Propofol
- 1. DR ASHARAB TAD DR P . N. JAIN
- 2. PROPOFOL INTRODUCED IN 1977 BY KAY & ROLLY BASIC PHARMACOLOGY It is one of the group of alkyl phenol. The chemical structure is 2-6 di iso propyl phenol. Propofol is insoluble in water and therfore initially prepared with cremaphor EL. PH of 7, Pka of propofol in water is 11. It is available as 1 % solution in 20 ml glasss ampoule or vials and in 50, 100 ml pre filled syringes
- 3. Propofol consist of a phenol ring substituted with two Isopropyl group is chemically described as 2,6- di isopropyl phenol PHYSICOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- 4. PREPARATIONS Propofol administered intravenously as 1% solution in an aqueous solution of 10% soybean oil, and 1.2% purified egg phospholipid added as emulsifier, with 2.25% of glycerol as a tonicity- adjusting agent, and sodium hydroxide to change the pH insoluble drug that requires a lipid vehicle for emulsification. Current formulations of propofol use a soybean oil as the oil phase and egg lecithin as the emulsifying agent that is composed of long chain triglycerides.4 This formulation supports bacterial growth and causes increased plasma triglyceride concentrations when prolonged IV infusions are used. Propofol has a pH of 7 and appears as a slightly viscous, milky white substance
- 5. MECHANISM OF ACTION GABA RECEPTOR COMPLEX ï Propofol is relatively selective modulator of GABA receptors ï g- amino butyric acid is inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain. ï Assemble to form cl- channel with GABA A receptor Activation of GABA receptors increases transmembrane CL conductance hyperpolarization of post synaptic membrane functional inhibition of the postsynaptic neuron Propofol decreases the rate of dissociation of GABA from its receptors, thereby increasing the duration of the GABA âactivated opening of chloride channel with resulting hyperpolarisation of cell membrane.
- 6. GABA RECEPTOR: CONSISTS OF 5 SUBUNITS
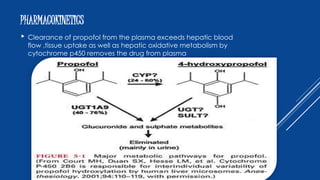
- 7. PHARMACOKINETICS ï Clearance of propofol from the plasma exceeds hepatic blood flow ,tissue uptake as well as hepatic oxidative metabolism by cytochrome p450 removes the drug from plasma
- 8. Clinical uses ï§ Induction of anaesthesia: (1 to 2.5 mg/kg/ iv) ï§ Intravenous sedation: (25 to 75 micro g/kg/iv) ï§ Maintenance of Anaesthetic: (50 to 150 micro g/kg/iv) ï§ Day care surgery ï§ Antiemetic effect: (10 to 15 mf i.v) ï§ Sub hypnotic doses of propofol (10 to 15mg/IV) may be used in the post anaesthesia care unit to treat nausea and vomiting. Very effective against Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting as it inhibits sub cortical pathways ï§ More effective than ondansetron in preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting. ï§ Antipruritic Effect: propofol depress spinal cord activity Propofol 10mg I.V is effective is the treatment of pruritis associated with Neuraxial opioid or cholestasis. ï§ ANTICONVULSANT ACTIVTY: 1 mg/kg iv decreases seizure duration.
- 9. CONTNâĶ Along with opioids it is agent of choice for total intravenous anaesthesia [TIVA] It can be used in icu for sedation. It is the agent of choice for induction in susceptible individuals for malignant hyperthermia
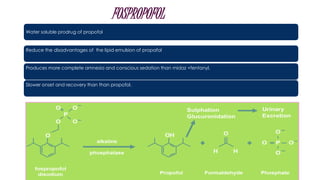
- 10. FOSPROPOFOL Water soluble prodrug of propofol Reduce the disadvantages of the lipid emulsion of propafol Produces more complete amnesia and conscious sedation than midaz +fentanyl. Slower onset and recovery than than propofol.
- 11. EFFECTS ON ORGAN SYSTEM âĒPropofol decreases the cerebral metabolic rate for oxygen (CMRO2) âĒDecreasing the cerebral blood flow. âĒDecreasing intracranial pressure. âĒDecrease in early component of somato sensory and motor evoked potential. Central nervous system âĒPropofol decreases systemic blood pressure âĒHence adequate hydration before I.V administered of propofol is recommended to minimize the blood pressure effect. âĒinhibition of sympathetic vasoconstrictor nerve activity.â vascular smooth muscle relaxation. âĒnegative inotropic effect of propofol results from decrease in intracellular ca+ availability due to inhibition of trans sarcolemmal ca+ influx âĒInfusion of propofol causes decrease in myocardial blood flow and oxygen consumption. âĒBradycardia and asystole Cardiovascular system
- 12. Respiration system: Propofol produces does-dependent depression of ventilation with apnoea. Maintenance infusion of propofol decreases tidal volume and frequency of breathing. It produces bronchodilation and decreases the incidence of intra-operative wheezing in patients with asthma. Propofol: Produces decrease in amplitudes of the early components of somatosensory evoked potential. Hepatic and Renal Function: It does not affect hepatic and renal function. Prolonged infusions of propofol have been associated with hepatocellular Injury accompanied by lactic acidosis, bradysrhythmias, and rhabdomyolysis as part of the propofol infusion syndrome Prolonged infusion of propofol may result in excretion of green coloured urine, which reflects, the presence of phenols in the urine. Eye: Decreases the intraocular pressure occur immediately after induction.
- 13. CONTRAINDICATIONS ï§ Hypersensitivity to propofol injectable emulsion or any of its components. Allergies to eggs , eggs products , soybeans or soy products .
- 14. ADVANTAGES OVER THIOPENTONE Rapid and smooth recovery Complete elimination from body in 4 hrs so patient is ambulatory early Anti emetic Antipruritic Bronchodilator
- 15. Allergic Reactions: Allergic components of propofol are phenyl nucleus and disopropyl side chain. Pain on Injection: It is the most common side effect associated with Propofol. Using large veins and avoiding veins in the dorsum of the hand and adding Lidocaine to the propofol solution reduce this. Abuse potential: Intense dreaming activity amorous behaviour and hallucinations has been seen during recovery from the effects of propofol. Addiction is reported. Bacterial Growth Propofol strongly supports growth of Escherichia coli and pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Hypotension: The most significant side effect on induction is the decrease in systemic blood pressure. Side Effect
- 16. THANK YOU






![CONTNâĶ
Along with opioids it is agent of choice for total intravenous
anaesthesia [TIVA]
It can be used in icu for sedation.
It is the agent of choice for induction in susceptible individuals for
malignant hyperthermia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/propofol-150817085219-lva1-app6892/85/Propofol-9-320.jpg)