Tc basics
- 1. Dive into TC ¨C TC basics Jeromy Fu
- 2. Agenda ? WhatˇŻs TC ? How it works ? Basic concepts ? Command and parameters
- 3. WhatˇŻs TC ? TC is abbr. of Traffic Control - Rate control - Bandwidth management - Active Queue Management(AQM) - Network Emulator, pkt loss, pkt disorder, pkt duplication, pkt delay - QoS ( diffserv + rsvp ) - Many more ˇ
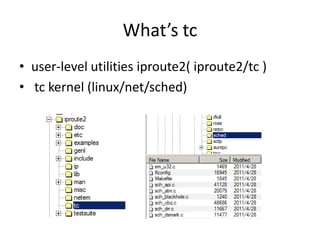
- 4. WhatˇŻs tc ? user-level utilities iproute2( iproute2/tc ) ? tc kernel (linux/net/sched)
- 5. How it works
- 6. How it works
- 7. Basic concepts- Qdisc ? Qdisc(Queue discipline) - Decide which ones to send first, which ones to delay, and which ones to drop - class/classful Qdisc: Qdisc with/without configurable internal subdivision ? Naming convention: - Kernel: sch_*.c (sch_netem.c, sch_tbf.c ) - iproute2: q_*.c (q_netem.c, q_tbf.c)
- 8. Qdisc list ? Class Based Queueing (CBQ) ? Hierarchical Token Bucket (HTB) ? Hierarchical Fair Service Curve (HFSC) ? ATM Virtual Circuits (ATM) ? Multi Band Priority Queueing (PRIO) ? Hardware Multiqueue-aware Multi Band Queuing (MULTIQ) ? Random Early Detection (RED) ? Stochastic Fairness Queueing (SFQ) ? True Link Equalizer (TEQL) ? Token Bucket Filter (TBF) ? Generic Random Early Detection (GRED) ? Differentiated Services marker (DSMARK) ? Network emulator (NETEM) ? Deficit Round Robin scheduler (DRR) ? Ingress Qdisc
- 9. Basic concepts- Classification ? Classification(Filter) - Used to distinguish among different classes of packets and process each class in a specific way. ? Naming convention: - Kernel: cls_*.c (cls_u32.c, cls_rsvp.c ) - iproute2: f_*.c (f_u32.c, f_rsvp.c)
- 10. Classification list ? Elementary classification (BASIC) ? Traffic-Control Index (TCINDEX) ? Routing decision (ROUTE) ? Netfilter mark (FW) ? Universal 32bit comparisons w/ hashing (U32) ? IPv4 Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) ? IPv6 Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP6) ? Flow classifier ? Control Group Classifier ? Extended Matches ? Metadata ? Incoming device classification
- 11. Basic concepts- Action ? Action Actions get attached to classifiers and are invoked after a successful classification. They are used to overwrite the classification result, instantly drop or redirect packets, etc. Works on ingress only. ? Naming convention: - Kernel: act_*.c (act_police.c, act_skbedit.c ) - iproute2: m_*.c (m_police.c, m_pedit.c)
- 12. Action list ? Traffic Policing ? Generic actions ? Probability support ? Redirecting and Mirroring ? IPtables targets ? Stateless NAT ? Packet Editing ? SKB Editing
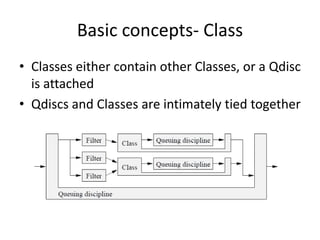
- 13. Basic concepts- Class ? Classes either contain other Classes, or a Qdisc is attached ? Qdiscs and Classes are intimately tied together
- 14. TC Commands ? OPTIONS: options are effective for all sub commands ? OBJECTS: the object of the tc command operates on ? COMMAND: the sub command for each object
- 15. TC Commands
- 16. TC Qdisc ? Operations on qdisc: add | del | replace | change | show ? Handle: qdisc handle used to identify qdisc ? root|ingress|parent CLASSID, specify the parent node
- 17. qdisc handle ? Qdisc handle is used to identify Qdisc - {none|major[:]} - none is TC_H_UNSPEC - major is 16bits HEX number(Without ˇ®0xˇŻ prefix) - : is optional ? Internally, qdisc_handle = major<<16
- 18. classid ? Classid is used to identify Class - {none|root|[major]:minor} - none is TC_H_UNSPEC, root is TC_H_ROOT - major/minor are both 16bits HEX numbers(Without ˇ®0xˇŻ prefix), major is optional ? Internally, classid = (major<<16)|minor
- 19. stab and rtab ? stab is Size table, rtab is rate table. ? TheyˇŻre used to speed up the calculation of the transmit time of packets. ? The packet size is aligned to a predefined size in the stab slot. ? Then the rtab is used to give the pre- calculated time of the aligned packet size.
- 20. Linklayer ? Link layer affects packet size, if linklayer is set, both mpu and overhead must also be set
- 21. Linklayer
- 22. stab internal ? szopts: stab relating specifications, some are specified by the command, some are calculated ? data: the size table.
- 23. stab internal - user space ? Averagely distribute(*2) the MTU size into size table which has tsize slots
- 24. stab internal - kernel
- 25. rtab internal - user space ? rtab size is constantly 256
- 26. rtab internal - kernel
- 30. TC Class ? Tc class can only be applied for classful qdisc, such as htb, cbq etc
- 32. tbf ? limit/latency ? buffer/burst/maxburst, capcity of token bucket: size[/cell] ? mpu: minimum process unit ? rate/peakrate ? Max(Rate/HZ,MTU)
- 33. tbf - user space ? latency convert to limit finally
- 34. tbf - user space ? rtab initialization
- 35. tbf - kernel
- 36. tbf - kernel
- 37. Tbf dequeue













![qdisc handle
? Qdisc handle is used to identify Qdisc
- {none|major[:]}
- none is TC_H_UNSPEC
- major is 16bits HEX number(Without ˇ®0xˇŻ prefix)
- : is optional
? Internally, qdisc_handle = major<<16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcbasics-121014205427-phpapp02/85/Tc-basics-17-320.jpg)
![classid
? Classid is used to identify Class
- {none|root|[major]:minor}
- none is TC_H_UNSPEC, root is TC_H_ROOT
- major/minor are both 16bits HEX numbers(Without
ˇ®0xˇŻ prefix), major is optional
? Internally, classid = (major<<16)|minor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcbasics-121014205427-phpapp02/85/Tc-basics-18-320.jpg)













![tbf
? limit/latency
? buffer/burst/maxburst, capcity of token
bucket: size[/cell]
? mpu: minimum process unit
? rate/peakrate
? Max(Rate/HZ,MTU)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcbasics-121014205427-phpapp02/85/Tc-basics-32-320.jpg)




