Structured Query Language (SQL)
- 2. GROUP MEMBERSADIL SHAKIRHAMMAD YOUSAFAMMAR YASIR HASEEB KHALIDAWAIS AFTAB BUTTMUDDASIR ABIDBILAL AHMED MOHAMMED IMRANFAIZA KHALID RAAZIA IRSHADHAMMAD RASHEED ZULQARNAIN BAJWA
- 4. ID : 05
- 6. DatabaseŌĆ£An organized collection of informationŌĆØOR ŌĆ£Set of tables each having different class of data.ŌĆØ
- 7. Structured Query Language ( SQL ) A language to communicate with the database
- 8. A tool to retrieve the required information from database
- 9. Elements
- 10. Syntax of SQL is in plain English
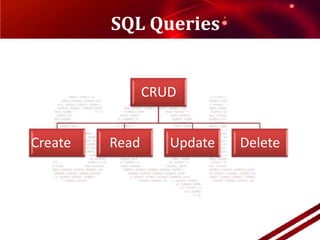
- 11. To question the databaseWhat SQL can do?With SQL you can:1. Execute queries against a database2. Perform CRUD function:CREATE ’āĀNew databases’āĀNew tables in a database ’āĀ Records in a databaseREAD ’āĀRetrieve data from a database
- 12. UPDATE ’āĀUpdate Records in a database
- 13. DELETE ’āĀ Delete Records from a database
- 14. Pre-requisites for SQLRelational Database
- 15. Tables
- 16. Fields
- 17. Records
- 19. 1-1
- 20. 1-m SYNTAXStatementTable NameConditionSELECT CustomerName, City, Country FROM Customer WHERE Country=ŌĆśUSAŌĆÖColumnsFROM ClauseWHERE ClauseSELECT Clause
- 21. ID : 11
- 22. QUERIES
- 23. SQL Queries
- 24. ID : 47
- 25. Function QueriesFunction queries in SQL involve manipulating functions in SQL statements to retrieve desired information from the database.Such function queries are of two broad categories:Aggregate Function Queries
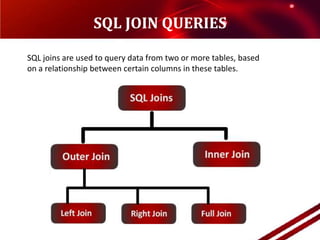
- 27. SQL JOIN QUERIESSQL joins are used to query data from two or more tables, based on a relationship between certain columns in these tables.
- 28. Inner JoinThe INNER JOIN keyword return rows when there is at least one match in both tables.SyntaxSELECT column_name(s)FROM table_name1INNER JOIN table_name2ON table_name1.column_name=table_name2.column_name
- 29. Outer JoinThe OUTER JOIN clause differs from the INNER JOIN in that rows are returned even when there are no matches through the JOIN critieria on the second table. Difference Explained:Assuming you're joining on columns with no duplicates, which is by far the most common case:An inner join of A and B gives the result of A intersect B, i.e. the inner part of a venn diagram intersection.An outer join of A and B gives the results of A union B, i.e. the outer parts of a venn diagram union.
- 30. Left Outer JoinThe LEFT JOIN keyword returns all rows from the left table (table_name1), even if there are no matches in the right table (table_name2)SyntaxSELECT column_name(s)FROM table_name1LEFT JOIN table_name2ON table_name1.column_name=table_name2.column_name
- 31. Right Outer JoinThe RIGHT JOIN keyword Return all rows from the right table (table_name2), even if there are no matches in the left table (table_name1)SyntaxSELECT column_name(s)FROM table_name1RIGHT JOIN table_name2ON table_name1.column_name=table_name2.column_name
- 32. Full JoinThe FULL JOIN keyword return rows when there is a match in one of the tables.SyntaxSELECT column_name(s)FROM table_name1FULL JOIN table_name2ON table_name1.column_name=table_name2.column_name
- 33. THANK YOU