1 of 7
Download to read offline
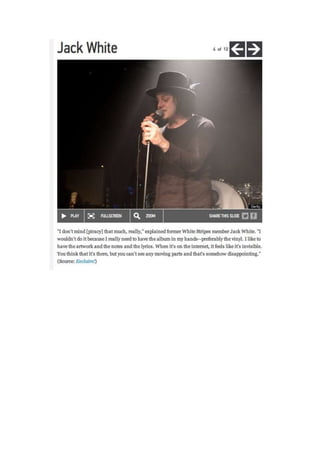






Recommended
Record Label Research Project



Record Label Research ProjectPieter Jollans
Ěý
EMI is one of the largest record labels in the world, operating globally with divisions in different countries. It owns several other record labels and has worked with famous artists like the Rolling Stones, Blur, the Beastie Boys, and Radiohead. EMI groups its owned labels according to genre to target different audiences, though these ideologies are continued despite the labels now being owned by large companies. Sony BMG and Warner Music Group have also had to adapt to changes in how music is consumed, such as file sharing and streaming, partnering with services like Amazon, YouTube, and Spotify to provide legal digital music. Universal Music Group has similarly worked to limit unauthorized use of its music online by removing videos from YouTube.Physics Investigatory Project Class 12



Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Self-employed
Ěý
This document appears to be a student project report on investigating the relationship between input/output voltage and number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of a transformer. It includes sections on introduction, theory, apparatus, procedure, observations, conclusion, and bibliography. The key points are that the output voltage of a transformer depends on the ratio of turns in the secondary coil to the primary coil, and that there are losses between the input and output resulting in the transformer's efficiency being less than 100%.Describe vs analyse



Describe vs analyseibz10
Ěý
The document contains two summaries of a scene from a film. The first summary describes the scene by stating that a woman cannot afford a dress and the shop assistant treats her harshly, showing their difference in power. The second summary analyzes how cinematography is used to represent gender through the use of an high angle shot that connotes weakness for the female character in a stereotypical way.11 describe vs analyse



11 describe vs analyseibz10
Ěý
This document provides guidance on writing strong Point, Evidence, Explanation (P.E.E.) paragraphs to analyze representations of gender in film. It instructs the reader to write P.E.E.s with an underline in colored pencil, defines what a point, evidence, and explanation are, and provides examples of stronger and weaker P.E.E. analysis with a focus on terminology, evidence, and explanation. The document also includes notes on areas to focus writing and criteria for marking P.E.E. analysis, focusing on use of examples, terminology, and clear analysis of how technical aspects construct representations.10 vocab



10 vocabibz10
Ěý
The document discusses developing an understanding of regional identity stereotypes through analyzing the micro-elements in the TV show "Doc Martin". Students are asked to watch episodes twice and take notes on how various micro-elements either conform to or subvert stereotypes about rural/urban and country/city identities. Examples given include the rural production design conforming to stereotypes of sparse population, while Doc Martin's southern urban accent and impatience initially conform but may later be subverted.09 final revision lesson



09 final revision lessonibz10
Ěý
Okay teams, get into pairs and decide who goes first. Remember the rules - no mentioning the word or micro-element directly. Good luck!08 final tv drama revision session



08 final tv drama revision sessionibz10
Ěý
The document provides guidance for a final exam on TV drama revision. It includes sections on writing down dos and don'ts for the exam, discussing high and low camera angles through example slides, anagrams and microelements identification, editing techniques like stereotypes conveyed through shots, and sound design choices like diegetic and non-diegetic music. The document offers content for reviewing key concepts and techniques in television drama.06 sexual identity in tv drama



06 sexual identity in tv dramaibz10
Ěý
This document discusses representing sexual identity in TV drama. It provides examples of stereotypical and non-stereotypical representations of gay men, straight men, lesbians, and straight women in TV shows. Students are instructed to analyze how sexual identity is portrayed through four micro elements: appearance, speech, occupation, and behavior. They will watch TV show clips and analyze the representations using these micro elements. The lesson aims to understand how sexual identity is commonly and alternatively depicted in media.05 regional identity



05 regional identityibz10
Ěý
This document discusses regional identity and stereotypes in the United Kingdom. It begins by defining regional identity as being connected to both the country and region one lives in, on a smaller scale than national identity. It then lists common stereotypes associated with different regions of the UK, such as Scots being money-obsessed and drinkers, Welsh people living rurally and being rugby fans, and Northerners being poorer and more working class than Southerners. The document encourages analyzing these stereotypes and considering where they come from and how individuals may subvert them.04 ethnicity revision day



04 ethnicity revision dayibz10
Ěý
The document outlines rules for a game to be played in pairs where participants cannot say a specific word or micro-element and the pair with the most correct answers wins a prize. Each pair will play twice with a member from the other team observing to prevent cheating. The rules specify 30 seconds per pair and that the member observing should stand over the pair's shoulder.03 editing disability



03 editing disabilityibz10
Ěý
This document provides guidance for revising to improve analysis of representations of disability in TV drama. It includes focusing on using the PEE structure, improving use of terminology and evidence, and using more analytical language. It discusses stereotypes around physical, mental and able-bodied representations. Examples of characters with disabilities in TV are given. The document also provides guidance on analyzing micro-elements like cinematography, mise-en-scene, sound and editing in exam responses.02 gender



02 genderibz10
Ěý
This lesson aims to analyze representations of gender within TV drama extracts. Students will watch an extract from Primeval four times, analyzing it using a worksheet to discuss how camera shots, editing, sound, and mise en scene construct gender representations. They will discuss camera techniques, editing, sound, and visual elements and how they represent gender without notes on the first viewing, and with notes for subsequent viewings.07 rep of social class



07 rep of social classibz10
Ěý
The upper class would typically be represented through editing, sound, mise-en-scene, and cinematography as follows:
Through editing, the upper class would be represented using techniques like graphic matches and eyeline matches to show their refined manners and lifestyle. Their dialogue would be represented through sound as being well-spoken and proper. Mise-en-scene would show their lavish homes filled with fine furnishings and their elegant clothing. Cinematography would frame them in wide shots set in expansive landscapes to depict their wealth and status through the environments they occupy.Music intro lesson



Music intro lessonibz10
Ěý
The document discusses how digitalization has impacted the music industry. It provides context about Section B and the assessment requirements. Some key points:
1) Digitalization has both benefited and harmed the music industry by enabling portable music formats but also piracy.
2) Students will be assessed on their knowledge and analysis of contemporary issues in the music industry, use of examples and evidence, and industry terminology.
3) Important websites are listed to stay informed on current topics in music and digital media.Student handout



Student handoutibz10
Ěý
The document discusses marketing and promotion of media products. It covers traditional marketing techniques, new digital marketing through technology and social networks, and how digital distribution has affected marketing and consumption. Target audiences and production are also mentioned as areas to cover.Sony lesson 2012



Sony lesson 2012ibz10
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the global music industry and Sony's role within it. The three main points are:
1) Sony is a major record label and conglomerate that dominates the global music industry through its network of subsidiary labels covering various genres and audiences.
2) As a conglomerate, Sony benefits from cross-promotion opportunities across its various media properties, allowing it to effectively market and distribute its music.
3) While digitalization has threatened Sony's dominance, its size and ownership of hardware/devices helps it maintain power, though independent labels have more opportunities in the shifting landscape.Sony company



Sony companyibz10
Ěý
This document discusses the music industry and is organized into three main sections: production, distribution, and marketing/promotion. It examines the different aspects of the industry and how piracy has impacted various parts of the business model. Strategies for combating piracy are also mentioned.Revision powerpoint



Revision powerpointibz10
Ěý
The document discusses four key areas of the music industry: production, distribution, marketing/targeting audiences, and consumption/exchange. It does not provide any details about each area. The areas are listed but the document consists only of headings and does not contain any explanatory text or examples about the music industry topics.Planning stages anaswer



Planning stages anasweribz10
Ěý
The document defines four stages of the music industry: production, which is the process of making and recording music using studios and software; marketing/targeting audiences, which is how music and artists are promoted to different target audiences; distribution, which is getting the music to audiences through physical CDs, downloads, or streaming; and consumption and exchange, which is how audiences access and share music through personal use, streaming, or downloading.Piracy and mock



Piracy and mockibz10
Ěý
Here are some key ways that independent labels combat piracy:
- Focus on building relationships with fans through social media, live performances, etc. This encourages fans to support the artists directly.
- Release music digitally quickly after recording to minimize pre-release piracy. Quick releases satisfy demand legally.
- Partner with digital distributors like Tunecore to get music onto streaming platforms like Spotify, helping generate legal streams and sales.
- Educate fans about the importance of paying for music to support the artists they love. Fans are more likely to pay when they understand the impact.
- Watermark or fingerprint tracks to help identify sources of leaks, helping take legal action against large pirate sites. Music week 3



Music week 3ibz10
Ěý
The seating plan arranges students in rows with some listed individually and some in pairs or groups. Elaine, Jovan, and Dominic have individual seats while Lemar and Micheal as well as Luke, Chelsie, and Jordan are listed together. The rest of the students including Henry, Yan, Segun, Ellen, and Keano are grouped without being paired specifically.Music intro lesson



Music intro lessonibz10
Ěý
The document discusses how digitalization has impacted the music industry. It provides context about Section B and the assessment requirements. Some key points:
1) Digitalization has both benefited and harmed the music industry by enabling easy sharing but disrupting traditional business models.
2) Students will be assessed on their understanding of how digitalization affects both audiences and institutions in the music industry.
3) Important websites are listed to stay informed about current issues and developments.Media 2012



Media 2012ibz10
Ěý
The document contains questions and prompts for students to prepare for an exam on music industry topics. It includes questions about how labels appeal to target audiences, how technology has changed music marketing, the positive and negative effects of new technology on labels and audiences, and how the type of label affects product development and marketing. It also defines terms like consumption, synergy, cross media promotion, proliferation, ownership, and convergence and asks students to provide examples. Other prompts cover combating piracy, traditional vs new ways of marketing music, distribution methods, and contemporary marketing strategies used by labels/artists.Citizenship day



Citizenship dayibz10
Ěý
The document discusses different types of independent artists in the music industry, asking who they are, what they have in common, and who the odd one out is. It suggests that they have all found global success despite not being signed to a major record label. However, it does not provide enough information to determine who specifically the people are or who would be considered the odd one out.Representation age..



Representation age..ibz10
Ěý
This document discusses representing different social groups in TV dramas and asks students to think about subgenres of TV dramas like The Wire, Skins, and Bleak House and how characters from different ethnicities, ages, and social classes are represented in them. Students are instructed to fill out a mindmap about TV drama subgenres and discuss in pairs how various social groups are represented in images and which groups are represented and in what ways.Introducing tv drama_and_representation_for_g322_ocr_media_studies



Introducing tv drama_and_representation_for_g322_ocr_media_studiesibz10
Ěý
This document provides information about the exam requirements and structure for the G322: Key Media Concepts (TV Drama) exam. It discusses the two sections of the exam - Section A focuses on textual analysis and representation of an unseen TV drama extract, while Section B focuses on institutions and audiences through a case study. It provides details on the requirements and focus of each section, including focusing on technical aspects like camerawork, editing, sound, and mise-en-scene in Section A and production, distribution and audiences in Section B. It also provides examples of topics that could be covered in the case study, like specific films and genres.Introducing tv drama_and_representation ad1



Introducing tv drama_and_representation ad1ibz10
Ěý
The document provides information about an exam on key media concepts related to TV drama. It outlines the structure and requirements of the exam, which has two sections. Section A focuses on textual analysis and representation through analyzing an unseen TV drama extract. Section B examines institutions and audiences within the music industry. The document provides details on the types of questions that may be asked in each section and the key areas of focus for analysis, such as camera work, editing, sound, and mise-en-scene in Section A.Introduction to representation revised ad1



Introduction to representation revised ad1ibz10
Ěý
TV drama is a story presented in a dramatic way that explores genres like soap opera, science fiction, and period pieces. It engages with current issues through relatable characters, fantastic plots and settings. It represents everyday life and social issues to audiences through compelling narratives and characters.More Related Content
More from ibz10 (20)
05 regional identity



05 regional identityibz10
Ěý
This document discusses regional identity and stereotypes in the United Kingdom. It begins by defining regional identity as being connected to both the country and region one lives in, on a smaller scale than national identity. It then lists common stereotypes associated with different regions of the UK, such as Scots being money-obsessed and drinkers, Welsh people living rurally and being rugby fans, and Northerners being poorer and more working class than Southerners. The document encourages analyzing these stereotypes and considering where they come from and how individuals may subvert them.04 ethnicity revision day



04 ethnicity revision dayibz10
Ěý
The document outlines rules for a game to be played in pairs where participants cannot say a specific word or micro-element and the pair with the most correct answers wins a prize. Each pair will play twice with a member from the other team observing to prevent cheating. The rules specify 30 seconds per pair and that the member observing should stand over the pair's shoulder.03 editing disability



03 editing disabilityibz10
Ěý
This document provides guidance for revising to improve analysis of representations of disability in TV drama. It includes focusing on using the PEE structure, improving use of terminology and evidence, and using more analytical language. It discusses stereotypes around physical, mental and able-bodied representations. Examples of characters with disabilities in TV are given. The document also provides guidance on analyzing micro-elements like cinematography, mise-en-scene, sound and editing in exam responses.02 gender



02 genderibz10
Ěý
This lesson aims to analyze representations of gender within TV drama extracts. Students will watch an extract from Primeval four times, analyzing it using a worksheet to discuss how camera shots, editing, sound, and mise en scene construct gender representations. They will discuss camera techniques, editing, sound, and visual elements and how they represent gender without notes on the first viewing, and with notes for subsequent viewings.07 rep of social class



07 rep of social classibz10
Ěý
The upper class would typically be represented through editing, sound, mise-en-scene, and cinematography as follows:
Through editing, the upper class would be represented using techniques like graphic matches and eyeline matches to show their refined manners and lifestyle. Their dialogue would be represented through sound as being well-spoken and proper. Mise-en-scene would show their lavish homes filled with fine furnishings and their elegant clothing. Cinematography would frame them in wide shots set in expansive landscapes to depict their wealth and status through the environments they occupy.Music intro lesson



Music intro lessonibz10
Ěý
The document discusses how digitalization has impacted the music industry. It provides context about Section B and the assessment requirements. Some key points:
1) Digitalization has both benefited and harmed the music industry by enabling portable music formats but also piracy.
2) Students will be assessed on their knowledge and analysis of contemporary issues in the music industry, use of examples and evidence, and industry terminology.
3) Important websites are listed to stay informed on current topics in music and digital media.Student handout



Student handoutibz10
Ěý
The document discusses marketing and promotion of media products. It covers traditional marketing techniques, new digital marketing through technology and social networks, and how digital distribution has affected marketing and consumption. Target audiences and production are also mentioned as areas to cover.Sony lesson 2012



Sony lesson 2012ibz10
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the global music industry and Sony's role within it. The three main points are:
1) Sony is a major record label and conglomerate that dominates the global music industry through its network of subsidiary labels covering various genres and audiences.
2) As a conglomerate, Sony benefits from cross-promotion opportunities across its various media properties, allowing it to effectively market and distribute its music.
3) While digitalization has threatened Sony's dominance, its size and ownership of hardware/devices helps it maintain power, though independent labels have more opportunities in the shifting landscape.Sony company



Sony companyibz10
Ěý
This document discusses the music industry and is organized into three main sections: production, distribution, and marketing/promotion. It examines the different aspects of the industry and how piracy has impacted various parts of the business model. Strategies for combating piracy are also mentioned.Revision powerpoint



Revision powerpointibz10
Ěý
The document discusses four key areas of the music industry: production, distribution, marketing/targeting audiences, and consumption/exchange. It does not provide any details about each area. The areas are listed but the document consists only of headings and does not contain any explanatory text or examples about the music industry topics.Planning stages anaswer



Planning stages anasweribz10
Ěý
The document defines four stages of the music industry: production, which is the process of making and recording music using studios and software; marketing/targeting audiences, which is how music and artists are promoted to different target audiences; distribution, which is getting the music to audiences through physical CDs, downloads, or streaming; and consumption and exchange, which is how audiences access and share music through personal use, streaming, or downloading.Piracy and mock



Piracy and mockibz10
Ěý
Here are some key ways that independent labels combat piracy:
- Focus on building relationships with fans through social media, live performances, etc. This encourages fans to support the artists directly.
- Release music digitally quickly after recording to minimize pre-release piracy. Quick releases satisfy demand legally.
- Partner with digital distributors like Tunecore to get music onto streaming platforms like Spotify, helping generate legal streams and sales.
- Educate fans about the importance of paying for music to support the artists they love. Fans are more likely to pay when they understand the impact.
- Watermark or fingerprint tracks to help identify sources of leaks, helping take legal action against large pirate sites. Music week 3



Music week 3ibz10
Ěý
The seating plan arranges students in rows with some listed individually and some in pairs or groups. Elaine, Jovan, and Dominic have individual seats while Lemar and Micheal as well as Luke, Chelsie, and Jordan are listed together. The rest of the students including Henry, Yan, Segun, Ellen, and Keano are grouped without being paired specifically.Music intro lesson



Music intro lessonibz10
Ěý
The document discusses how digitalization has impacted the music industry. It provides context about Section B and the assessment requirements. Some key points:
1) Digitalization has both benefited and harmed the music industry by enabling easy sharing but disrupting traditional business models.
2) Students will be assessed on their understanding of how digitalization affects both audiences and institutions in the music industry.
3) Important websites are listed to stay informed about current issues and developments.Media 2012



Media 2012ibz10
Ěý
The document contains questions and prompts for students to prepare for an exam on music industry topics. It includes questions about how labels appeal to target audiences, how technology has changed music marketing, the positive and negative effects of new technology on labels and audiences, and how the type of label affects product development and marketing. It also defines terms like consumption, synergy, cross media promotion, proliferation, ownership, and convergence and asks students to provide examples. Other prompts cover combating piracy, traditional vs new ways of marketing music, distribution methods, and contemporary marketing strategies used by labels/artists.Citizenship day



Citizenship dayibz10
Ěý
The document discusses different types of independent artists in the music industry, asking who they are, what they have in common, and who the odd one out is. It suggests that they have all found global success despite not being signed to a major record label. However, it does not provide enough information to determine who specifically the people are or who would be considered the odd one out.Representation age..



Representation age..ibz10
Ěý
This document discusses representing different social groups in TV dramas and asks students to think about subgenres of TV dramas like The Wire, Skins, and Bleak House and how characters from different ethnicities, ages, and social classes are represented in them. Students are instructed to fill out a mindmap about TV drama subgenres and discuss in pairs how various social groups are represented in images and which groups are represented and in what ways.Introducing tv drama_and_representation_for_g322_ocr_media_studies



Introducing tv drama_and_representation_for_g322_ocr_media_studiesibz10
Ěý
This document provides information about the exam requirements and structure for the G322: Key Media Concepts (TV Drama) exam. It discusses the two sections of the exam - Section A focuses on textual analysis and representation of an unseen TV drama extract, while Section B focuses on institutions and audiences through a case study. It provides details on the requirements and focus of each section, including focusing on technical aspects like camerawork, editing, sound, and mise-en-scene in Section A and production, distribution and audiences in Section B. It also provides examples of topics that could be covered in the case study, like specific films and genres.Introducing tv drama_and_representation ad1



Introducing tv drama_and_representation ad1ibz10
Ěý
The document provides information about an exam on key media concepts related to TV drama. It outlines the structure and requirements of the exam, which has two sections. Section A focuses on textual analysis and representation through analyzing an unseen TV drama extract. Section B examines institutions and audiences within the music industry. The document provides details on the types of questions that may be asked in each section and the key areas of focus for analysis, such as camera work, editing, sound, and mise-en-scene in Section A.Introduction to representation revised ad1



Introduction to representation revised ad1ibz10
Ěý
TV drama is a story presented in a dramatic way that explores genres like soap opera, science fiction, and period pieces. It engages with current issues through relatable characters, fantastic plots and settings. It represents everyday life and social issues to audiences through compelling narratives and characters.