Aarti Sip
Download as ppt, pdf3 likes519 views
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is used to initiate, manage and terminate multimedia sessions over the Internet. It supports text, voice and video sessions between one or more participants using unicast or multicast. SIP entities include user agents, proxy servers, redirect servers and registrars. SIP uses request and response message types to establish and terminate calls. It allows for call redirection, proxying and instant messaging. SIP can be used for Internet telephony between IP phones and analog phones using gateways. Additional applications include PINT and Internet call waiting. While SIP is still a proposed standard, it promises interoperability for IM and competition with H.323.
1 of 18
Downloaded 38 times













Ad
Recommended
Aarti sip
Aarti sipgaderamesh
╠²
The document discusses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), including its purpose for initiating and managing multimedia sessions over the Internet, the various SIP entities like user agents and servers, common SIP message types, how SIP establishes and terminates calls, call redirection and proxying, using SIP for instant messaging and Internet telephony, additional SIP applications, and the future of SIP. It provides an overview of SIP, describing its core functionality and some key aspects of how it works at a high level.Sip & its application
Sip & its applicationPoulami Pal
╠²
SIP is a signaling protocol used to set up multimedia communication sessions between endpoints over IP networks. It allows for user location, capabilities, availability, call setup and handling. SIP uses client-server architecture with user agents, proxies, registrars, and other entities. Common SIP methods include INVITE, ACK, BYE, and REGISTER. Responses are categorized by class with 1xx for provisional, 2xx for success, 3xx for redirect, 4xx for client error, 5xx for server error, and 6xx for global errors. The Via header tracks the path of SIP requests. SIP supports voice and video calls as well as instant messaging through extensions like SIMPLE.SIP servers on embedded systems: Powering SoHo communications
SIP servers on embedded systems: Powering SoHo communicationsRADVISION Ltd.
╠²
The document discusses the functionality and applications of SIP servers over embedded systems, highlighting their importance in modern communication solutions like IP telephony and integrated multimedia services. It outlines the technological requirements and challenges faced in developing SIP servers for embedded devices, including performance, memory management, and flexibility. Additionally, it presents RadvisionÔÇÖs SIP server framework as a solution, emphasizing its compatibility, low footprint, and high transaction performance.Understanding Session Border Controllers
Understanding Session Border Controllersstefansayer
╠²
The document discusses the evolution of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and the role of Session Border Controllers (SBCs) in addressing its limitations. It highlights how SBCs emerged to resolve issues like NAT traversal and security vulnerabilities in SIP deployments while providing features that enhance the functionality of communication services. The document outlines the general behavior of SBCs, their impact on SIP messaging, and their importance in modern telephony and multimedia communications.session-initiation-protocol
session-initiation-protocolSailee Choudhary
╠²
The document provides an overview of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), detailing its role in initiating, managing, and terminating communications on the internet. It outlines key network elements such as user agents, proxy servers, and message types including requests and responses. Additionally, it covers processes for session establishment, call redirection, and proxying.Session Initiation Protocol - In depth analysis
Session Initiation Protocol - In depth analysischinmaypadhye1985
╠²
This document describes a CMPE 208 Fall 2008 project on the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) carried out by Chinmay Padhye, Amit More, Abhishek Sharma, and Nihar Dandekar. The project introduces SIP, describes its entities and functions, and outlines test cases the group planned to carry out including softphone registration, call setup, call forwarding, and call forking using softphones like Xlite and a Hamachi server.Session initiation-protocol
Session initiation-protocolSanthosh Somu
╠²
The document discusses the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), which allows for multimedia communication sessions over IP networks. SIP establishes sessions for voice, video, messaging and other applications. It uses requests and responses to initiate sessions between users, locate users, invite them to sessions, and terminate sessions. SIP relies on user agents, proxy servers, redirect servers and registrar servers. It enables mobility and flexibility in setting up and modifying communication sessions across different devices.Lync 2010 Top New Features
Lync 2010 Top New FeaturesTimur Bayazitov
╠²
The document summarizes new features in Microsoft Lync 2010. Key features include an improved client experience with contact cards, activity feeds, and conversation view. It features enhanced audio, video, and web conferencing. Enterprise voice features are improved with enhanced phone experiences, call delegation, and quality notifications. Manageability is improved with tools for planning, deployment, administration, and monitoring. The partner ecosystem supports a range of IP phones and devices. Interoperability is expanded through SIP trunking and standards-based alliances. Extensibility is enhanced through managed APIs for client and server customization.FutureComm 2010: SIP Server Applications on Embedded Platforms
FutureComm 2010: SIP Server Applications on Embedded PlatformsRADVISION Ltd.
╠²
This document discusses SIP server applications on embedded platforms. It begins with an agenda and overview of modern communications including IP phones, video phones, and soft phones. It then discusses using a SIP server on embedded systems to provide PBX functionality, address challenges of limited resources, and provide features like call control, presence, and media processing. Examples are given of SIP servers for devices like set-top boxes and residential gateways. The document concludes by describing RADVISION's SIP server framework solution for embedded systems, which provides core server capabilities and components while allowing for custom application logic.7 Ways SIP Trunking Can Change Your Business
7 Ways SIP Trunking Can Change Your BusinessCoreDial, LLC
╠²
The SIP trunking market is rapidly growing, expected to reach $8 billion by 2018, driven by the adoption of cloud and unified communications. Key benefits include reduced costs, scalability, and mobility, making it easier for businesses to expand geographically while maintaining phone service features. Adoption rates are rising; 50% of companies currently use SIP trunking, projected to increase to 78% by 2016 as traditional systems decline.Jason Fischl The Softphone And The Pbx
Jason Fischl The Softphone And The PbxCarl Ford
╠²
CounterPath is a leading developer of VoIP softphone applications, with over 100 employees. It aims to provide carrier-grade softphone solutions that are highly interoperable with existing infrastructures. Some challenges in deploying softphones and PBXes include simplifying installation and configuration, centralized management of credentials and directories, enabling remote upgrades, and ensuring interoperability between elements. CounterPath works with Digium, the creator of Asterisk, to provide tightly integrated softphone and PBX solutions that address these challenges.Introduction to SIP
Introduction to SIP neerav_adhikari
╠²
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application-layer signaling protocol used for establishing multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as voice or video calls. SIP can be used to initiate a call, invite participants and manage a call. It defines several methods for call setup, maintenance and termination. Common SIP methods include INVITE for call initiation, ACK to acknowledge call setup, BYE to terminate a call, and REGISTER for registering location. SIP uses SDP for negotiating media capabilities and RTP for transporting media streams.Asterisk - Glen Bastes
Asterisk - Glen Bastessoss
╠²
The document discusses the open source Asterisk PBX software. It provides an overview of Asterisk including that it was created in 1999 as a free and open source alternative to expensive proprietary PBX systems. Asterisk allows users to build their own software-based phone systems using inexpensive hardware and can provide many of the same features as traditional PBXs through its flexible architecture and extensive capabilities. The document outlines some of Asterisk's main functionalities and how it works as well as hardware that can be used with it.04b-radcliffe
04b-radcliffeDavid Radcliffe
╠²
This document discusses prospects for managed and hosted voice services. It identifies over 200 work products involved in voice services that could be managed, such as call detail recording, trunk configuration analysis, and fraud detection. It describes how to select a support model based on whether the service needs to be on-site, remote, or mobile. Finally, it outlines some key components of managed voice services, including fault management, configuration management, and security management.Voip
VoipZohaib Hussain
╠²
The document provides an overview of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), detailing its history, architecture, operational mechanics, and key protocols such as H.323, SIP, and MGCP. It compares VoIP with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), highlighting advantages like cost-effectiveness and ease of use, along with disadvantages like dependency on power and internet connectivity. Additionally, it outlines the equipment requirements for implementing VoIP and summarizes various features associated with both VoIP and PSTN.PBX.NET Hosted PBX | Business VOIP Sales Presentation
PBX.NET Hosted PBX | Business VOIP Sales PresentationPBX.NET Corporation
╠²
The document provides an overview of VoIP technology and PBX.NET's VoIP products and services. It discusses how VoIP works and its benefits over traditional phone systems. PBX.NET offers two main solutions: a Broadband PBX hosted service and Virtual Telephone Line broadband phone service. Both solutions provide business phone features over broadband at a lower cost than traditional phone lines. PBX.NET has reliable nationwide infrastructure and offers 24/7 customer support.Introduction into SIP protocol
Introduction into SIP protocolMichal Hrncirik
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) used in VoIP communication, detailing its functions, structure, and how it operates to facilitate multimedia sessions. It discusses SIP user credentials, common methods, troubleshooting techniques, and SIP trunking for unified communication services. Additionally, it highlights typical problems and solutions related to SIP deployment, emphasizing the importance of proper configuration for optimal performance.Sip
SipAnirban Roy
╠²
The document provides an overview of Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), a signaling protocol used to create and manage multimedia sessions over IP networks. It covers SIP's components, call flow, and response codes, detailing the roles of user agents, proxy servers, and registrars in facilitating voice over IP (VoIP) communications. The history of SIP development and its applications, including video conferencing and instant messaging, are also discussed.Pbx presentation ingate_itexpoeast2014
Pbx presentation ingate_itexpoeast2014Atif Ahmad
╠²
Kwader is a technical business organization in Saudi Arabia that specializes in providing IT solutions including IP-PBXs. An IP-PBX is a phone system that allows a business to share phone lines across locations using an IP network rather than separate phone lines. IP-PBXs provide advantages like cost savings, easy management, mobility features, and integration of technologies like video conferencing. Grandstream is a provider of IP-PBX and VoIP solutions that Kwader represents to help businesses improve communication and productivity.Nexge Technologies - MVNx Offerings
Nexge Technologies - MVNx OfferingsNitin Raj Gupta
╠²
This document provides an overview of Nexge Technologies, which offers VoIP, OTT, SMS, and VAS solutions to over 250 telecom service providers globally. It summarizes Nexge's key competencies including softswitches, billing systems, messaging platforms, conferencing solutions, and mobile apps. It also outlines Nexge's architecture and solutions for areas like class 4 and 5 switching, SMS, conferencing, call recording, lawful intercept, broadcasting, and more.IP PBX
IP PBXMuzzamil Shaikh
╠²
This document is a thesis on the implementation of an Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange (IP-PBX) system, focusing on unified communication using Elastix software based on Asterisk server. The project aims to enhance communication capabilities through voice and video calls over a local Wi-Fi network, enabling mobility and efficiency in organizations. The study covers hardware and software integration, features of the system, and its applications in various sectors like healthcare and education.Introduction To SIP
Introduction To SIPChris McAndrew
╠²
1. The document introduces Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), explaining that it is an application layer signaling protocol for initiating, modifying, and terminating multimedia communication sessions over IP such as voice and video calls.
2. It describes why SIP is used, including for conferencing, distance learning, video conferencing, instant messaging, and voice calls. It also outlines the main components of a SIP network including user agents, proxies, and redirects servers.
3. The document provides an overview of how SIP works by outlining the signaling process for registration, call setup and teardown, redirection, and media routing between user agents.Hosted PBX- Should You Be a Provider or a Reseller?
Hosted PBX- Should You Be a Provider or a Reseller?NetSapiens
╠²
The document discusses considerations for becoming a hosted PBX provider versus a reseller, emphasizing market opportunities and key factors such as cost, control, staffing, and quality of service. It highlights the growing demand for SIP and the importance of having robust diagnostics and redundancy in service offerings. The document concludes that while reselling may be suitable for smaller operations, larger businesses may benefit more from being direct providers.Session initiation protocol
Session initiation protocolAung Thu Rha Hein
╠²
SIP is a signaling protocol that establishes, manages, and terminates multimedia sessions over IP networks. It uses components like user agents, registrars, proxies, and redirect servers. A SIP call is established through a three-way handshake between these components. SIP supports features like registration, redirection, forking, and mobility through its architecture and use of protocols like SIP, SDP, RTP, and MGCP.session initiation protocol - SIP
session initiation protocol - SIPMahmoud Abudaqa
╠²
SIP is an application-layer protocol for establishing multimedia sessions over IP networks. It can be used to initiate voice, video, and instant messaging communications. SIP works by having user agents (clients and servers) exchange SIP request and response messages. These messages contain information about session setup, modification, and termination. Some key SIP components include user agents, proxy servers, registrar servers, and redirect servers. SIP messages use a request-response transaction model and contain start lines, headers, and optional message bodies. Common request methods are INVITE, ACK, BYE, and REGISTER. Typical response codes include 100-199 (informational), 200-299 (success), 300-399 (redirection), 400-499Voip
Voipjamesdownham
╠²
VOIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol and allows users to make phone calls using an Internet connection rather than a traditional phone line. Common VOIP software like Skype can be used on computers, mobile devices, and gaming consoles to place calls. Skype has become one of the most widely used VOIP programs because its basic functionality is free, allowing users to make video and voice calls between devices as long as both parties have Skype installed.What is an SBC? A look at the role of the Session Border Controller
What is an SBC? A look at the role of the Session Border ControllerAlan Percy
╠²
The document explains the role and functionalities of Session Border Controllers (SBCs) in managing SIP traffic and protecting networks from various security threats like DDoS attacks and unauthorized access. It covers how SBCs operate, their applications in enterprise and service provider settings, and their deployment models including hardware and virtualized solutions. Additionally, it addresses the evolution of SBC technology towards software-centric architectures and provides resources for further learning.Complete VoIP Software Solution to fulfill Your VoIP Business needs
Complete VoIP Software Solution to fulfill Your VoIP Business needsAdore Infotech
╠²
Adore Infotech offers a comprehensive range of VoIP solutions, including softswitches, mobile dialers, and integrated billing systems, aimed at enhancing communication for businesses. Their products, such as class 5 softswitches and customized softphones, are designed for reliability and cost-effectiveness, helping companies manage voice and data traffic efficiently. The company supports various VoIP services, providing solutions like calling card systems and hosted VoIP, catering to an expanding market need for telecommunication solutions.VoIP
VoIPPurushottam Dahal
╠²
This document summarizes Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology. It begins by defining VoIP as using Internet Protocol networks to deliver voice communications. It then explains how VoIP works by continuously sampling and digitizing audio for transmission over the Internet in packets. The document outlines key advantages of VoIP such as lower costs compared to traditional phone service. It also discusses some disadvantages like reliance on internet connectivity and potential for lost audio. Additionally, it provides overviews of important VoIP standards and protocols including SIP, IP telephone systems, and how telephone numbers are mapped and routed over the Internet.Download It
Download ItVideoguy
╠²
J2EE technology can be used to empower SIP applications and address challenges in SIP application development. A use case of an audio/video conferencing application is presented that leverages J2EE and SIP. Key benefits of using J2EE include a standards-based infrastructure, simplified SIP handling, integration with back-end systems, and reduced development and maintenance costs.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
FutureComm 2010: SIP Server Applications on Embedded Platforms
FutureComm 2010: SIP Server Applications on Embedded PlatformsRADVISION Ltd.
╠²
This document discusses SIP server applications on embedded platforms. It begins with an agenda and overview of modern communications including IP phones, video phones, and soft phones. It then discusses using a SIP server on embedded systems to provide PBX functionality, address challenges of limited resources, and provide features like call control, presence, and media processing. Examples are given of SIP servers for devices like set-top boxes and residential gateways. The document concludes by describing RADVISION's SIP server framework solution for embedded systems, which provides core server capabilities and components while allowing for custom application logic.7 Ways SIP Trunking Can Change Your Business
7 Ways SIP Trunking Can Change Your BusinessCoreDial, LLC
╠²
The SIP trunking market is rapidly growing, expected to reach $8 billion by 2018, driven by the adoption of cloud and unified communications. Key benefits include reduced costs, scalability, and mobility, making it easier for businesses to expand geographically while maintaining phone service features. Adoption rates are rising; 50% of companies currently use SIP trunking, projected to increase to 78% by 2016 as traditional systems decline.Jason Fischl The Softphone And The Pbx
Jason Fischl The Softphone And The PbxCarl Ford
╠²
CounterPath is a leading developer of VoIP softphone applications, with over 100 employees. It aims to provide carrier-grade softphone solutions that are highly interoperable with existing infrastructures. Some challenges in deploying softphones and PBXes include simplifying installation and configuration, centralized management of credentials and directories, enabling remote upgrades, and ensuring interoperability between elements. CounterPath works with Digium, the creator of Asterisk, to provide tightly integrated softphone and PBX solutions that address these challenges.Introduction to SIP
Introduction to SIP neerav_adhikari
╠²
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application-layer signaling protocol used for establishing multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as voice or video calls. SIP can be used to initiate a call, invite participants and manage a call. It defines several methods for call setup, maintenance and termination. Common SIP methods include INVITE for call initiation, ACK to acknowledge call setup, BYE to terminate a call, and REGISTER for registering location. SIP uses SDP for negotiating media capabilities and RTP for transporting media streams.Asterisk - Glen Bastes
Asterisk - Glen Bastessoss
╠²
The document discusses the open source Asterisk PBX software. It provides an overview of Asterisk including that it was created in 1999 as a free and open source alternative to expensive proprietary PBX systems. Asterisk allows users to build their own software-based phone systems using inexpensive hardware and can provide many of the same features as traditional PBXs through its flexible architecture and extensive capabilities. The document outlines some of Asterisk's main functionalities and how it works as well as hardware that can be used with it.04b-radcliffe
04b-radcliffeDavid Radcliffe
╠²
This document discusses prospects for managed and hosted voice services. It identifies over 200 work products involved in voice services that could be managed, such as call detail recording, trunk configuration analysis, and fraud detection. It describes how to select a support model based on whether the service needs to be on-site, remote, or mobile. Finally, it outlines some key components of managed voice services, including fault management, configuration management, and security management.Voip
VoipZohaib Hussain
╠²
The document provides an overview of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), detailing its history, architecture, operational mechanics, and key protocols such as H.323, SIP, and MGCP. It compares VoIP with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), highlighting advantages like cost-effectiveness and ease of use, along with disadvantages like dependency on power and internet connectivity. Additionally, it outlines the equipment requirements for implementing VoIP and summarizes various features associated with both VoIP and PSTN.PBX.NET Hosted PBX | Business VOIP Sales Presentation
PBX.NET Hosted PBX | Business VOIP Sales PresentationPBX.NET Corporation
╠²
The document provides an overview of VoIP technology and PBX.NET's VoIP products and services. It discusses how VoIP works and its benefits over traditional phone systems. PBX.NET offers two main solutions: a Broadband PBX hosted service and Virtual Telephone Line broadband phone service. Both solutions provide business phone features over broadband at a lower cost than traditional phone lines. PBX.NET has reliable nationwide infrastructure and offers 24/7 customer support.Introduction into SIP protocol
Introduction into SIP protocolMichal Hrncirik
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) used in VoIP communication, detailing its functions, structure, and how it operates to facilitate multimedia sessions. It discusses SIP user credentials, common methods, troubleshooting techniques, and SIP trunking for unified communication services. Additionally, it highlights typical problems and solutions related to SIP deployment, emphasizing the importance of proper configuration for optimal performance.Sip
SipAnirban Roy
╠²
The document provides an overview of Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), a signaling protocol used to create and manage multimedia sessions over IP networks. It covers SIP's components, call flow, and response codes, detailing the roles of user agents, proxy servers, and registrars in facilitating voice over IP (VoIP) communications. The history of SIP development and its applications, including video conferencing and instant messaging, are also discussed.Pbx presentation ingate_itexpoeast2014
Pbx presentation ingate_itexpoeast2014Atif Ahmad
╠²
Kwader is a technical business organization in Saudi Arabia that specializes in providing IT solutions including IP-PBXs. An IP-PBX is a phone system that allows a business to share phone lines across locations using an IP network rather than separate phone lines. IP-PBXs provide advantages like cost savings, easy management, mobility features, and integration of technologies like video conferencing. Grandstream is a provider of IP-PBX and VoIP solutions that Kwader represents to help businesses improve communication and productivity.Nexge Technologies - MVNx Offerings
Nexge Technologies - MVNx OfferingsNitin Raj Gupta
╠²
This document provides an overview of Nexge Technologies, which offers VoIP, OTT, SMS, and VAS solutions to over 250 telecom service providers globally. It summarizes Nexge's key competencies including softswitches, billing systems, messaging platforms, conferencing solutions, and mobile apps. It also outlines Nexge's architecture and solutions for areas like class 4 and 5 switching, SMS, conferencing, call recording, lawful intercept, broadcasting, and more.IP PBX
IP PBXMuzzamil Shaikh
╠²
This document is a thesis on the implementation of an Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange (IP-PBX) system, focusing on unified communication using Elastix software based on Asterisk server. The project aims to enhance communication capabilities through voice and video calls over a local Wi-Fi network, enabling mobility and efficiency in organizations. The study covers hardware and software integration, features of the system, and its applications in various sectors like healthcare and education.Introduction To SIP
Introduction To SIPChris McAndrew
╠²
1. The document introduces Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), explaining that it is an application layer signaling protocol for initiating, modifying, and terminating multimedia communication sessions over IP such as voice and video calls.
2. It describes why SIP is used, including for conferencing, distance learning, video conferencing, instant messaging, and voice calls. It also outlines the main components of a SIP network including user agents, proxies, and redirects servers.
3. The document provides an overview of how SIP works by outlining the signaling process for registration, call setup and teardown, redirection, and media routing between user agents.Hosted PBX- Should You Be a Provider or a Reseller?
Hosted PBX- Should You Be a Provider or a Reseller?NetSapiens
╠²
The document discusses considerations for becoming a hosted PBX provider versus a reseller, emphasizing market opportunities and key factors such as cost, control, staffing, and quality of service. It highlights the growing demand for SIP and the importance of having robust diagnostics and redundancy in service offerings. The document concludes that while reselling may be suitable for smaller operations, larger businesses may benefit more from being direct providers.Session initiation protocol
Session initiation protocolAung Thu Rha Hein
╠²
SIP is a signaling protocol that establishes, manages, and terminates multimedia sessions over IP networks. It uses components like user agents, registrars, proxies, and redirect servers. A SIP call is established through a three-way handshake between these components. SIP supports features like registration, redirection, forking, and mobility through its architecture and use of protocols like SIP, SDP, RTP, and MGCP.session initiation protocol - SIP
session initiation protocol - SIPMahmoud Abudaqa
╠²
SIP is an application-layer protocol for establishing multimedia sessions over IP networks. It can be used to initiate voice, video, and instant messaging communications. SIP works by having user agents (clients and servers) exchange SIP request and response messages. These messages contain information about session setup, modification, and termination. Some key SIP components include user agents, proxy servers, registrar servers, and redirect servers. SIP messages use a request-response transaction model and contain start lines, headers, and optional message bodies. Common request methods are INVITE, ACK, BYE, and REGISTER. Typical response codes include 100-199 (informational), 200-299 (success), 300-399 (redirection), 400-499Voip
Voipjamesdownham
╠²
VOIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol and allows users to make phone calls using an Internet connection rather than a traditional phone line. Common VOIP software like Skype can be used on computers, mobile devices, and gaming consoles to place calls. Skype has become one of the most widely used VOIP programs because its basic functionality is free, allowing users to make video and voice calls between devices as long as both parties have Skype installed.What is an SBC? A look at the role of the Session Border Controller
What is an SBC? A look at the role of the Session Border ControllerAlan Percy
╠²
The document explains the role and functionalities of Session Border Controllers (SBCs) in managing SIP traffic and protecting networks from various security threats like DDoS attacks and unauthorized access. It covers how SBCs operate, their applications in enterprise and service provider settings, and their deployment models including hardware and virtualized solutions. Additionally, it addresses the evolution of SBC technology towards software-centric architectures and provides resources for further learning.Complete VoIP Software Solution to fulfill Your VoIP Business needs
Complete VoIP Software Solution to fulfill Your VoIP Business needsAdore Infotech
╠²
Adore Infotech offers a comprehensive range of VoIP solutions, including softswitches, mobile dialers, and integrated billing systems, aimed at enhancing communication for businesses. Their products, such as class 5 softswitches and customized softphones, are designed for reliability and cost-effectiveness, helping companies manage voice and data traffic efficiently. The company supports various VoIP services, providing solutions like calling card systems and hosted VoIP, catering to an expanding market need for telecommunication solutions.Similar to Aarti Sip (20)
VoIP
VoIPPurushottam Dahal
╠²
This document summarizes Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology. It begins by defining VoIP as using Internet Protocol networks to deliver voice communications. It then explains how VoIP works by continuously sampling and digitizing audio for transmission over the Internet in packets. The document outlines key advantages of VoIP such as lower costs compared to traditional phone service. It also discusses some disadvantages like reliance on internet connectivity and potential for lost audio. Additionally, it provides overviews of important VoIP standards and protocols including SIP, IP telephone systems, and how telephone numbers are mapped and routed over the Internet.Download It
Download ItVideoguy
╠²
J2EE technology can be used to empower SIP applications and address challenges in SIP application development. A use case of an audio/video conferencing application is presented that leverages J2EE and SIP. Key benefits of using J2EE include a standards-based infrastructure, simplified SIP handling, integration with back-end systems, and reduced development and maintenance costs.Download It
Download ItVideoguy
╠²
J2EE technology can be used to empower SIP applications and address challenges in SIP application development. A use case of an audio/video conferencing application is presented that leverages J2EE and SIP. Key benefits of using J2EE include a standards-based infrastructure, simplified SIP handling, integration with back-end systems, and reduced development and maintenance costs.1 VoIP Overview[1]
1 VoIP Overview[1]William Giba
╠²
This document provides an overview of three common voice over IP protocols: SIP, H.323, and MGCP. It describes the basic architecture and components of SIP, including users agents, proxies, registrars, and how SIP establishes calls. It also summarizes H.323, describing its terminals, gateways, gatekeepers, and call establishment. MGCP is briefly mentioned as another VOIP protocol.1 Vo Ip Overview
1 Vo Ip OverviewMohsin Fakhar
╠²
The document provides an overview of three common voice over IP protocols: SIP, H.323, and MGCP. It describes the basic architecture and components of SIP and H.323, how they establish communication sessions, and compares some of their key differences and strengths.The ssca® sip training program course outline
The ssca® sip training program course outlineswap3731
╠²
This document provides an overview of the SSCA® SIP training program. It discusses the following:
1. Who would benefit from the training program including manufacturers, service providers, and sales/marketing personnel working with VoIP.
2. What is included in the training program which is 11 modules on topics like SIP, security, QoS, and more.
3. The total running time is approximately 19 hours including time for labs. It does not include study time for the certification exam.
4. The goal of the training is to help students gain the SSCA® certification which is recognized in the telecommunications industry.Sip Protocol
Sip ProtocolTata Docomo Business Service
╠²
SIP (Session Initial Protocol) is an IETF standard used to initiate multimedia communication sessions over the internet. It establishes and terminates voice or video calls between two or more participants. SIP also allows modification of existing calls, such as adding or removing participants. Key network elements that enable SIP connectivity include user agents, SIP phones, proxy servers, registrars, and gateways.1 Vo Ip Overview
1 Vo Ip OverviewMayank Vora
╠²
The document provides an overview of three main voice over IP protocols: SIP, H.323, and MGCP. It describes the architecture and components of SIP and H.323, how they establish calls, and compares some key differences between the two protocols. MGCP is also introduced but not described in detail.1 Vo I P Overview
1 Vo I P OverviewMayank Vora
╠²
The document provides an overview of three main voice over IP protocols: SIP, H.323, and MGCP. It describes the architecture and components of SIP and H.323, including user agents, proxies, registrars, and gateways. It also discusses how SIP and H.323 establish communication sessions and handle registration, call setup and teardown. MGCP is mentioned but not described in detail.AN OVERVIEW OF VOICE OVER INTERNET PROTOCOL (VOIP
AN OVERVIEW OF VOICE OVER INTERNET PROTOCOL (VOIPSean Flores
╠²
This document discusses Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) including its protocols, security issues, benefits, and challenges. It begins by introducing VoIP and describing its basic operation and advantages like lower costs. It then covers specific VoIP protocols like SIP and H.323. The document analyzes VoIP considerations like delay, jitter, packet loss, and discusses how these issues can affect call quality. It also provides an overview of VoIP technologies and their benefits for businesses. Finally, it presents a case study on assessing network readiness for VoIP deployment.Vo ip sip
Vo ip sipIazon Danelia
╠²
This document provides an overview and introduction to VoIP and SIP signaling. It discusses key topics such as VoIP architecture and components, the process of a VoIP telephone call including conversion between analog and digital signals and quality of service, SIP architecture including what SIP is, its capabilities and message format, and SIP call flow. The document is intended as a training presentation that includes definitions of terms, descriptions of concepts, diagrams, and quizzes related to VoIP and SIP.Review of SIP based DoS attacks
Review of SIP based DoS attacksEditor IJCATR
╠²
This document provides an overview of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) based Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) infrastructure. It first introduces VoIP and SIP, describing SIP components and messages. It then discusses security issues with SIP such as eavesdropping, message tampering, and spoofing. Several types of SIP DoS attacks are classified, including SIP message payload tampering, SIP message flow tampering, and SIP message flooding attacks. The document concludes by stating that SIP DoS attacks can render SIP services inoperable and discussing previous work on analyzing the robustness of SIP servers under DoS attacks.Ip
Ipmangal das
╠²
This document provides an overview of Internet Protocol Telephony (VoIP). It discusses how VoIP works by digitizing and compressing voice into packets transmitted over the Internet. It also covers some of the common protocols used, including Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and H.323, and compares their advantages. Potential applications and challenges of VoIP are also mentioned.Ip
Ipmangal das
╠²
The document discusses Internet Protocol Telephony, focusing on Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology and its components, such as the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and H.323 protocol. It highlights the advantages of VoIP, including cost reduction and efficiency, while also addressing challenges such as packet loss during transmission. The future of communication is emphasized, with ongoing efforts to optimize bandwidth utilization for various applications.VOIP
VOIPguest43d211
╠²
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) enables voice communication over packet-switched networks, using various protocols such as SIP for session establishment and RTP for data transfer. It offers free or cheaper calls, integration of voice and data services, and additional features like call forwarding and voicemail. Key protocols and methods used include SIP, RTP, and specific packet formats for managing calls and sessions.Sip1
Sip1ClubExpress
╠²
The document discusses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and SIP trunking. It provides information on SIP, SIP trunking, benefits of SIP trunking, and SIP Connect, which is a standards-based approach for direct IP peering between SIP-enabled IP PBXs and VoIP service provider networks. It also discusses Cbeyond, a managed service provider that has helped pioneer SIP trunking services for SMB markets.Vo Ip Rajibdeka
Vo Ip Rajibdekarajibdk
╠²
The document provides an overview of Voice over IP (VoIP), detailing its architecture, protocols, and the importance of quality of service (QoS) in ensuring effective communication. Key topics include the functionalities of signaling protocols like SIP and H.323, the components involved in VoIP systems, and the economic advantages of using IP telephony over traditional systems. It concludes by highlighting ongoing challenges regarding compatibility with existing telephony infrastructures.Sip
SipPinak Dey
╠²
SIP is a signaling protocol used to create, manage, and terminate multimedia sessions over IP networks. It allows for establishing the location of users, negotiating features between participants in a session, and managing calls by adding, dropping or transferring participants. SIP is responsible for setting up sessions but not for transmitting media or controlling quality of service - those functions are handled by other protocols. A typical SIP call involves a SIP client sending an INVITE request which is forwarded through SIP proxies to the destination, where if accepted, a 200 OK response confirms call setup along with an ACK from the initiator.Sip summary
Sip summaryAhmed Noaman
╠²
SIP is a signaling protocol used to establish, modify, and terminate multimedia sessions over IP networks. It was originally designed in 1996 to make voice and video calls over IP and has since expanded to support additional applications like instant messaging, file transfer, and presence information. SIP works by defining messages passed between endpoints to initiate, manage, and terminate calls or sessions. It is an application layer protocol that can operate over various transport protocols like TCP, UDP, and SCTP.sip trunking design and deployment in uc networks
sip trunking design and deployment in uc networksalbertolongoria3
╠²
The document discusses SIP trunk design and deployment in enterprise UC networks, highlighting the benefits of using SIP over other protocols for interconnecting UC systems. It covers SIP basics, session establishment, essential features of CUCM SIP trunks, and large-scale designs, along with a detailed appendix. The presentation emphasizes SIP's growing popularity and features like improved interoperability and video support.Ad
Aarti Sip
- 1. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Aarti Gupta
- 2. Agenda Why do we need SIP ? The protocol Instant Messaging using SIP Internet Telephony with SIP Additional applications Future Directions
- 3. Introduction SIP is the core protocol for initiating, managing and terminating sessions in the Internet These sessions may be text, voice, video or a combination of these SIP sessions involve one or more participants and can use unicast or multicast communication.
- 4. SIP entities User Agent User Agent Client User Agent Server Proxy Server Redirect server Registrar
- 5. SIP Message Types Requests ÔÇô sent from client to server INVITE ACK BYE CANCEL OPTIONS REGISTER INFO
- 6. SIP Message Types (Contd.) Responses ÔÇô sent from server to the client Success Redirection Forwarding Request failure Server failure Global failure
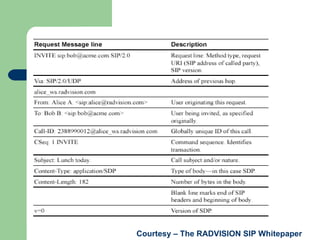
- 7. Courtesy ÔÇô The RADVISION SIP Whitepaper
- 8. SIP Session Establishment and Call Termination From the RADVISION whitepaper on SIP
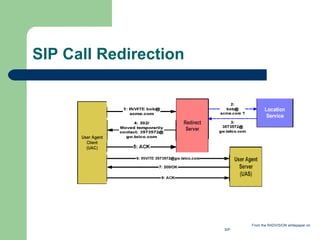
- 9. SIP Call Redirection From the RADVISION whitepaper on SIP
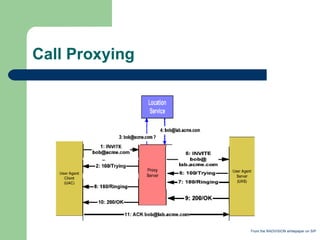
- 10. Call Proxying From the RADVISION whitepaper on SIP
- 11. Instant messaging based on SIP SIMPLE ÔÇô IM protocol based on SIP SIP promises interoperability between various IM vendors ÔÇ£Forking proxy ÔÇ£ SIP has unique user tracking features. SIP addressing
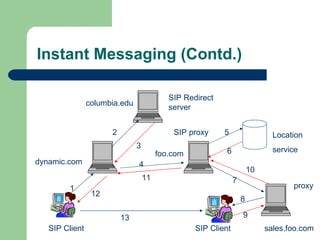
- 12. Instant Messaging (Contd.) SIP Client SIP Client dynamic.com columbia.edu SIP Redirect server SIP proxy foo.com Location service proxy sales.foo.com 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
- 13. SIP for Internet Telephony Two types of phones ÔÇô IP phones and conventional analog phones. Uses phone numbers instead of IP addresses To place a call to an IP phone, DNS is used To place a call to an analog phone, gateway protocols like BGP are used
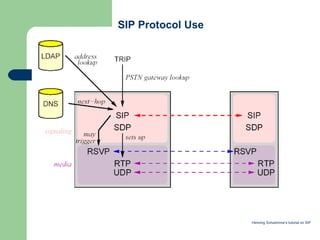
- 14. SIP Protocol Use Henning SchulzrinneÔÇÖs tutorial on SIP
- 15. Additional SIP applications PINT (PSTN and Internetworking) protocol Internet call waiting
- 16. What is the future of SIP SIP is still a ÔÇÿproposed standardÔÇÖ Competing protocol ÔÇô H.323 IM vendors have not adopted SIP
- 17. References Computer Telephony ÔÇô June 2000 http://www.radvision.com www.cs.columbia.edu/hgs/ www.networkcomputing.com www.wikipedia.com
- 18. Thank you
