Sulfurcycle.odt
- 1. The Sulfur Cycle A presentation by Group 4 Jeremy Magdaong CJ Balicanta Joey Torres Emman Perez Die go Evangelista
- 2. The Sulfur Cycle What is sulfur?
- 3. Why do we need sulfur?
- 5. Is this cycle balanced?
- 6. The effects of too much sulfur
- 7. The Sulfur Cycle Before we get started on the sulfur cycle, we need to know what sulfur is anyway. SULFUR is.... An element
- 8. An essential element of life
- 9. Used in fertilizers, gunpowder, pesticides and fungicides
- 10. Found in two amino acids: ┬Ā cysteine ┬Āand┬Ā methionine
- 11. The Sulfur Cycle Why do we need it? Sulfur is an important nutrient for organisms, being a key constituent of certain amino acids, proteins and other biochemicals. Plants get sulfur by acquiring simple mineral compounds from the soil. Animals then get the organic form of sulfur by eating plants or animals who eat plants. Sulfur is also an important mineral commodity. It is obtained through pollution control in factories where it is collected in its natural gas state. Then it may be used for sulfate fertilization in some prairie agriculture.
- 12. The Sulfur Cycle A Crash Course on the Elements and Compounds involved in the cycle S is for SULFUR SO 4 ^-2 is for Sulfate SO 2 is for Sulfur Dioxide H 2 S is for Hydrogen Sulfide FeS2 is Iron Sulfide, or pyrite
- 13. The Sulfur Cycle
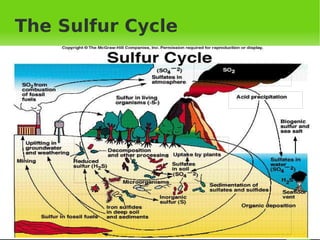
- 14. The Sulfur Cycle To understand more about the cycle, we have to start at one point, say the SO2 emissions by the volcanoes, which occur naturally. They either go up in the air, or be decomposed to become H 2 S. SO2 HOME
- 15. The Sulfur Cycle In the air, the sulfates promote condensation, then when it precipitates it goes to either land or water. HOME
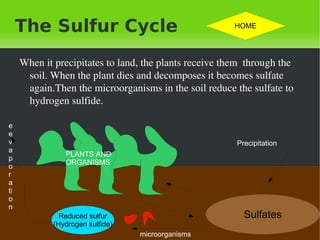
- 16. The Sulfur Cycle When it precipitates to land, the plants receive them through the soil. When the plant dies and decomposes it becomes sulfate again.Then the microorganisms in the soil reduce the sulfate to hydrogen sulfide. microorganisms PLANTS AND ORGANISMS eevaporation Precipitation Sulfates Reduced sulfur (Hydrogen sulfide) HOME
- 17. The Sulfur Cycle The decaying of organisms may lead to the sedimentation of sulfates and sulfides and the organic sedimentation. In the organic sedimentations, it takes millions of years to turn them into fossil fuel. Fossil Fuels are then dug up by energy companies, which produces smoke in the process. Decay and decompostion SMOKE with SO2
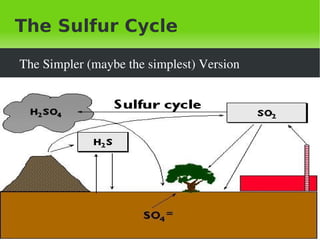
- 18. The Sulfur Cycle The Simpler (maybe the simplest) Version