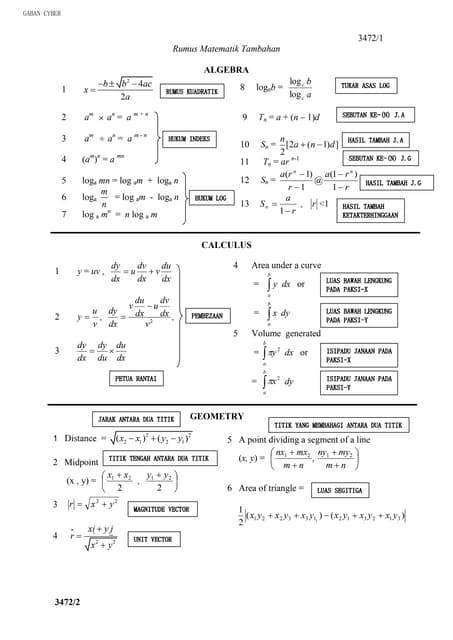
SOALAN AMALI FIZIK PERCUBAAN PAHANG 2022.pdf
- 1. SULIT 4531/3 1 ┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang Nama: ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” Tingkatan: ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” MODUL PINTAS FIZIK 2022 MPMS PAHANG UJIAN AMALI SAINS (FIZIK) TAHUN 2022 UJIAN AMALI FIZIK 4531/3 15 markah (45 minit) (termasuk 5 minit untuk menyemak radas dan bahan) Arahan kepada calon: 1. Calon dilarang memulakan sebarang eksperimen sehingga mendapat arahan daripada Ketua Pengawas (KP) bertugas. 2. 5 minit diperuntukkan bagi setiap mata pelajaran untuk menyemak radas dan bahan dan maklumkan segera kepada Pengawas Peperiksaan (PP) jika tidak mencukupi. Isikan Borang Senarai Semak Radas dan Bahan di halaman 2 dengan lengkap. 3. Calon boleh memulakan eksperimen daripada mana-mana soalan setelah mendapat arahan daripada KP. 4. Sekiranya calon tidak dapat meneruskan eksperimen selepas 15 minit, calon boleh meneruskan eksperimen di soalan yang lain. 5. Jika calon masih tidak dapat meneruskan eksperimen di setiap bahagian, calon bolehlah berjumpa KP dan meminta pertolongan. Sedikit markah mungkin dipotong. 6. Sentiasa amalkan langkah-langkah keselamatan semasa menjalan amali dan segera maklumkan kepada KP atau PP jika berlaku sesuatu yang membahayakan keselamatan diri dan orang lain. Buku soalan ini mengandungi 6 halaman bercetak. Untuk kegunaan guru sahaja: 15
- 2. SULIT 4531/3 2 ┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang SENARAI SEMAK CALON CANDIDATESŌĆÖ CHECK LIST ARAHAN Anda tidak dibenarkan bekerja dengan radas bagi lima belas minit pertama. Tempoh ini hendaklah digunakan untuk menyemak senarai radas, membaca soalan dan merancang eksperimen yang akan dijalankan. Tandakan (’ā╝) pada ruangan kotak yang disediakan untuk menyemak bahan dan radas yang disedia dan dibekalkan. INSTRUCTION You are not allowed to work with apparatus in first fifteen minutes. This period is used to check the apparatus list, read the questions, and plan the experiment which will carry out. Mark (’ā╝ ) in the box provided to check the material and apparatus prepared and supplied. Soalan 1 Question 1 Bil. No. Radas dan bahan Apparatus and materials Kuantiti Quantity Ya (’ā╝)/ Tidak (X) Yes (’ā╝)/ No (X) 1. Sel kering 1.5 V saiz D Dry cell 1.5 V D size 2 2. Pemegang bateri Battery holder 1 3. Wayar penyambung dengan klip buaya Connecting wire with crocodile clips 6 4. Suis satu hala One way switch 1 5. Voltmeter DC 0 ~ 5.0 V 1 6. Ammeter 0 ~ 1.0 A 1 7. Pembaris 50 cm dengan dawai nikrom 50 cm ruler with nichrome wire 1
- 3. SULIT 4531/3 3 ┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang 1. Rintangan suatu konduktor dipengaruhi oleh beberapa faktor. Anda dikehendaki menjalankan eksperimen bagi menentukan rintangan suatu dawai nikrom yang telah dibekalkan bagi panjang dawai yang berbeza. The resistance of a conductor is influenced by several factors. You are required to conduct an experiment to determine the resistance of a nichrome wire that has been supplied for different lengths of wire. (a) Sambungkan litar seperti yang ditujukkan dalam Rajah 1. Pastikan suis dibuka terlebih dahulu. Connect the circuit as shown in Diagram 1. Make sure the switch is open first. Rajah 1 Diagram 1 (i) Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang sesuai bagi eksperimen ini. State a suitable hypothesis for this experiment. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. [1 markah] [1 mark] A B ’üĄ C D ’üĄ E
- 4. SULIT 4531/3 4 ┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang (ii) Ukur dan catatkan panjang dawai nikrom, l, dari A ke B. Measure and record the length of the nichrome wire, l, from A to B. l = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” [1 markah] [1 mark] Gerakkan wayar penyambung dari voltmeter ke pembaris supaya berada di kedudukan B, tutup suis dan rekod bacaan I dan V ke dalam Jadual 1. Buka semula suis setelah bacaan dibuat. Move the connecting wire from voltmeter to the ruler to position B, close the switch and record the reading of I and V in Table 1. Open the switch again after the reading is taken. Hitung rintangan dawai, R menggunakan formula yang diberi. Catat jawapan anda dalam Jadual 1. Calculate the resistance of the wire, R, using the given formula. Record your answer in Table 1. Øæģ = Øæē ØÉ╝
- 5. SULIT 4531/3 5 ┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang (b) Ulang langkah (a) (i) hingga (a) (ii) dengan menggerakkan klip buaya ke C, D dan E. Rekod semua keputusan yang diperolehi bagi panjang dawai nikrom, l, dan rintangan dawai nikrom, R, bagi jarak AC, AD dan AE dalam Jadual 1. Repeat steps (a) (i) to (a) (ii) by moving the crocodile clip to C, D and E. Record all the results for length of nichrome wire, l, and resistance of nichrome wire, R, of lengths of AC, AD and AE in Table 1. Panjang dawai nikrom, l /cm Length of nichrome wire, l AB = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”. AC = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”. AD = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”. AE = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”. Jadual 1 Table 1 [5 markah] [5 marks] (c) (i) Plot graf R melawan l berdasarkan data yang anda perolehi dalam Jadual 1. Plot a graph of R against l based on the data you obtained in Table 1. [3 markah] [3 marks] (c) (ii) Dengan menggunakan graf yang ada plot di (c)(i), hitungkan kecerunan bagi graf tersebut. Tunjukkan dengan jelas bagaimana kecerunan dihitung. Using the graph that has plotted in (c)(i), calculate the gradient of the graph. Show clearly how the gradient is calculated. [3 markah] [3 marks]
- 6. SULIT 4531/3 6 ┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang (d) Sebuah pengering rambut akan mengeluarkan udara yang telah dipanaskan oleh elemen pemanas yang diperbuat daripada nikrom di dalam pengering rambut tersebut seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 2. A hair dryer will release air that has been heated by the heating element made from nichrome inside the hair dryer as shown in Diagram 2. Rajah 2 Diagram 2 Berdasarkan eksperimen yang telah anda jalankan, mengapa elemen pemanas tersebut dibina bergegelung? Based on the experiments you have conducted, why the heating element is constructed coiled? ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” [2 markah] [2 marks] KERTAS SOALAN TAMAT END OF QUESTION PAPER Elemen pemanas dalam pengiring rambut Heating element inside a hair dryer Udara sejuk masuk Cold air in Udara panas keluar Hot air out



![SULIT 4531/3
3
┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang
1. Rintangan suatu konduktor dipengaruhi oleh beberapa faktor. Anda dikehendaki
menjalankan eksperimen bagi menentukan rintangan suatu dawai nikrom yang telah
dibekalkan bagi panjang dawai yang berbeza.
The resistance of a conductor is influenced by several factors. You are required to
conduct an experiment to determine the resistance of a nichrome wire that has been
supplied for different lengths of wire.
(a) Sambungkan litar seperti yang ditujukkan dalam Rajah 1. Pastikan suis dibuka
terlebih dahulu.
Connect the circuit as shown in Diagram 1. Make sure the switch is open first.
Rajah 1
Diagram 1
(i) Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang sesuai bagi eksperimen ini.
State a suitable hypothesis for this experiment.
ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”..
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
A B
’üĄ
C D
’üĄ
E](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soalanamalifizikpercubaanpahang2022-221213061448-3e1aec87/85/SOALAN-AMALI-FIZIK-PERCUBAAN-PAHANG-2022-pdf-3-320.jpg)
![SULIT 4531/3
4
┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang
(ii) Ukur dan catatkan panjang dawai nikrom, l, dari A ke B.
Measure and record the length of the nichrome wire, l, from A to B.
l = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
Gerakkan wayar penyambung dari voltmeter ke pembaris supaya berada di
kedudukan B, tutup suis dan rekod bacaan I dan V ke dalam Jadual 1. Buka
semula suis setelah bacaan dibuat.
Move the connecting wire from voltmeter to the ruler to position B, close the
switch and record the reading of I and V in Table 1. Open the switch again
after the reading is taken.
Hitung rintangan dawai, R menggunakan formula yang diberi. Catat jawapan
anda dalam Jadual 1.
Calculate the resistance of the wire, R, using the given formula. Record your
answer in Table 1.
Øæģ =
Øæē
ØÉ╝](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soalanamalifizikpercubaanpahang2022-221213061448-3e1aec87/85/SOALAN-AMALI-FIZIK-PERCUBAAN-PAHANG-2022-pdf-4-320.jpg)
![SULIT 4531/3
5
┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang
(b) Ulang langkah (a) (i) hingga (a) (ii) dengan menggerakkan klip buaya ke C, D dan E.
Rekod semua keputusan yang diperolehi bagi panjang dawai nikrom, l, dan rintangan
dawai nikrom, R, bagi jarak AC, AD dan AE dalam Jadual 1.
Repeat steps (a) (i) to (a) (ii) by moving the crocodile clip to C, D and E. Record all
the results for length of nichrome wire, l, and resistance of nichrome wire, R, of
lengths of AC, AD and AE in Table 1.
Panjang dawai
nikrom, l /cm
Length of nichrome
wire, l
AB = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.
AC = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.
AD = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.
AE = ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.
Jadual 1
Table 1
[5 markah]
[5 marks]
(c) (i) Plot graf R melawan l berdasarkan data yang anda perolehi dalam Jadual 1.
Plot a graph of R against l based on the data you obtained in Table 1.
[3 markah]
[3 marks]
(c) (ii) Dengan menggunakan graf yang ada plot di (c)(i), hitungkan kecerunan bagi
graf tersebut. Tunjukkan dengan jelas bagaimana kecerunan dihitung.
Using the graph that has plotted in (c)(i), calculate the gradient of the graph.
Show clearly how the gradient is calculated.
[3 markah]
[3 marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soalanamalifizikpercubaanpahang2022-221213061448-3e1aec87/85/SOALAN-AMALI-FIZIK-PERCUBAAN-PAHANG-2022-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![SULIT 4531/3
6
┬®2022 Hak Cipta Terpelihara MPSM Pahang
(d) Sebuah pengering rambut akan mengeluarkan udara yang telah dipanaskan
oleh elemen pemanas yang diperbuat daripada nikrom di dalam pengering
rambut tersebut seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 2.
A hair dryer will release air that has been heated by the heating element made
from nichrome inside the hair dryer as shown in Diagram 2.
Rajah 2
Diagram 2
Berdasarkan eksperimen yang telah anda jalankan, mengapa elemen pemanas tersebut
dibina bergegelung?
Based on the experiments you have conducted, why the heating element is constructed
coiled?
ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”
ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
KERTAS SOALAN TAMAT
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Elemen pemanas dalam pengiring rambut
Heating element inside a hair dryer
Udara sejuk
masuk
Cold air in
Udara panas keluar
Hot air out](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soalanamalifizikpercubaanpahang2022-221213061448-3e1aec87/85/SOALAN-AMALI-FIZIK-PERCUBAAN-PAHANG-2022-pdf-6-320.jpg)































![Chem juj k3 (soalan) [set 1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chemjujk3soalanset1-171126023802-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Trial penang 2014 spm physics k3 [scan]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/trialpenang2014spmphysicsk3scan-141015095920-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)







![Trial spm kedah_2013_maths_paper2_[q]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/trial-spm-kedah-2013-maths-paper2-5bq-5d-131008111843-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Trial spm kedah_2013_maths_paper2_[q]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/trial-spm-kedah-2013-maths-paper2-5bq-5d-131008111831-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


![Trial penang 2014 spm physics k2 [scan]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/trialpenang2014spmphysicsk2scan-141015095919-conversion-gate01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)




























