Chapter 1 General Anatomy
- 2. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY: ANATOMICAL POSITION, BODY PLANES/REGIONS/CAVITIES, DIRECTIONAL TERMS AND MOVEMENTS, BODY SYSTEMS
- 3. What is Anatomy? Anatomy is the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts and their relationships to one another. a. Gross Anatomy b. Microscopic Anatomy
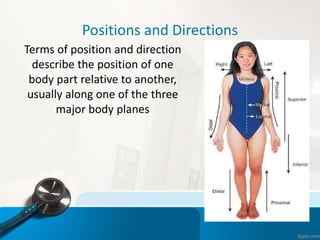
- 4. Anatomical Position тАв Standing erect, with palms and feet facing forward тАв Is the standard reference point in which all positions, movements, and planes are described
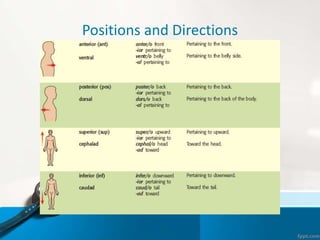
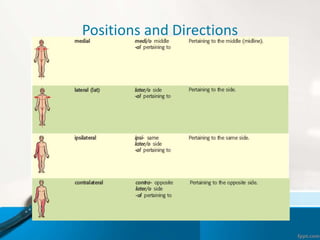
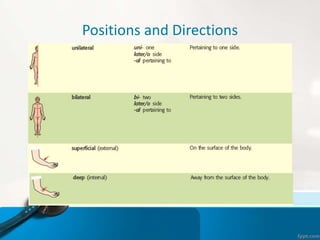
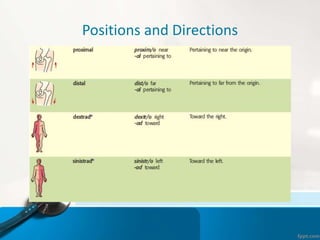
- 5. Positions and Directions Terms of position and direction describe the position of one body part relative to another, usually along one of the three major body planes
- 10. Positions and Directions Prone тАв Lying face down тАУ Like a Pro Baseball player sliding into Home. Supine тАв Lying face up тАУ Lying on your spine and you can have soup poured into your mouth.
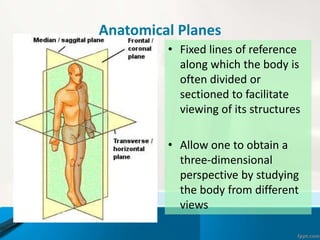
- 11. Anatomical Planes тАв Fixed lines of reference along which the body is often divided or sectioned to facilitate viewing of its structures тАв Allow one to obtain a three-dimensional perspective by studying the body from different views
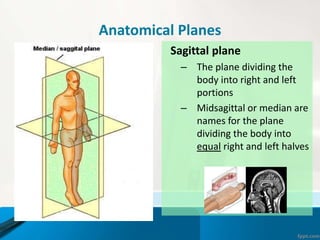
- 12. Anatomical Planes Sagittal plane тАУ The plane dividing the body into right and left portions тАУ Midsagittal or median are names for the plane dividing the body into equal right and left halves
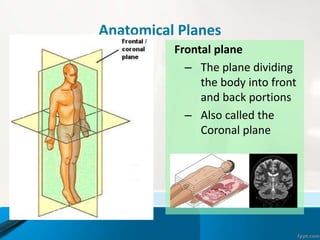
- 13. Anatomical Planes Frontal plane тАУ The plane dividing the body into front and back portions тАУ Also called the Coronal plane
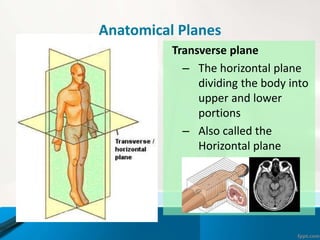
- 14. Anatomical Planes Transverse plane тАУ The horizontal plane dividing the body into upper and lower portions тАУ Also called the Horizontal plane
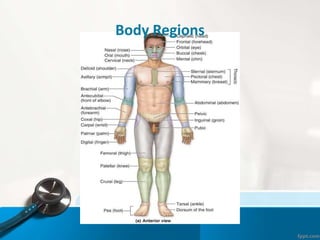
- 15. Body Regions
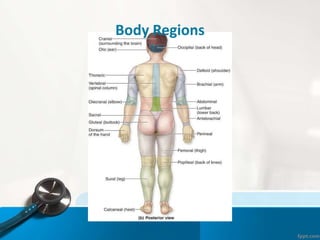
- 16. Body Regions
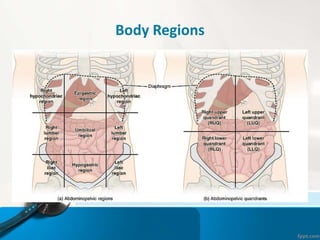
- 17. Body Regions
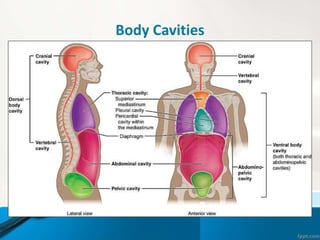
- 18. Body Cavities
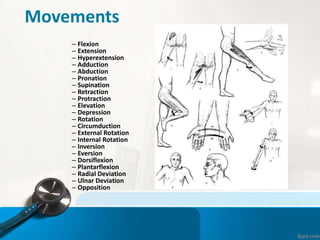
- 19. Movements тАУ Flexion тАУ Extension тАУ Hyperextension тАУ Adduction тАУ Abduction тАУ Pronation тАУ Supination тАУ Retraction тАУ Protraction тАУ Elevation тАУ Depression тАУ Rotation тАУ Circumduction тАУ External Rotation тАУ Internal Rotation тАУ Inversion тАУ Eversion тАУ Dorsiflexion тАУ Plantarflexion тАУ Radial Deviation тАУ Ulnar Deviation тАУ Opposition
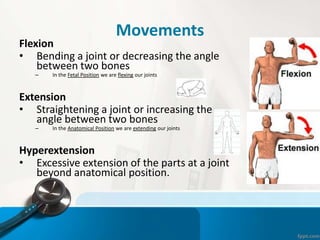
- 20. Movements Flexion тАв Bending a joint or decreasing the angle between two bones тАУ In the Fetal Position we are flexing our joints Extension тАв Straightening a joint or increasing the angle between two bones тАУ In the Anatomical Position we are extending our joints Hyperextension тАв Excessive extension of the parts at a joint beyond anatomical position.
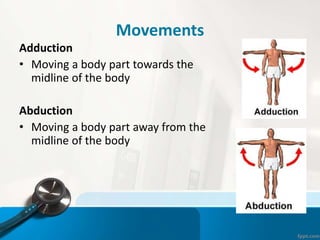
- 21. Movements Adduction тАв Moving a body part towards the midline of the body Abduction тАв Moving a body part away from the midline of the body
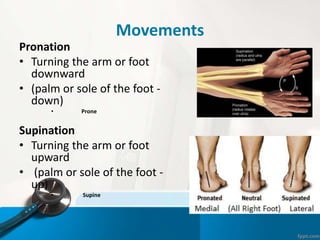
- 22. Movements Pronation тАв Turning the arm or foot downward тАв (palm or sole of the foot - down) тАв Prone Supination тАв Turning the arm or foot upward тАв (palm or sole of the foot - up) тАв Supine
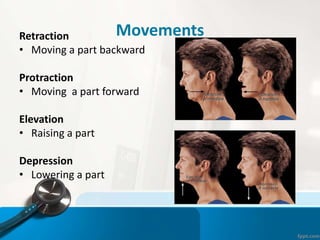
- 23. MovementsRetraction тАв Moving a part backward Protraction тАв Moving a part forward Elevation тАв Raising a part Depression тАв Lowering a part
- 24. Movements Rotation тАв Turning on a single axis Circumduction тАв Tri-planar, circular motion at the hip or shoulder Internal rotation тАв Rotation of the hip or shoulder toward the midline External rotation тАв Rotation of the hip or shoulder away from the midline
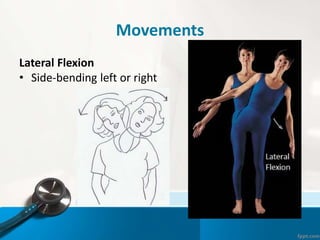
- 25. Movements Lateral Flexion тАв Side-bending left or right
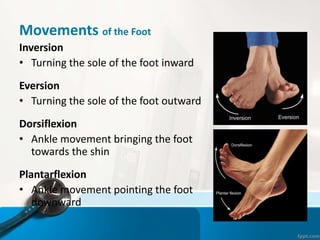
- 26. Movements of the Foot Inversion тАв Turning the sole of the foot inward Eversion тАв Turning the sole of the foot outward Dorsiflexion тАв Ankle movement bringing the foot towards the shin Plantarflexion тАв Ankle movement pointing the foot downward
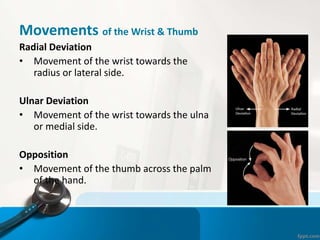
- 27. Movements of the Wrist & Thumb Radial Deviation тАв Movement of the wrist towards the radius or lateral side. Ulnar Deviation тАв Movement of the wrist towards the ulna or medial side. Opposition тАв Movement of the thumb across the palm of the hand.
- 28. Body Systems