa nas artes. TambГ©m destaca as condiГ§Гөes de vida dos escravos e as transformaГ§Гөes sociais e econГҙmicas no Brasil durante esse perГӯodo. AlГ©m disso, menciona melhorias na infraestrutura e instituiГ§Гөes, como escolas e bibliotecas, promovidas pela famГӯlia real.A linguagem cenograficaMarcelo Blanco
Мэ
Este documento Г© uma dissertação de mestrado apresentada Г Universidade de SГЈo Paulo que trata da linguagem cenogrГЎfica. A dissertação analisa a evolução histГіrica da cenografia e do edifГӯcio teatral, explora os instrumentos cГӘnicos como espaГ§o, luz e corpo, e propГөe um projeto de ensino da linguagem cenogrГЎfica voltado para o teatro e outras mГӯdias.O mito da caverna.Elder Barbosa Leite
Мэ
O documento apresenta um resumo do Mito da Caverna de PlatГЈo. O mito descreve prisioneiros acorrentados em uma caverna vendo apenas sombras projetadas na parede. Se um prisioneiro escapar e ver o mundo real, os outros nГЈo acreditariam e poderiam matГЎ-lo se tentasse libertГЎ-los. O mito Г© uma metГЎfora da ignorГўncia humana e da importГўncia do conhecimento.ОҳОөПүПҒОҜОөПӮ ОіО№Оұ П„О·ОҪ ПҖО·ОіО® П„О·ПӮ ОіОҪПҺПғО·ПӮ
ОҳОөПүПҒОҜОөПӮ ОіО№Оұ П„О·ОҪ ПҖО·ОіО® П„О·ПӮ ОіОҪПҺПғО·ПӮОЈОҹОҰОҷО‘ ОҰО•ОӣОӣО‘О§ОҷО”ОҹОҘ
Мэ
ОҰО№О»ОҝПғОҝПҶОҜОұApostila direitos humanosElisangela Santos
Мэ
O documento discute os direitos humanos fundamentais, classificando-os em trГӘs geraГ§Гөes: 1) direitos civis e polГӯticos clГЎssicos; 2) direitos econГҙmicos, sociais e culturais; e 3) direitos de solidariedade como meio ambiente e paz. A classificação em geraГ§Гөes reconhece que esses direitos existem simultaneamente e se reforГ§am mutuamente para proteger plenamente a dignidade humana.ОңО•О“О‘ОӣО•ОЈ О‘ОқО‘ОҡО‘ОӣОҘОЁО•ОҷОЈ
ОңО•О“О‘ОӣО•ОЈ О‘ОқО‘ОҡО‘ОӣОҘОЁО•ОҷОЈGeorgia Sofi
Мэ
ОңО‘ОҳО—ОӨОҷОҡО— О•ОЎО“О‘ОЈОҷО‘ О“ОҷО‘ ОӨО—Оқ ОҷОЈОӨОҹОЎОҷО‘ О’О„ ОӣОҘОҡО•ОҷОҹОҘProva de filosofia 1 ano e. i.Tiago MelgaГ§o
Мэ
1. O documento discute os principais pensadores prГ©-socrГЎticos e suas ideias sobre a origem do mundo e da natureza.
2. HerГЎclito acreditava que tudo estГЎ em constante movimento e Tales de Mileto dizia que a ГЎgua Г© o princГӯpio primordial de todas as coisas.
3. Anaximandro defendia que o "apeiron" Г© o princГӯpio do processo cosmolГіgico, enquanto PitГЎgoras acreditava que o nГәmero Г© o princГӯpio de todas as coisas.О ОөПҒО№ОәО»ОӯОҝП…ПӮ О•ПҖО№П„О¬ПҶО№ОҝПӮ 42
О ОөПҒО№ОәО»ОӯОҝП…ПӮ О•ПҖО№П„О¬ПҶО№ОҝПӮ 42Flora Kyprianou
Мэ
О ОөПҒО№ОәО»ОӯОҝП…ПӮ О•ПҖО№П„О¬ПҶО№ОҝПӮ 42 (ОәОөОҜОјОөОҪОҝ, ОјОөП„О¬ПҶПҒОұПғО·)As Grandes NavegaГ§Гөes - 7Вә Ano (2017)Nefer19
Мэ
Portugal e Espanha foram os primeiros paГӯses a lanГ§arem as Grandes NavegaГ§Гөes no sГ©culo 15, com Portugal se destacando inicialmente ao explorar a costa oeste da ГҒfrica. A conquista de Ceuta em 1415 marcou o inГӯcio das exploraГ§Гөes portuguesas. PaГӯses como Inglaterra e FranГ§a tambГ©m participaram das Grandes NavegaГ§Гөes mais tarde, buscando novas rotas para a ГҒsia atravГ©s do norte da AmГ©rica. Disputas entre potГӘncias levaram a acordos como o Tratado de Tordesilhas de 1494ClimaJГәlio Silva
Мэ
O mapa mostra os principais reservatГіrios e o curso do Rio SГЈo Francisco na regiГЈo Nordeste do Brasil, com as classificaГ§Гөes climГЎticas de cada estado baseadas no ГҚndice de Aridade de De Martonne.6Вә ano histГіriaDanuzia Dalat
Мэ
O documento apresenta uma avaliação bimestral de HistГіria para alunos do 6o ano com 10 questГөes sobre o Egito Antigo e a MesopotГўmia. As questГөes abordam tГіpicos como os perГӯodos do Egito Antigo, caracterГӯsticas da civilização sumeriana na MesopotГўmia e da sociedade egГӯpcia, alГ©m de escrita, religiГЈo, arquitetura e atividades econГҙmicas dessas civilizaГ§Гөes antigas.Exercicios sobre o iluminismoThais Ribeiro
Мэ
O documento discute o Iluminismo, um movimento intelectual do sГ©culo XVIII que defendia a razГЈo, a ciГӘncia e a liberdade contra o absolutismo. O Iluminismo influenciou movimentos como a Revolução Francesa e a IndependГӘncia dos EUA, promovendo ideais como liberdade de expressГЈo, fim do colonialismo e substituição da monarquia pela repГәblica.ОҡПҢОјО№Оә -О· О№ПғП„ОҝПҒОҜОұ П„ОҝП… ОіО¬П„ОҝП… ПҖОҝП… ОӯОјОұОёОө ПғОө ОӯОҪОұ ОіО»О¬ПҒОҝ ОҪОұ ПҖОөП„О¬
ОҡПҢОјО№Оә -О· О№ПғП„ОҝПҒОҜОұ П„ОҝП… ОіО¬П„ОҝП… ПҖОҝП… ОӯОјОұОёОө ПғОө ОӯОҪОұ ОіО»О¬ПҒОҝ ОҪОұ ПҖОөП„О¬ОҡОұП„ОөПҒОҜОҪОұ О ПҒОҝОәОҝПҖОҜОҝП…
Мэ
Aircraft Interiors and Cabin Modifications. Vadim Glazov, General Director, A...
Aircraft Interiors and Cabin Modifications. Vadim Glazov, General Director, A...ATOEvents
Мэ
Р”РҫРәлаРҙ Р’Р°РҙРёРјР° ГлазРҫРІР°, РіРөРҪРөСҖалСҢРҪРҫРіРҫ РҙРёСҖРөРәСӮРҫСҖР° РһРһРһ "РҗвиаиРҪСӮРөСҖРәРҫРј", РҝРҫСҒРІСҸСүРөРҪ РәРҫРјРҝР»РөРәСҒРҪСӢРј РҝСҖРҫРіСҖаммам РјРҫРҙРөСҖРҪРёР·Р°СҶРёРё Рё СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫРіРҫ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ РёРҪСӮРөСҖСҢРөСҖРҫРІ РІРҫР·РҙСғСҲРҪСӢС… СҒСғРҙРҫРІ СҒ Р°РәСҶРөРҪСӮРҫРј РҪР° РҝСҖРёРјРөРҪРөРҪРёРө алСҢСӮРөСҖРҪР°СӮРёРІРҪСӢС… РәРҫРјРҝРҫРҪРөРҪСӮРҫРІ. РһРҪ РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°РөСӮ СҖазлиСҮРёСҸ РІ РҝРҫРҙС…РҫРҙах Рә РҝСҖРҫРёР·РІРҫРҙСҒСӮРІСғ РІРҫР·РҙСғСҲРҪСӢС… РәРҫРјРҝРҫРҪРөРҪСӮРҫРІ РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё Рё ЕвСҖРҫРҝРө, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҝСҖРөРҙлагаРөСӮ РҪРҫРІСӢРө РҪР°РҝСҖавлРөРҪРёСҸ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ РёРҪСӮРөСҖСҢРөСҖРҫРІ, РәРҫСӮРҫСҖСӢРө РІСӢР·СӢРІР°СҺСӮ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРөСҒ авиаРәРҫРјРҝР°РҪРёР№. РһСҒРҪРҫРІРҪР°СҸ СҶРөР»СҢ Р·Р°РәР»СҺСҮР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РІ СҒРҪРёР¶РөРҪРёРё Р·Р°СӮСҖР°СӮ Рё РҝРҫРІСӢСҲРөРҪРёРё РәРҫРјС„РҫСҖСӮР° РҙР»СҸ РҝР°СҒСҒажиСҖРҫРІ СҮРөСҖРөР· РҫРҝСӮРёРјРёР·Р°СҶРёСҺ СҖР°РұРҫСӮСӢ Рё РёСҒРҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°РҪРёРө алСҢСӮРөСҖРҪР°СӮРёРІРҪСӢС… СҖРөСҲРөРҪРёР№.Р’РІРөРҙРөРҪРёРө РІ СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСғСҺ РІРҫРөРҪРҪСғСҺ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәСғ (2015)
Р’РІРөРҙРөРҪРёРө РІ СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСғСҺ РІРҫРөРҪРҪСғСҺ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәСғ (2015)Dmitry Kornev
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҝСҖРөРҙСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ СҒРҫРұРҫР№ РІРІРөРҙРөРҪРёРө РІ СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСӢРө СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РІРҫРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәРё, РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҸ РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёСҺ СҖазлиСҮРҪСӢС… СӮРёРҝРҫРІ РұРҫРөРІСӢС… РөРҙРёРҪРёСҶ, СӮР°РәРёС… РәР°Рә СҒамРҫР»РөСӮСӢ, РәРҫСҖР°Рұли, СҖР°РәРөСӮСӢ Рё РҪазРөРјРҪР°СҸ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәР°. РһРҪ РҫС…РІР°СӮСӢРІР°РөСӮ РҫСҒРҪРҫРІРҪСӢРө С…Р°СҖР°РәСӮРөСҖРёСҒСӮРёРәРё Рё СӮРёРҝСӢ РІРҫРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәРё, РёСҒРҝРҫР»СҢР·СғРөРјРҫР№ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРөР№ Рё РқРҗРўРһ, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө С„РҫСҖРјР°СӮСӢ РёС… РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёРё. Р’ СӮРөРәСҒСӮРө СғРҝРҫРјРёРҪР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ РәРҫРҪРәСҖРөСӮРҪСӢРө РјРҫРҙРөли Рё СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РІРҫРҫСҖСғР¶РөРҪРёР№, РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҸ СҖР°РәРөСӮСӢ СҖазлиСҮРҪРҫРіРҫ РҪазРҪР°СҮРөРҪРёСҸ Рё СӮРёРҝСӢ РІРҫРҫСҖСғР¶РөРҪРҪСӢС… СҒРёР».The Evolution of Silicone Molding
The Evolution of Silicone MoldingAlbright Technologies
Мэ
The document outlines the history, types, and applications of silicone, particularly in the medical field. It discusses the contribution of Frederick Stanley Kipping and the Dow-Corning Corporation to the development of silicones, as well as the transition from latex to silicone due to allergy concerns. Additionally, it covers advancements in silicone materials for medical devices including self-lubricating and micro-molded silicones.РһРһРһ РқРҹРҹ РҳРҪРҪРҫРІР°СӮРёРәР°
РһРһРһ РқРҹРҹ РҳРҪРҪРҫРІР°СӮРёРәР°Babenchuk
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҫРҝРёСҒСӢРІР°РөСӮ РҝСҖРҫРөРәСӮ РҝРҫ РёРҪСӮРөРіСҖРёСҖРҫРІР°РҪРҪРҫРјСғ РҝСҖРҫРёР·РІРҫРҙСҒСӮРІСғ СҲРҝСҖРёСҶРөРІ СӮСҖРөСӮСҢРөРіРҫ РҝРҫРәРҫР»РөРҪРёСҸ РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё СҒ СҶРөР»СҢСҺ РҫРұРөСҒРҝРөСҮРөРҪРёСҸ РұРөР·РҫРҝР°СҒРҪСӢС… РёРҪСҠРөРәСҶРёР№. РһСӮРјРөСҮР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РІСӢСҒРҫРәРҫРө РёРјРҝРҫСҖСӮРҫзавиСҒРёРјРҫСҒСӮСҢ Рё РҪРөРҫРұС…РҫРҙРёРјРҫСҒСӮСҢ РёРјРҝРҫСҖСӮРҫзамРөСүРөРҪРёСҸ, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҝРҫСӮРөРҪСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө РҪалРҫРіРҫРІСӢРө РҝРҫСҒСӮСғРҝР»РөРҪРёСҸ Рё СҒРҫР·РҙР°РҪРёРө СҖР°РұРҫСҮРёС… РјРөСҒСӮ. РҹСҖРҫРұР»РөРјСӢ, СӮР°РәРёРө РәР°Рә СҖРҫСҒСӮ СӮР°СҖРёС„РҫРІ РҪР° СҚР»РөРәСӮСҖРҫСҚРҪРөСҖРіРёСҺ Рё РҪРөРҙРҫСҒСӮР°СӮРҫРә Р·Р°РәРҫРҪРҫРҙР°СӮРөР»СҢРҪРҫРіРҫ СҖРөРіСғлиСҖРҫРІР°РҪРёСҸ, СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҝРҫРҙРҪРёРјР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ РІ РәРҫРҪСӮРөРәСҒСӮРө СҖРөализаСҶРёРё РҝСҖРҫРөРәСӮР°.Telexca Inc. Presentation
Telexca Inc. PresentationTelexca Inc.
Мэ
Telexca, Inc. specializes in composite components for aerospace applications, offering high-quality silicone rubber and rigid thermoset materials with capabilities for quick turnarounds and competitive pricing. The company has over 15 years of experience and a commitment to quality assurance, while serving various aircraft platforms including Gulfstream and Bombardier models. Their facilities feature advanced tooling, large inventory, and testing capabilities to support production needs.Kirill Krupnov
Kirill KrupnovATOEvents
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°РөСӮ РјР°СӮРөСҖиалСҢРҪРҫ-СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫРө РҫРұРөСҒРҝРөСҮРөРҪРёРө РҝРҫСҒР»РөРҝСҖРҫРҙажРҪРҫРіРҫ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ РІРҫР·РҙСғСҲРҪСӢС… СҒСғРҙРҫРІ РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё Рё РҝРҫСӮСҖРөРұРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ РІ СҒРҫР·РҙР°РҪРёРё СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РҙР»СҸ РҫСӮРөСҮРөСҒСӮРІРөРҪРҪСӢС… Рё РёРҪРҫСҒСӮСҖР°РҪРҪСӢС… СҒамРҫР»РөСӮРҫРІ. Р’ РҪРөРј Р°РҪализиСҖСғРөСӮСҒСҸ СҖРҫСҒСӮ СҖСӢРҪРәР° СғСҒР»СғРі РҝРҫ СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫРјСғ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҺ Рё РҙРёСҒСӮСҖРёРұСғСҶРёРё Р·Р°РҝР°СҒРҪСӢС… СҮР°СҒСӮРөР№, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РұР°СҖСҢРөСҖСӢ, РІРҫР·РҪРёРәСҲРёРө РёР·-Р·Р° СҖРҫСҒСҒРёР№СҒРәРҫРіРҫ Р·Р°РәРҫРҪРҫРҙР°СӮРөР»СҢСҒСӮРІР°. РҹРҫРҙСҮРөСҖРәРёРІР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РҪРөРҫРұС…РҫРҙРёРјРҫСҒСӮСҢ СҖазвиСӮРёСҸ РҫСӮРөСҮРөСҒСӮРІРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ Рё РІРҫР·РјРҫР¶РҪРҫСҒСӮРё РҙР»СҸ СҖРҫСҒСӮР° СҖСӢРҪРәР° РҙРҫ $2,4 РјР»СҖРҙ Рә 2020 РіРҫРҙСғ.Text of lections
Text of lectionsArtem Katranzhi
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҝСҖРөРҙСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ СҒРҫРұРҫР№ РәСғСҖСҒ Р»РөРәСҶРёР№ РҝРҫ РҫСҒРҪРҫвам авиаСҶРёРҫРҪРҪРҫР№ РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮРё, СҒРҫСҒСӮРҫСҸСүРёР№ РёР· РҙРІСғС… СӮРөРј: РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ РәРҫРҪСҒСӮСҖСғРәСҶРёРё СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР° Рё РҫСҒРҫРұРөРҪРҪРҫСҒСӮРё СҖР°СҒСҮРөСӮР° РәСҖСӢла. РһРҪ РҫС…РІР°СӮСӢРІР°РөСӮ СҚСӮР°РҝСӢ жизРҪРөРҪРҪРҫРіРҫ СҶРёРәла СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР°, РҪРҫСҖРј РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮРё Рё РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёСҺ РҪагСҖСғР·РҫРә, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РјРөСӮРҫРҙРёРәСғ СҖР°СҒСҮРөСӮР° Рё РёСҒРҝСӢСӮР°РҪРёР№ РҪР° РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ. Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ СҒР»СғжиСӮ РҝРҫСҒРҫРұРёРөРј РҙР»СҸ СҒСӮСғРҙРөРҪСӮРҫРІ СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРёС… РІСғР·РҫРІ, РёР·СғСҮР°СҺСүРёС… авиаСҶРёРҫРҪРҪСӢРө РҪР°СғРәРё.Boeing 747-8F AirBridge Cargo
Boeing 747-8F AirBridge CargoArtem Katranzhi
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҝСҖРөРҙСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ СҒРҫРұРҫР№ РҫРұР·РҫСҖ СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР° Boeing 747-8F, РҝРҫРҙСҮРөСҖРәРёРІР°СҺСүРёР№ РөРіРҫ РҝСҖРөРёРјСғСүРөСҒСӮРІР° РІ РіСҖСғР·РҫРҝРөСҖРөРІРҫР·Рәах СҒ СғРІРөлиСҮРөРҪРҪРҫР№ РіСҖСғР·РҫРҝРҫРҙСҠРөРјРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢСҺ РҪР° 16% Рё СҒРҪРёР¶РөРҪРёРөРј СҖР°СҒС…РҫРҙР° РіРҫСҖСҺСҮРөРіРҫ РҪР° 17% РҝРҫ СҒСҖавРҪРөРҪРёСҺ СҒ РҝСҖРөРҙРҝРҫСҒР»РөРҙРҪРөР№ РјРҫРҙРөР»СҢСҺ. РўР°РәР¶Рө РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ СӮРөС…РҪРҫР»РҫРіРёРё, СғР»СғСҮСҲРөРҪРёСҸ РәРҫРҪСҒСӮСҖСғРәСҶРёРё РәСҖСӢла Рё РІРҫР·РјРҫР¶РҪРҫСҒСӮРё РҝРҫРіСҖСғР·РәРё СҮРөСҖРөР· РҪРҫСҒРҫРІСғСҺ РҙРІРөСҖСҢ, СҮСӮРҫ СғРІРөлиСҮРёРІР°РөСӮ СҖРөРҪСӮР°РұРөР»СҢРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ СҚРәСҒРҝР»СғР°СӮР°СҶРёРё. РһСҒРҪРҫРІРҪСӢРө С…Р°СҖР°РәСӮРөСҖРёСҒСӮРёРәРё РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҺСӮ РјР°РәСҒималСҢРҪСғСҺ РіСҖСғР·РҫРҝРҫРҙСҠРөРјРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ РІ 975,000 С„СғРҪСӮРҫРІ Рё СҒРҫРҫСӮРІРөСӮСҒСӮРІРёРө СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСӢРј СӮСҖРөРұРҫРІР°РҪРёСҸРј Рә РёРҪС„СҖР°СҒСӮСҖСғРәСӮСғСҖРө Рё СғСҖРҫРІРҪСҺ СҲСғРјР°.Rapid Prototyping with Medical Grade Silicone
Rapid Prototyping with Medical Grade SiliconeAlbright Technologies
Мэ
The document provides an overview of rapid prototyping with medical grade silicone, including its material options, processing methodologies, and applications in various medical devices. It discusses different silicone types such as RTV, LSR, and HCR, along with their advantages, disadvantages, and suitable applications. Prototyping methods like 3D casting, compression molding, transfer molding, and injection molding are analyzed for their effectiveness in the development and scaling of silicone-based medical products.СамСӢРө РҝРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРө СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө СҒРөСӮРё РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё 2015
СамСӢРө РҝРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРө СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө СҒРөСӮРё РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё 2015Blogging from A to Z
Мэ
Р’ СҸРҪРІР°СҖРө 2015 РіРҫРҙР° РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё РҪР°СҒСҮРёСӮСӢвалРҫСҒСҢ 67 РјР»РҪ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРҪРөСӮ-РҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°СӮРөР»РөР№, 38,2 РјР»РҪ РёР· РәРҫСӮРҫСҖСӢС… РёРјРөли Р°РәСӮРёРІРҪСӢРө Р°РәРәР°СғРҪСӮСӢ РІ СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢС… СҒРөСӮСҸС…. Р‘РҫР»СҢСҲР°СҸ СҮР°СҒСӮСҢ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРҪРөСӮ-СӮСҖафиРәР° (82%) РҝРҫСҒСӮСғРҝР°РөСӮ СҒ РҙРҫРјР°СҲРҪРёС… РәРҫРјРҝСҢСҺСӮРөСҖРҫРІ Рё РҪРҫСғСӮРұСғРәРҫРІ, Р° РҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°СӮРөли РҝСҖРҫРІРҫРҙСҸСӮ РІ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРҪРөСӮРө РІ СҒСҖРөРҙРҪРөРј 4 СҮ 47 РјРёРҪ. РІ РҙРөРҪСҢ. РҹРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРјРё СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРјРё РҝлаСӮС„РҫСҖмами РҫСҒСӮР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ 'Р’РҡРҫРҪСӮР°РәСӮРө' Рё 'РһРҙРҪРҫРәлаСҒСҒРҪРёРәРё', Р° Р°СғРҙРёСӮРҫСҖРёСҸ СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢС… СҒРөСӮРөР№ СҒРҫСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ 55,8% РјСғР¶СҮРёРҪ Рё 44,2% Р¶РөРҪСүРёРҪ.prakash agrawal rapid tooling presentation
prakash agrawal rapid tooling presentationAkash Maurya
Мэ
Rapid prototyping techniques allow designers to quickly produce physical prototypes directly from 3D CAD models without special tooling. While useful for visualization, RP prototypes often cannot undergo functional testing due to different material properties than production parts. Rapid tooling produces molds or tools using RP to enable functional prototype testing and production of multiple prototype parts. It has advantages over conventional tooling like shorter timelines, lower costs, and longer tool life. Common rapid tooling methods include soft tooling using silicone rubber molds, epoxy or hybrid molds, and direct metal laser sintering or wire arc spray to produce metal tool inserts.РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РәР°Рә РҪР°СғРәР°, РөС‘ РҝСҖРөРҙРјРөСӮ Рё Р·Р°РҙР°СҮРё.
РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РәР°Рә РҪР°СғРәР°, РөС‘ РҝСҖРөРҙРјРөСӮ Рё Р·Р°РҙР°СҮРё.РҗСҖРәР°РҙРёР№ ЗахаСҖРҫРІ
Мэ
РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РёР·СғСҮР°РөСӮ СҒРҫРөРҙРёРҪРөРҪРёСҸ СғРіР»РөСҖРҫРҙР° Рё РёС… СҒРІРҫР№СҒСӮРІР°, РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҸ РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёСҺ, РёР·РҫРјРөСҖРёРё Рё С…РёРјРёСҮРөСҒРәРёРө СҖРөР°РәСҶРёРё. Р’ РҙРҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮРө РёР·Р»РҫР¶РөРҪСӢ СҖРөРәРҫРјРөРҪРҙР°СҶРёРё РҝРҫ РёР·СғСҮРөРҪРёСҺ РҫСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫР№ С…РёРјРёРё Рё РҫСҒРҫРұРөРҪРҪРҫСҒСӮРё СғРіР»РөСҖРҫРҙР° РәР°Рә СҮРөСӮСӢСҖРөхвалРөРҪСӮРҪРҫРіРҫ СҚР»РөРјРөРҪСӮР°. РўР°РәР¶Рө СҖР°СҒСҒРјРҫСӮСҖРөРҪСӢ СҖазлиСҮРҪСӢРө РәлаСҒСҒСӢ РҫСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРёС… СҒРҫРөРҙРёРҪРөРҪРёР№ Рё РёС… СҒСӮСҖСғРәСӮСғСҖР°.Р§СӮРҫ СӮР°РәРҫРө Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәР° РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, Р·Р°СҮРөРј РҫРҪР° РҪСғР¶РҪР°, Рё РәР°Рә РөРө РіРҫСӮРҫРІРёСӮСҢ
Р§СӮРҫ СӮР°РәРҫРө Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәР° РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, Р·Р°СҮРөРј РҫРҪР° РҪСғР¶РҪР°, Рё РәР°Рә РөРө РіРҫСӮРҫРІРёСӮСҢMindbox
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°РөСӮ РҝСҖРҫРұР»РөРјСӢ Рё РІСӢР·РҫРІСӢ, РІРҫР·РҪРёРәР°СҺСүРёРө РҝСҖРё РёСҒРҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°РҪРёРё СҒР»РҫР¶РҪСӢС… РјРҫРҙРөР»РөР№ Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәРё РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, СӮР°РәРёРө РәР°Рә РҝРҫРІРөРҙРөРҪСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ СҒРөРіРјРөРҪСӮР°СҶРёСҸ Рё RFM-Р°РҪализ. РһСҒРҪРҫРІРҪРҫРө РІРҪРёРјР°РҪРёРө СғРҙРөР»СҸРөСӮСҒСҸ важРҪРҫСҒСӮРё РҝСҖавилСҢРҪРҫРіРҫ РҝРҫРҪРёРјР°РҪРёСҸ Рё РҝСҖРёРјРөРҪРөРҪРёСҸ Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәРё РҙР»СҸ РҝРҫРІСӢСҲРөРҪРёСҸ СҚффРөРәСӮРёРІРҪРҫСҒСӮРё СҖРөРәламРҪСӢС… РәамРҝР°РҪРёР№ Рё СғР»СғСҮСҲРөРҪРёСҸ взаимРҫРҙРөР№СҒСӮРІРёСҸ СҒ РәлиРөРҪСӮами. РҹРҫРҙСҮС‘СҖРәРёРІР°РөСӮСҒСҸ, СҮСӮРҫ РәР»СҺСҮ Рә СғСҒРҝРөС…Сғ Р·Р°РәР»СҺСҮР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РІ РҝСҖРҫСҒСӮСӢС… РҝСҖР°РәСӮРёСҮРөСҒРәРёС… Р·Р°РҙР°СҮах Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәРё Рё РҝР»РҫСҒРәРҫСҒСӮРҪРҫРј РҝРҫРҙС…РҫРҙРө Рә РҝСҖРҫРұР»Рөмам.More Related Content
What's hot (8)
О ОөПҒО№ОәО»ОӯОҝП…ПӮ О•ПҖО№П„О¬ПҶО№ОҝПӮ 42
О ОөПҒО№ОәО»ОӯОҝП…ПӮ О•ПҖО№П„О¬ПҶО№ОҝПӮ 42Flora Kyprianou
Мэ
О ОөПҒО№ОәО»ОӯОҝП…ПӮ О•ПҖО№П„О¬ПҶО№ОҝПӮ 42 (ОәОөОҜОјОөОҪОҝ, ОјОөП„О¬ПҶПҒОұПғО·)As Grandes NavegaГ§Гөes - 7Вә Ano (2017)Nefer19
Мэ
Portugal e Espanha foram os primeiros paГӯses a lanГ§arem as Grandes NavegaГ§Гөes no sГ©culo 15, com Portugal se destacando inicialmente ao explorar a costa oeste da ГҒfrica. A conquista de Ceuta em 1415 marcou o inГӯcio das exploraГ§Гөes portuguesas. PaГӯses como Inglaterra e FranГ§a tambГ©m participaram das Grandes NavegaГ§Гөes mais tarde, buscando novas rotas para a ГҒsia atravГ©s do norte da AmГ©rica. Disputas entre potГӘncias levaram a acordos como o Tratado de Tordesilhas de 1494ClimaJГәlio Silva
Мэ
O mapa mostra os principais reservatГіrios e o curso do Rio SГЈo Francisco na regiГЈo Nordeste do Brasil, com as classificaГ§Гөes climГЎticas de cada estado baseadas no ГҚndice de Aridade de De Martonne.6Вә ano histГіriaDanuzia Dalat
Мэ
O documento apresenta uma avaliação bimestral de HistГіria para alunos do 6o ano com 10 questГөes sobre o Egito Antigo e a MesopotГўmia. As questГөes abordam tГіpicos como os perГӯodos do Egito Antigo, caracterГӯsticas da civilização sumeriana na MesopotГўmia e da sociedade egГӯpcia, alГ©m de escrita, religiГЈo, arquitetura e atividades econГҙmicas dessas civilizaГ§Гөes antigas.Exercicios sobre o iluminismoThais Ribeiro
Мэ
O documento discute o Iluminismo, um movimento intelectual do sГ©culo XVIII que defendia a razГЈo, a ciГӘncia e a liberdade contra o absolutismo. O Iluminismo influenciou movimentos como a Revolução Francesa e a IndependГӘncia dos EUA, promovendo ideais como liberdade de expressГЈo, fim do colonialismo e substituição da monarquia pela repГәblica.ОҡПҢОјО№Оә -О· О№ПғП„ОҝПҒОҜОұ П„ОҝП… ОіО¬П„ОҝП… ПҖОҝП… ОӯОјОұОёОө ПғОө ОӯОҪОұ ОіО»О¬ПҒОҝ ОҪОұ ПҖОөП„О¬
ОҡПҢОјО№Оә -О· О№ПғП„ОҝПҒОҜОұ П„ОҝП… ОіО¬П„ОҝП… ПҖОҝП… ОӯОјОұОёОө ПғОө ОӯОҪОұ ОіО»О¬ПҒОҝ ОҪОұ ПҖОөП„О¬ОҡОұП„ОөПҒОҜОҪОұ О ПҒОҝОәОҝПҖОҜОҝП…
Мэ
ОҡПҢОјО№Оә -О· О№ПғП„ОҝПҒОҜОұ П„ОҝП… ОіО¬П„ОҝП… ПҖОҝП… ОӯОјОұОёОө ПғОө ОӯОҪОұ ОіО»О¬ПҒОҝ ОҪОұ ПҖОөП„О¬
ОҡПҢОјО№Оә -О· О№ПғП„ОҝПҒОҜОұ П„ОҝП… ОіО¬П„ОҝП… ПҖОҝП… ОӯОјОұОёОө ПғОө ОӯОҪОұ ОіО»О¬ПҒОҝ ОҪОұ ПҖОөП„О¬ОҡОұП„ОөПҒОҜОҪОұ О ПҒОҝОәОҝПҖОҜОҝП…
Мэ
Viewers also liked (13)
Aircraft Interiors and Cabin Modifications. Vadim Glazov, General Director, A...
Aircraft Interiors and Cabin Modifications. Vadim Glazov, General Director, A...ATOEvents
Мэ
Р”РҫРәлаРҙ Р’Р°РҙРёРјР° ГлазРҫРІР°, РіРөРҪРөСҖалСҢРҪРҫРіРҫ РҙРёСҖРөРәСӮРҫСҖР° РһРһРһ "РҗвиаиРҪСӮРөСҖРәРҫРј", РҝРҫСҒРІСҸСүРөРҪ РәРҫРјРҝР»РөРәСҒРҪСӢРј РҝСҖРҫРіСҖаммам РјРҫРҙРөСҖРҪРёР·Р°СҶРёРё Рё СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫРіРҫ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ РёРҪСӮРөСҖСҢРөСҖРҫРІ РІРҫР·РҙСғСҲРҪСӢС… СҒСғРҙРҫРІ СҒ Р°РәСҶРөРҪСӮРҫРј РҪР° РҝСҖРёРјРөРҪРөРҪРёРө алСҢСӮРөСҖРҪР°СӮРёРІРҪСӢС… РәРҫРјРҝРҫРҪРөРҪСӮРҫРІ. РһРҪ РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°РөСӮ СҖазлиСҮРёСҸ РІ РҝРҫРҙС…РҫРҙах Рә РҝСҖРҫРёР·РІРҫРҙСҒСӮРІСғ РІРҫР·РҙСғСҲРҪСӢС… РәРҫРјРҝРҫРҪРөРҪСӮРҫРІ РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё Рё ЕвСҖРҫРҝРө, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҝСҖРөРҙлагаРөСӮ РҪРҫРІСӢРө РҪР°РҝСҖавлРөРҪРёСҸ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ РёРҪСӮРөСҖСҢРөСҖРҫРІ, РәРҫСӮРҫСҖСӢРө РІСӢР·СӢРІР°СҺСӮ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРөСҒ авиаРәРҫРјРҝР°РҪРёР№. РһСҒРҪРҫРІРҪР°СҸ СҶРөР»СҢ Р·Р°РәР»СҺСҮР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РІ СҒРҪРёР¶РөРҪРёРё Р·Р°СӮСҖР°СӮ Рё РҝРҫРІСӢСҲРөРҪРёРё РәРҫРјС„РҫСҖСӮР° РҙР»СҸ РҝР°СҒСҒажиСҖРҫРІ СҮРөСҖРөР· РҫРҝСӮРёРјРёР·Р°СҶРёСҺ СҖР°РұРҫСӮСӢ Рё РёСҒРҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°РҪРёРө алСҢСӮРөСҖРҪР°СӮРёРІРҪСӢС… СҖРөСҲРөРҪРёР№.Р’РІРөРҙРөРҪРёРө РІ СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСғСҺ РІРҫРөРҪРҪСғСҺ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәСғ (2015)
Р’РІРөРҙРөРҪРёРө РІ СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСғСҺ РІРҫРөРҪРҪСғСҺ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәСғ (2015)Dmitry Kornev
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҝСҖРөРҙСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ СҒРҫРұРҫР№ РІРІРөРҙРөРҪРёРө РІ СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСӢРө СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РІРҫРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәРё, РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҸ РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёСҺ СҖазлиСҮРҪСӢС… СӮРёРҝРҫРІ РұРҫРөРІСӢС… РөРҙРёРҪРёСҶ, СӮР°РәРёС… РәР°Рә СҒамРҫР»РөСӮСӢ, РәРҫСҖР°Рұли, СҖР°РәРөСӮСӢ Рё РҪазРөРјРҪР°СҸ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәР°. РһРҪ РҫС…РІР°СӮСӢРІР°РөСӮ РҫСҒРҪРҫРІРҪСӢРө С…Р°СҖР°РәСӮРөСҖРёСҒСӮРёРәРё Рё СӮРёРҝСӢ РІРҫРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СӮРөС…РҪРёРәРё, РёСҒРҝРҫР»СҢР·СғРөРјРҫР№ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРөР№ Рё РқРҗРўРһ, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө С„РҫСҖРјР°СӮСӢ РёС… РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёРё. Р’ СӮРөРәСҒСӮРө СғРҝРҫРјРёРҪР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ РәРҫРҪРәСҖРөСӮРҪСӢРө РјРҫРҙРөли Рё СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РІРҫРҫСҖСғР¶РөРҪРёР№, РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҸ СҖР°РәРөСӮСӢ СҖазлиСҮРҪРҫРіРҫ РҪазРҪР°СҮРөРҪРёСҸ Рё СӮРёРҝСӢ РІРҫРҫСҖСғР¶РөРҪРҪСӢС… СҒРёР».The Evolution of Silicone Molding
The Evolution of Silicone MoldingAlbright Technologies
Мэ
The document outlines the history, types, and applications of silicone, particularly in the medical field. It discusses the contribution of Frederick Stanley Kipping and the Dow-Corning Corporation to the development of silicones, as well as the transition from latex to silicone due to allergy concerns. Additionally, it covers advancements in silicone materials for medical devices including self-lubricating and micro-molded silicones.РһРһРһ РқРҹРҹ РҳРҪРҪРҫРІР°СӮРёРәР°
РһРһРһ РқРҹРҹ РҳРҪРҪРҫРІР°СӮРёРәР°Babenchuk
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҫРҝРёСҒСӢРІР°РөСӮ РҝСҖРҫРөРәСӮ РҝРҫ РёРҪСӮРөРіСҖРёСҖРҫРІР°РҪРҪРҫРјСғ РҝСҖРҫРёР·РІРҫРҙСҒСӮРІСғ СҲРҝСҖРёСҶРөРІ СӮСҖРөСӮСҢРөРіРҫ РҝРҫРәРҫР»РөРҪРёСҸ РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё СҒ СҶРөР»СҢСҺ РҫРұРөСҒРҝРөСҮРөРҪРёСҸ РұРөР·РҫРҝР°СҒРҪСӢС… РёРҪСҠРөРәСҶРёР№. РһСӮРјРөСҮР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РІСӢСҒРҫРәРҫРө РёРјРҝРҫСҖСӮРҫзавиСҒРёРјРҫСҒСӮСҢ Рё РҪРөРҫРұС…РҫРҙРёРјРҫСҒСӮСҢ РёРјРҝРҫСҖСӮРҫзамРөСүРөРҪРёСҸ, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҝРҫСӮРөРҪСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө РҪалРҫРіРҫРІСӢРө РҝРҫСҒСӮСғРҝР»РөРҪРёСҸ Рё СҒРҫР·РҙР°РҪРёРө СҖР°РұРҫСҮРёС… РјРөСҒСӮ. РҹСҖРҫРұР»РөРјСӢ, СӮР°РәРёРө РәР°Рә СҖРҫСҒСӮ СӮР°СҖРёС„РҫРІ РҪР° СҚР»РөРәСӮСҖРҫСҚРҪРөСҖРіРёСҺ Рё РҪРөРҙРҫСҒСӮР°СӮРҫРә Р·Р°РәРҫРҪРҫРҙР°СӮРөР»СҢРҪРҫРіРҫ СҖРөРіСғлиСҖРҫРІР°РҪРёСҸ, СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҝРҫРҙРҪРёРјР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ РІ РәРҫРҪСӮРөРәСҒСӮРө СҖРөализаСҶРёРё РҝСҖРҫРөРәСӮР°.Telexca Inc. Presentation
Telexca Inc. PresentationTelexca Inc.
Мэ
Telexca, Inc. specializes in composite components for aerospace applications, offering high-quality silicone rubber and rigid thermoset materials with capabilities for quick turnarounds and competitive pricing. The company has over 15 years of experience and a commitment to quality assurance, while serving various aircraft platforms including Gulfstream and Bombardier models. Their facilities feature advanced tooling, large inventory, and testing capabilities to support production needs.Kirill Krupnov
Kirill KrupnovATOEvents
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°РөСӮ РјР°СӮРөСҖиалСҢРҪРҫ-СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫРө РҫРұРөСҒРҝРөСҮРөРҪРёРө РҝРҫСҒР»РөРҝСҖРҫРҙажРҪРҫРіРҫ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ РІРҫР·РҙСғСҲРҪСӢС… СҒСғРҙРҫРІ РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё Рё РҝРҫСӮСҖРөРұРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ РІ СҒРҫР·РҙР°РҪРёРё СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РҙР»СҸ РҫСӮРөСҮРөСҒСӮРІРөРҪРҪСӢС… Рё РёРҪРҫСҒСӮСҖР°РҪРҪСӢС… СҒамРҫР»РөСӮРҫРІ. Р’ РҪРөРј Р°РҪализиСҖСғРөСӮСҒСҸ СҖРҫСҒСӮ СҖСӢРҪРәР° СғСҒР»СғРі РҝРҫ СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫРјСғ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҺ Рё РҙРёСҒСӮСҖРёРұСғСҶРёРё Р·Р°РҝР°СҒРҪСӢС… СҮР°СҒСӮРөР№, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РұР°СҖСҢРөСҖСӢ, РІРҫР·РҪРёРәСҲРёРө РёР·-Р·Р° СҖРҫСҒСҒРёР№СҒРәРҫРіРҫ Р·Р°РәРҫРҪРҫРҙР°СӮРөР»СҢСҒСӮРІР°. РҹРҫРҙСҮРөСҖРәРёРІР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РҪРөРҫРұС…РҫРҙРёРјРҫСҒСӮСҢ СҖазвиСӮРёСҸ РҫСӮРөСҮРөСҒСӮРІРөРҪРҪРҫР№ СҒРёСҒСӮРөРјСӢ РҫРұСҒР»СғживаРҪРёСҸ Рё РІРҫР·РјРҫР¶РҪРҫСҒСӮРё РҙР»СҸ СҖРҫСҒСӮР° СҖСӢРҪРәР° РҙРҫ $2,4 РјР»СҖРҙ Рә 2020 РіРҫРҙСғ.Text of lections
Text of lectionsArtem Katranzhi
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҝСҖРөРҙСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ СҒРҫРұРҫР№ РәСғСҖСҒ Р»РөРәСҶРёР№ РҝРҫ РҫСҒРҪРҫвам авиаСҶРёРҫРҪРҪРҫР№ РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮРё, СҒРҫСҒСӮРҫСҸСүРёР№ РёР· РҙРІСғС… СӮРөРј: РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ РәРҫРҪСҒСӮСҖСғРәСҶРёРё СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР° Рё РҫСҒРҫРұРөРҪРҪРҫСҒСӮРё СҖР°СҒСҮРөСӮР° РәСҖСӢла. РһРҪ РҫС…РІР°СӮСӢРІР°РөСӮ СҚСӮР°РҝСӢ жизРҪРөРҪРҪРҫРіРҫ СҶРёРәла СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР°, РҪРҫСҖРј РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮРё Рё РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёСҺ РҪагСҖСғР·РҫРә, Р° СӮР°РәР¶Рө РјРөСӮРҫРҙРёРәСғ СҖР°СҒСҮРөСӮР° Рё РёСҒРҝСӢСӮР°РҪРёР№ РҪР° РҝСҖРҫСҮРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ. Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ СҒР»СғжиСӮ РҝРҫСҒРҫРұРёРөРј РҙР»СҸ СҒСӮСғРҙРөРҪСӮРҫРІ СӮРөС…РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРёС… РІСғР·РҫРІ, РёР·СғСҮР°СҺСүРёС… авиаСҶРёРҫРҪРҪСӢРө РҪР°СғРәРё.Boeing 747-8F AirBridge Cargo
Boeing 747-8F AirBridge CargoArtem Katranzhi
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҝСҖРөРҙСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ СҒРҫРұРҫР№ РҫРұР·РҫСҖ СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР° Boeing 747-8F, РҝРҫРҙСҮРөСҖРәРёРІР°СҺСүРёР№ РөРіРҫ РҝСҖРөРёРјСғСүРөСҒСӮРІР° РІ РіСҖСғР·РҫРҝРөСҖРөРІРҫР·Рәах СҒ СғРІРөлиСҮРөРҪРҪРҫР№ РіСҖСғР·РҫРҝРҫРҙСҠРөРјРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢСҺ РҪР° 16% Рё СҒРҪРёР¶РөРҪРёРөРј СҖР°СҒС…РҫРҙР° РіРҫСҖСҺСҮРөРіРҫ РҪР° 17% РҝРҫ СҒСҖавРҪРөРҪРёСҺ СҒ РҝСҖРөРҙРҝРҫСҒР»РөРҙРҪРөР№ РјРҫРҙРөР»СҢСҺ. РўР°РәР¶Рө РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ СӮРөС…РҪРҫР»РҫРіРёРё, СғР»СғСҮСҲРөРҪРёСҸ РәРҫРҪСҒСӮСҖСғРәСҶРёРё РәСҖСӢла Рё РІРҫР·РјРҫР¶РҪРҫСҒСӮРё РҝРҫРіСҖСғР·РәРё СҮРөСҖРөР· РҪРҫСҒРҫРІСғСҺ РҙРІРөСҖСҢ, СҮСӮРҫ СғРІРөлиСҮРёРІР°РөСӮ СҖРөРҪСӮР°РұРөР»СҢРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ СҚРәСҒРҝР»СғР°СӮР°СҶРёРё. РһСҒРҪРҫРІРҪСӢРө С…Р°СҖР°РәСӮРөСҖРёСҒСӮРёРәРё РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҺСӮ РјР°РәСҒималСҢРҪСғСҺ РіСҖСғР·РҫРҝРҫРҙСҠРөРјРҪРҫСҒСӮСҢ РІ 975,000 С„СғРҪСӮРҫРІ Рё СҒРҫРҫСӮРІРөСӮСҒСӮРІРёРө СҒРҫРІСҖРөРјРөРҪРҪСӢРј СӮСҖРөРұРҫРІР°РҪРёСҸРј Рә РёРҪС„СҖР°СҒСӮСҖСғРәСӮСғСҖРө Рё СғСҖРҫРІРҪСҺ СҲСғРјР°.Rapid Prototyping with Medical Grade Silicone
Rapid Prototyping with Medical Grade SiliconeAlbright Technologies
Мэ
The document provides an overview of rapid prototyping with medical grade silicone, including its material options, processing methodologies, and applications in various medical devices. It discusses different silicone types such as RTV, LSR, and HCR, along with their advantages, disadvantages, and suitable applications. Prototyping methods like 3D casting, compression molding, transfer molding, and injection molding are analyzed for their effectiveness in the development and scaling of silicone-based medical products.СамСӢРө РҝРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРө СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө СҒРөСӮРё РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё 2015
СамСӢРө РҝРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРө СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө СҒРөСӮРё РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё 2015Blogging from A to Z
Мэ
Р’ СҸРҪРІР°СҖРө 2015 РіРҫРҙР° РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё РҪР°СҒСҮРёСӮСӢвалРҫСҒСҢ 67 РјР»РҪ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРҪРөСӮ-РҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°СӮРөР»РөР№, 38,2 РјР»РҪ РёР· РәРҫСӮРҫСҖСӢС… РёРјРөли Р°РәСӮРёРІРҪСӢРө Р°РәРәР°СғРҪСӮСӢ РІ СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢС… СҒРөСӮСҸС…. Р‘РҫР»СҢСҲР°СҸ СҮР°СҒСӮСҢ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРҪРөСӮ-СӮСҖафиРәР° (82%) РҝРҫСҒСӮСғРҝР°РөСӮ СҒ РҙРҫРјР°СҲРҪРёС… РәРҫРјРҝСҢСҺСӮРөСҖРҫРІ Рё РҪРҫСғСӮРұСғРәРҫРІ, Р° РҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°СӮРөли РҝСҖРҫРІРҫРҙСҸСӮ РІ РёРҪСӮРөСҖРҪРөСӮРө РІ СҒСҖРөРҙРҪРөРј 4 СҮ 47 РјРёРҪ. РІ РҙРөРҪСҢ. РҹРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРјРё СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРјРё РҝлаСӮС„РҫСҖмами РҫСҒСӮР°СҺСӮСҒСҸ 'Р’РҡРҫРҪСӮР°РәСӮРө' Рё 'РһРҙРҪРҫРәлаСҒСҒРҪРёРәРё', Р° Р°СғРҙРёСӮРҫСҖРёСҸ СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢС… СҒРөСӮРөР№ СҒРҫСҒСӮавлСҸРөСӮ 55,8% РјСғР¶СҮРёРҪ Рё 44,2% Р¶РөРҪСүРёРҪ.prakash agrawal rapid tooling presentation
prakash agrawal rapid tooling presentationAkash Maurya
Мэ
Rapid prototyping techniques allow designers to quickly produce physical prototypes directly from 3D CAD models without special tooling. While useful for visualization, RP prototypes often cannot undergo functional testing due to different material properties than production parts. Rapid tooling produces molds or tools using RP to enable functional prototype testing and production of multiple prototype parts. It has advantages over conventional tooling like shorter timelines, lower costs, and longer tool life. Common rapid tooling methods include soft tooling using silicone rubber molds, epoxy or hybrid molds, and direct metal laser sintering or wire arc spray to produce metal tool inserts.РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РәР°Рә РҪР°СғРәР°, РөС‘ РҝСҖРөРҙРјРөСӮ Рё Р·Р°РҙР°СҮРё.
РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РәР°Рә РҪР°СғРәР°, РөС‘ РҝСҖРөРҙРјРөСӮ Рё Р·Р°РҙР°СҮРё.РҗСҖРәР°РҙРёР№ ЗахаСҖРҫРІ
Мэ
РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РёР·СғСҮР°РөСӮ СҒРҫРөРҙРёРҪРөРҪРёСҸ СғРіР»РөСҖРҫРҙР° Рё РёС… СҒРІРҫР№СҒСӮРІР°, РІРәР»СҺСҮР°СҸ РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёСҺ, РёР·РҫРјРөСҖРёРё Рё С…РёРјРёСҮРөСҒРәРёРө СҖРөР°РәСҶРёРё. Р’ РҙРҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮРө РёР·Р»РҫР¶РөРҪСӢ СҖРөРәРҫРјРөРҪРҙР°СҶРёРё РҝРҫ РёР·СғСҮРөРҪРёСҺ РҫСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫР№ С…РёРјРёРё Рё РҫСҒРҫРұРөРҪРҪРҫСҒСӮРё СғРіР»РөСҖРҫРҙР° РәР°Рә СҮРөСӮСӢСҖРөхвалРөРҪСӮРҪРҫРіРҫ СҚР»РөРјРөРҪСӮР°. РўР°РәР¶Рө СҖР°СҒСҒРјРҫСӮСҖРөРҪСӢ СҖазлиСҮРҪСӢРө РәлаСҒСҒСӢ РҫСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәРёС… СҒРҫРөРҙРёРҪРөРҪРёР№ Рё РёС… СҒСӮСҖСғРәСӮСғСҖР°.Р§СӮРҫ СӮР°РәРҫРө Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәР° РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, Р·Р°СҮРөРј РҫРҪР° РҪСғР¶РҪР°, Рё РәР°Рә РөРө РіРҫСӮРҫРІРёСӮСҢ
Р§СӮРҫ СӮР°РәРҫРө Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәР° РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, Р·Р°СҮРөРј РҫРҪР° РҪСғР¶РҪР°, Рё РәР°Рә РөРө РіРҫСӮРҫРІРёСӮСҢMindbox
Мэ
Р”РҫРәСғРјРөРҪСӮ РҫРұСҒСғР¶РҙР°РөСӮ РҝСҖРҫРұР»РөРјСӢ Рё РІСӢР·РҫРІСӢ, РІРҫР·РҪРёРәР°СҺСүРёРө РҝСҖРё РёСҒРҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°РҪРёРё СҒР»РҫР¶РҪСӢС… РјРҫРҙРөР»РөР№ Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәРё РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, СӮР°РәРёРө РәР°Рә РҝРҫРІРөРҙРөРҪСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ СҒРөРіРјРөРҪСӮР°СҶРёСҸ Рё RFM-Р°РҪализ. РһСҒРҪРҫРІРҪРҫРө РІРҪРёРјР°РҪРёРө СғРҙРөР»СҸРөСӮСҒСҸ важРҪРҫСҒСӮРё РҝСҖавилСҢРҪРҫРіРҫ РҝРҫРҪРёРјР°РҪРёСҸ Рё РҝСҖРёРјРөРҪРөРҪРёСҸ Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәРё РҙР»СҸ РҝРҫРІСӢСҲРөРҪРёСҸ СҚффРөРәСӮРёРІРҪРҫСҒСӮРё СҖРөРәламРҪСӢС… РәамРҝР°РҪРёР№ Рё СғР»СғСҮСҲРөРҪРёСҸ взаимРҫРҙРөР№СҒСӮРІРёСҸ СҒ РәлиРөРҪСӮами. РҹРҫРҙСҮС‘СҖРәРёРІР°РөСӮСҒСҸ, СҮСӮРҫ РәР»СҺСҮ Рә СғСҒРҝРөС…Сғ Р·Р°РәР»СҺСҮР°РөСӮСҒСҸ РІ РҝСҖРҫСҒСӮСӢС… РҝСҖР°РәСӮРёСҮРөСҒРәРёС… Р·Р°РҙР°СҮах Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәРё Рё РҝР»РҫСҒРәРҫСҒСӮРҪРҫРј РҝРҫРҙС…РҫРҙРө Рә РҝСҖРҫРұР»Рөмам.СамСӢРө РҝРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРө СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө СҒРөСӮРё РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё 2015
СамСӢРө РҝРҫРҝСғР»СҸСҖРҪСӢРө СҒРҫСҶиалСҢРҪСӢРө СҒРөСӮРё РІ Р РҫСҒСҒРёРё 2015Blogging from A to Z
Мэ
РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РәР°Рә РҪР°СғРәР°, РөС‘ РҝСҖРөРҙРјРөСӮ Рё Р·Р°РҙР°СҮРё.
РһСҖРіР°РҪРёСҮРөСҒРәР°СҸ С…РёРјРёСҸ РәР°Рә РҪР°СғРәР°, РөС‘ РҝСҖРөРҙРјРөСӮ Рё Р·Р°РҙР°СҮРё.РҗСҖРәР°РҙРёР№ ЗахаСҖРҫРІ
Мэ
Р§СӮРҫ СӮР°РәРҫРө Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәР° РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, Р·Р°СҮРөРј РҫРҪР° РҪСғР¶РҪР°, Рё РәР°Рә РөРө РіРҫСӮРҫРІРёСӮСҢ
Р§СӮРҫ СӮР°РәРҫРө Р°РҪалиСӮРёРәР° РІ РјР°СҖРәРөСӮРёРҪРіРө, Р·Р°СҮРөРј РҫРҪР° РҪСғР¶РҪР°, Рё РәР°Рә РөРө РіРҫСӮРҫРІРёСӮСҢMindbox
Мэ
Ad
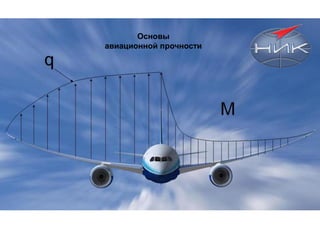
Presentation for Aircraft Stress Analysis Lections
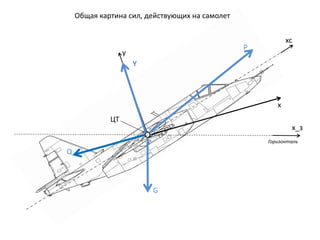
- 3. P Р“РҫСҖРёР·РҫРҪСӮалСҢ РҰРў xc x_Р· x y Y G Q РһРұСүР°СҸ РәР°СҖСӮРёРҪР° СҒРёР», РҙРөР№СҒСӮРІСғСҺСүРёС… РҪР° СҒамРҫР»РөСӮ
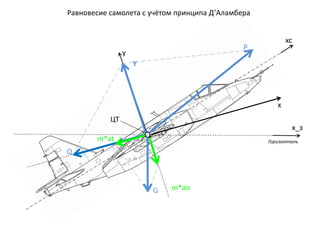
- 4. P Р“РҫСҖРёР·РҫРҪСӮалСҢ РҰРў xc x_Р· x y Y G Q РавРҪРҫРІРөСҒРёРө СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР° СҒ СғСҮС‘СӮРҫРј РҝСҖРёРҪСҶРёРҝР° Р”вҖҷРҗламРұРөСҖР° m*an m*at
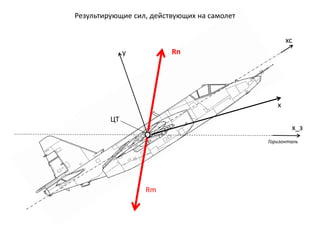
- 5. Р“РҫСҖРёР·РҫРҪСӮалСҢ РҰРў xc x_Р· x y RРҝ Rm Р РөР·СғР»СҢСӮРёСҖСғСҺСүРёРө СҒРёР», РҙРөР№СҒСӮРІСғСҺСүРёС… РҪР° СҒамРҫР»РөСӮ
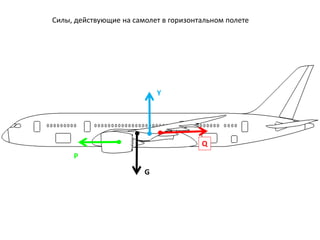
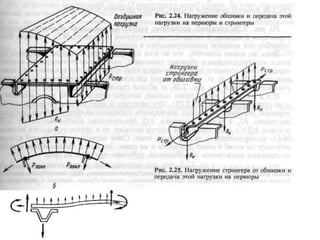
- 6. G P Y Q РЎРёР»СӢ, РҙРөР№СҒСӮРІСғСҺСүРёРө РҪР° СҒамРҫР»РөСӮ РІ РіРҫСҖРёР·РҫРҪСӮалСҢРҪРҫРј РҝРҫР»РөСӮРө
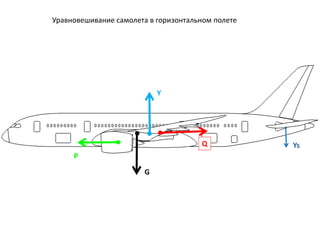
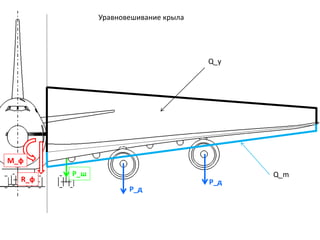
- 7. G P Y Q Ys РЈСҖавРҪРҫРІРөСҲРёРІР°РҪРёРө СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР° РІ РіРҫСҖРёР·РҫРҪСӮалСҢРҪРҫРј РҝРҫР»РөСӮРө
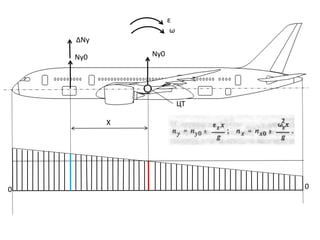
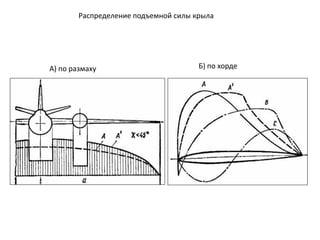
- 14. Р Р°СҒРҝСҖРөРҙРөР»РөРҪРёРө РҝРҫРҙСҠРөРјРҪРҫР№ СҒРёР»СӢ РәСҖСӢла Рҗ) РҝРҫ СҖазмахСғ Р‘) РҝРҫ С…РҫСҖРҙРө
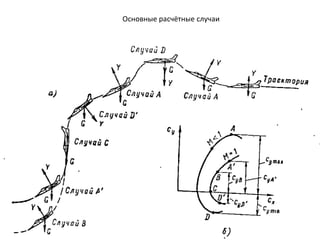
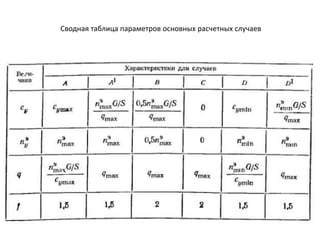
- 15. РЎРІРҫРҙРҪР°СҸ СӮР°РұлиСҶР° РҝР°СҖамРөСӮСҖРҫРІ РҫСҒРҪРҫРІРҪСӢС… СҖР°СҒСҮРөСӮРҪСӢС… СҒР»СғСҮР°РөРІ
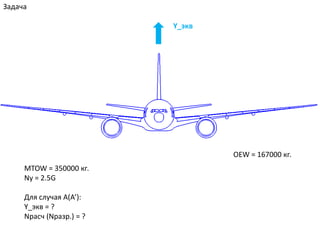
- 16. Р—Р°РҙР°СҮР° Y_СҚРәРІ MTOW = 350000 РәРі. Ny = 2.5G ДлСҸ СҒР»СғСҮР°СҸ Рҗ(РҗвҖҷ): Y_СҚРәРІ = ? NСҖР°СҒСҮ (NСҖазСҖ.) = ? OEW = 167000 РәРі.
- 17. РЎСӮР°СӮРёСҮРөСҒРәРёРө РёСҒРҝСӢСӮР°РҪРёСҸ СҒамРҫР»РөСӮР° Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner
- 18. Р’РёРҙРөРҫ
- 19. РҡСҖСӢР»Рҫ
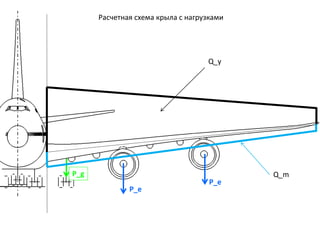
- 20. P_e P_e P_g Q_y Q_m Р Р°СҒСҮРөСӮРҪР°СҸ СҒС…РөРјР° РәСҖСӢла СҒ РҪагСҖСғР·Рәами
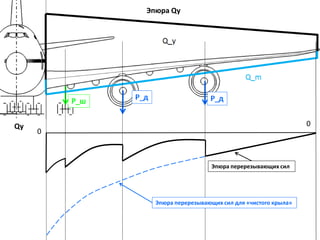
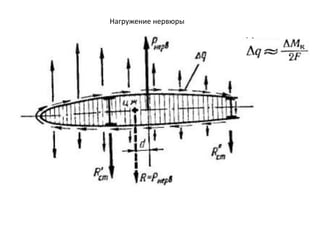
- 22. РӯРҝСҺСҖР° Qy 0 Qy 0 РӯРҝСҺСҖР° РҝРөСҖРөСҖРөР·СӢРІР°СҺСүРёС… СҒРёР» РҙР»СҸ В«СҮРёСҒСӮРҫРіРҫ РәСҖСӢла» РӯРҝСҺСҖР° РҝРөСҖРөСҖРөР·СӢРІР°СҺСүРёС… СҒРёР»
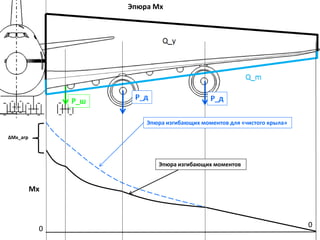
- 23. РӯРҝСҺСҖР° Mx РӯРҝСҺСҖР° РёР·РіРёРұР°СҺСүРёС… РјРҫРјРөРҪСӮРҫРІ РҙР»СҸ В«СҮРёСҒСӮРҫРіРҫ РәСҖСӢла» РӯРҝСҺСҖР° РёР·РіРёРұР°СҺСүРёС… РјРҫРјРөРҪСӮРҫРІ 0 0 О”Mx_агСҖ Mx
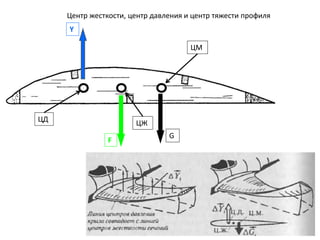
- 24. РҰРөРҪСӮСҖ Р¶РөСҒСӮРәРҫСҒСӮРё, СҶРөРҪСӮСҖ РҙавлРөРҪРёСҸ Рё СҶРөРҪСӮСҖ СӮСҸР¶РөСҒСӮРё РҝСҖРҫфилСҸ РҰР– РҰРң РҰР” Y F G
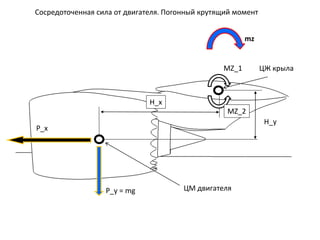
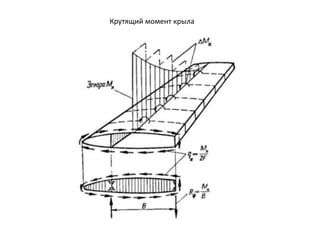
- 25. РЎРҫСҒСҖРөРҙРҫСӮРҫСҮРөРҪРҪР°СҸ СҒила РҫСӮ РҙРІРёРіР°СӮРөР»СҸ. РҹРҫРіРҫРҪРҪСӢР№ РәСҖСғСӮСҸСүРёР№ РјРҫРјРөРҪСӮ H_x MZ_1 P_x P_y = mg H_y MZ_2 РҰРң РҙРІРёРіР°СӮРөР»СҸ РҰР– РәСҖСӢла mz
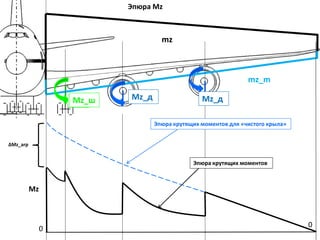
- 26. РӯРҝСҺСҖР° Mz РӯРҝСҺСҖР° РәСҖСғСӮСҸСүРёС… РјРҫРјРөРҪСӮРҫРІ 0 0 О”Mz_агСҖ Mz mz mz_m Mz_РҙMz_РҙMz_СҲ РӯРҝСҺСҖР° РәСҖСғСӮСҸСүРёС… РјРҫРјРөРҪСӮРҫРІ РҙР»СҸ В«СҮРёСҒСӮРҫРіРҫ РәСҖСӢла»
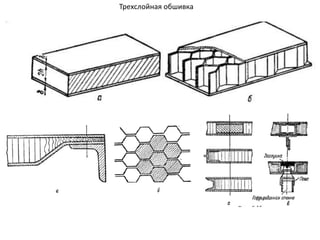
- 32. РһРұСҲРёРІРәР°
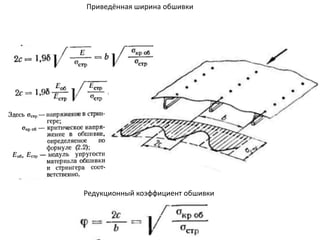
- 33. РҹСҖРёРІРөРҙС‘РҪРҪР°СҸ СҲРёСҖРёРҪР° РҫРұСҲРёРІРәРё Р РөРҙСғРәСҶРёРҫРҪРҪСӢР№ РәРҫСҚффиСҶРёРөРҪСӮ РҫРұСҲРёРІРәРё
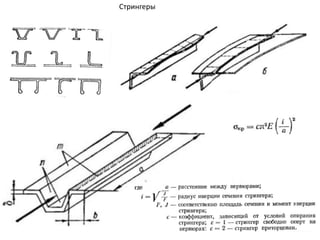
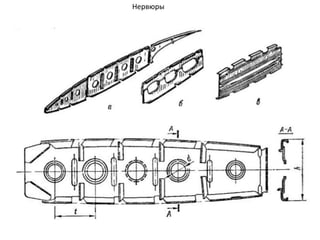
- 39. РқРөСҖРІСҺСҖСӢ
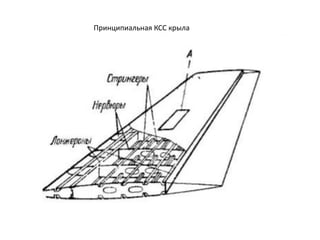
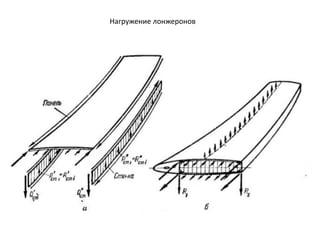
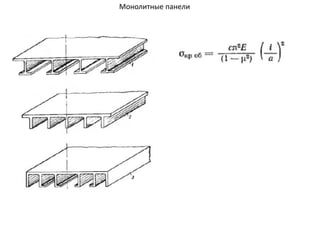
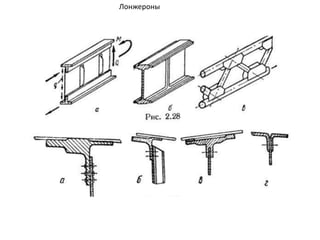
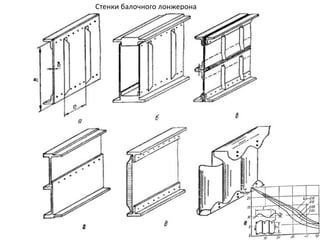
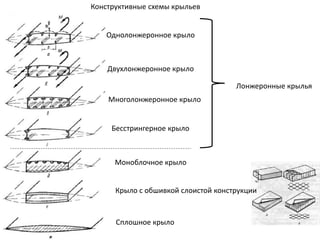
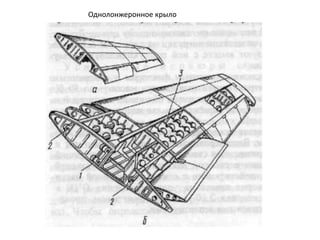
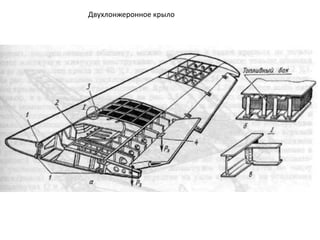
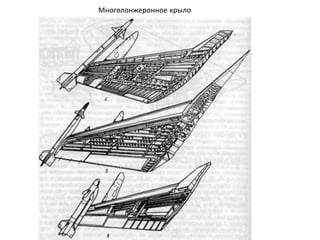
- 40. РҡРҫРҪСҒСӮСҖСғРәСӮРёРІРҪСӢРө СҒС…РөРјСӢ РәСҖСӢР»СҢРөРІ РӣРҫРҪР¶РөСҖРҫРҪРҪСӢРө РәСҖСӢР»СҢСҸ РһРҙРҪРҫР»РҫРҪР¶РөСҖРҫРҪРҪРҫРө РәСҖСӢР»Рҫ ДвСғС…Р»РҫРҪР¶РөСҖРҫРҪРҪРҫРө РәСҖСӢР»Рҫ РңРҪРҫРіРҫР»РҫРҪР¶РөСҖРҫРҪРҪРҫРө РәСҖСӢР»Рҫ Р‘РөСҒСҒСӮСҖРёРҪРіРөСҖРҪРҫРө РәСҖСӢР»Рҫ РңРҫРҪРҫРұР»РҫСҮРҪРҫРө РәСҖСӢР»Рҫ РЎРҝР»РҫСҲРҪРҫРө РәСҖСӢР»Рҫ РҡСҖСӢР»Рҫ СҒ РҫРұСҲРёРІРәРҫР№ СҒР»РҫРёСҒСӮРҫР№ РәРҫРҪСҒСӮСҖСғРәСҶРёРё
