Italy and agriculture
- 1. ITALY Under the Tuscan Sun Tuscan Farm House, oil on wood, 4"x5.5", (10cm x 14cm ) http://www.lonelyplanet.com/maps/europe/italy/
- 2. Geography Southern Europe with an area of about 301,000 sq. kilometers The variety of climatic and morphological conditions Heterogeneous nature of the soil
- 3. italian culture Food is part of the rythm of life. Enjoying a meal with friends or family is the main ingredient of any Italian dish. Sunday lunch is usually spent at some relativeâs home 5% of Italians eat out on Sundays 95% are at home eating as much as humanly possible. Tradition and regional diversity : Every dish, even the most simple, has roots in the past and traditions of that particular region.
- 4. Two cardinal rules of Italian cuisine Eat Locally Eat seasonally - faithful Italian cooks would never eat asparagus, tomatoes or artichokes out of the seasons.
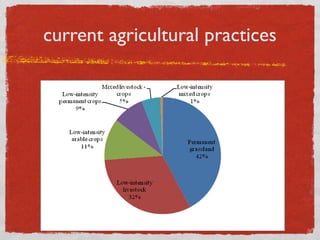
- 5. 1. agricultural history PEASANT AND CAPITALISTIC FORMS OF AGRICULTURE Family Farming Sharecropping Till second WW, agricultural structure based on the nature of the relationship existing between land ownership, labour and entreprenuiral function Over 90% of holdings have been classified within same group as direct farming on own land (farms run directly by farmer)
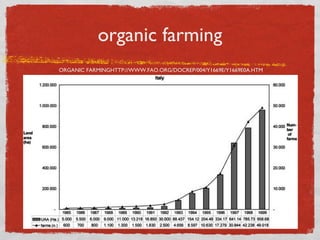
- 6. types of Food industry Three different types of food productions Industrial Organic Local
- 7. major ITALIAN crops FRUITS (GRAPS, CITRUS FRUITS,APPLE, PEACHES, STRAWBERRIES, RASBERRIES) GRAINS (WHEAT, MAZES, RICE) VEGETABLES NUTS ( CHESTNUTS, HAZELNUTS) OLIVES TRUFFLES AND MUSHROOMS
- 8. land Tenure situation in Italy there are a number of ways of registering ownership of the property 1. 2. 3. 4. Family ownership Sole and joint ownership Shared ownership co-ownership under Italian law, anyone with a share of a willed property can insist on receiving their share âĶ now.
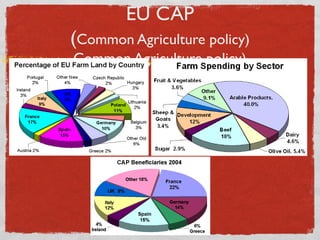
- 9. EU CAP (Common Agriculture policy) Common Agriculture policy)
- 10. AGRICULTURE POLICIES EU spent overEU billion on subsidies in 2008. 50 in General Largest receipient of these funds was France (10.1 billion) Has many different regions for specific production methods and culinary traditions for quality control Three quality logos : (1) PDO (2) TSG (3) PGI 1102 Registered Products
- 14. sustainability Sound Ecology Water & Air Quality Protected Natural Resources Managed Sustain Viable Biodiversity Feasible Implementation Public Supports Proposal Adequate Resources Available Laws & Regulations Work or Can be Changed Sufficient Energy Enhance Use of Renewables Careful Allocation of CarbonBased Fuel Resources Invest in Research Viable Economy Investment $$$ Available Positive Affect on Local Economy Adequate Infrastructure Landowner Objectives Balanced Land Use Planning Landowner Contributions Recognized and Valued What is Their Vision? Social Equity All Segments of Society Share Wealth Public Has Opportunity for Input Rewards Fairly Distributed
- 15. source and acknowledgement http://www.fao.org/farmingsystems/pdf/IFSA/Abstracts.pdf http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/24426/1/sp05ro01.p ( âFrom households to firms with independent legal status: the spectrum of institutional units in the development of European agriculture â) Paper prepared for presentation at the 94th EAAE Seminar http://www.oecd.org/tad/sustainableagriculture/45447828.pdf
Editor's Notes
- #2: {}