It 405 materi 1 pengantar
- 1. IT 405: Konstruksi Perangkat Lunak Berorientasi Objek Pengantar Ayi Purbasari, ST., MT. Unpas, 2014
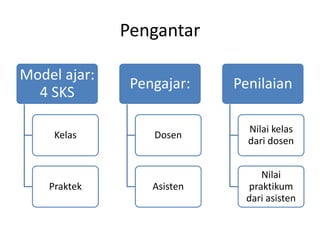
- 2. Pengantar Model ajar: 4 SKS Kelas Praktek Pengajar: Dosen Asisten Penilaian Nilai kelas dari dosen Nilai praktikum dari asisten
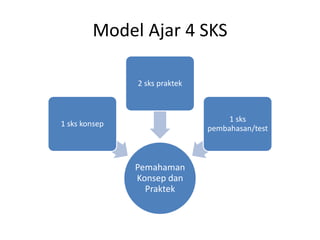
- 3. Model Ajar 4 SKS Pemahaman Konsep dan Praktek 1 sks konsep 2 sks praktek 1 sks pembahasan/test
- 4. Para Pengajar dan Asisten Ayi Purbasari ŌĆó Kelas B ŌĆó Koordinator Ade Sukendar ŌĆó Kelas A ŌĆó Kelas D Hendra Komara ŌĆó Kelas C Wanda Gusdya ŌĆó Kelas E ŌĆó Kelas F ŌĆó Para Asisten
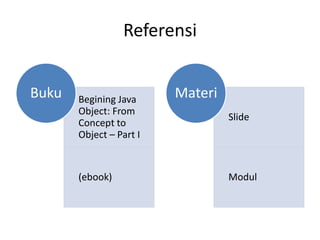
- 5. Referensi Begining Java Object: From Concept to Object ŌĆō Part I (ebook) Buku ║▌║▌▀Ż Modul Materi
- 6. Tujuan Instruksional Umum ŌĆó Mampu memahami konsep konstruksi dan pemrograman berorientasi objek menggunakan teknologi Java. ŌĆó Java? Takut ketemu Java?
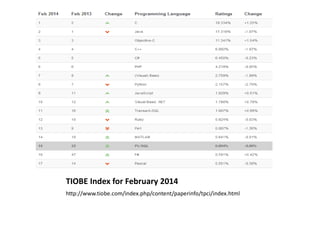
- 7. TIOBE Index for February 2014 http://www.tiobe.com/index.php/content/paperinfo/tpci/index.html
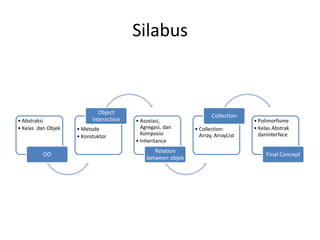
- 8. Silabus ŌĆó Abstraksi ŌĆó Kelas dan Objek OO ŌĆó Metode ŌĆó Konstuktor Object Interaction ŌĆó Asosiasi, Agregasi, dan Komposisi ŌĆó Inheritance Relation between objek ŌĆó Collection: Array, ArrayLIst Collection ŌĆó Polimorfisme ŌĆó Kelas Abstrak danInterface Final Concept
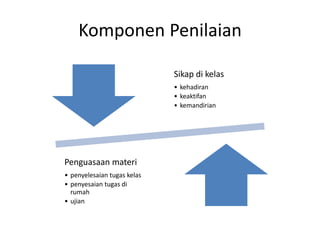
- 9. Komponen Penilaian Sikap di kelas ŌĆó kehadiran ŌĆó keaktifan ŌĆó kemandirian Penguasaan materi ŌĆó penyelesaian tugas kelas ŌĆó penyesaian tugas di rumah ŌĆó ujian
- 10. SESI I: KONSEP MODEL DAN ABSTRAKSI
- 11. Konstruksi Perangkat Lunak Berorientasi Objek Apa itu konstruksi?
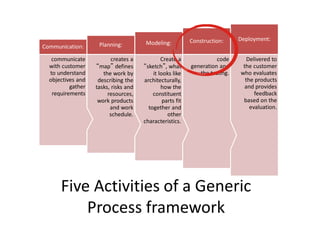
- 12. Five Activities of a Generic Process framework Delivered to the customer who evaluates the products and provides feedback based on the evaluation. Deployment: code generation and the testing. Construction: Create a ŌĆ£sketchŌĆØ, what it looks like architecturally, how the constituent parts fit together and other characteristics. Modeling: creates a ŌĆ£mapŌĆØ defines the work by describing the tasks, risks and resources, work products and work schedule. Planning: communicate with customer to understand objectives and gather requirements Communication:
- 13. Konstruksi Perangkat Lunak Setelah Pemodelan: Harus menguasai UML, terutama kelas diagram. Koding (IT 405) Testing (IT 852)
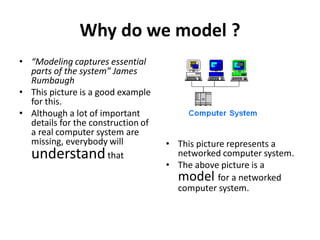
- 14. Why do we model ? ŌĆó ŌĆ£Modeling captures essential parts of the systemŌĆØ James Rumbaugh ŌĆó This picture is a good example for this. ŌĆó Although a lot of important details for the construction of a real computer system are missing, everybody will understandthat ŌĆó This picture represents a networked computer system. ŌĆó The above picture is a model for a networked computer system.
- 15. Why do we model visually ? ŌĆó ŌĆ£Graphics reveal dataŌĆØ -- Edward Tufte. The Visual Display of Quantitative Information, 1983 ŌĆó 1 bitmap = 1 megaword. -- Anonymous visual modeler
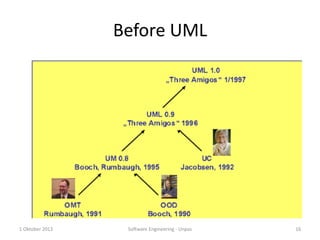
- 16. Before UML 1 Oktober 2013 Software Engineering - Unpas 16
- 18. WHY IS UNDERSTANDING OBJECTS SO CRITICAL TO BEING A SUCCESSFUL OO PROGRAMMER? (sesi membaca buku FROM CONCEPT TO OBJECT)
- 19. SESI II DAN III: PRAKTIKUM REVIEW JAVA DASAR
- 20. SESI IV: ŌĆó Pembahasan Java Dasar (dari modul) ŌĆó Pengumuman Tugas I: membuat makalah 6 halaman tentang Java (sejarah, aplikasi, dll) dilengkapi dengan contoh program kecil dengan penggunaan if dan for. ŌĆó Format tugas = format makalah/paper
- 21. TERIMA KASIH