Living with schizophrenia WMHD 2014
- 1. LIVING WITH ŌĆś SCHIZOPHRENIAŌĆÖ Dr Jaimon P M Assistant Professor ESIC Medical College Parippally, Kerala
- 3. HEALTH World Health Organization-WHO ’āÆ State of complete physical, mental and social well being ’āÆ Not merely the absence of disease ’āÆ Other dimensions; ’āē Spiritual ’āē Intellectual ’āē Emotional
- 4. MENTAL HEALTH ’āÆ Successful performance of mental functions, in terms of thought, mood and behavior ’āÆ Results in productive activities ’āÆ Fulfilling relationship with others ’āÆ Ability to adapt to changes ’āÆ To cope with adversity
- 5. MENTAL HEALTH ’āÆ Mental health is a state of emotional and social well-being. ’āÆ Numerous factors affect oneŌĆÖs mental health ’āē Biological Factors ’āē Physical abilities and disabilities ’āē Social and environmental conditions and stressors 5
- 6. WMHD 2014 ’āÆ Introduce a quantified national reduction in premature mortality ŌĆō a major health inequality is people with mental ill health dying 20 years younger than the general population ’āÆ Everyone should have access to high quality, safe and speedy access to crisis care and be able to access psychological therapies
- 7. SCHIZOPHRENIA ’āÆ Distortions of thinking & perception and inappropriate/blunted affect. ’āÆ Clear consciousness & intellectual capacity are usually maintained.
- 8. SCHIZOPHRENIA ’āÆ Emil Kraeplin (1856-1926) ’āÆ Eugene Bleuler (1857-1939) ’āÆ Kurt Schneider (1887-1967)
- 9. EPIDEMIOLOGY ’āÆ Life time prevalence- 1% ’āÆ All societies/all classes ’āÆ Male= female ’āÆ Onset earlier in males ’āÆ Peak age - 10-25 yrs Males ’āÆ - 25-35 yrs Females ’āÆ Bimodal peak females- > 40 yrs
- 10. ETIOLOGY ’āÆ Biological Factors ’āē Genetic ’āē Neurochemical ’āē Neuropathological ’āē Neurocircuitory ’āē Brain metabolism ’āē Evoked potential ’āē Psychoneuroimmunology ’āē Psychoneuroendocrinology ’āē Other theories ’āÆ Psychosocial Factors
- 11. FAMILY STUDIES ’āÆ General population -1 % ’āÆ Non-twin sibling of F20 - 8% ’āÆ Child with one parent with F20 - 12% ’āÆ Dizygotic twin of F20 - 12% ’āÆ Child of two parents with F20 - 40% ’āÆ Monozygotic twin of F20 - 47% ’āÆ Paternal age >60 yrs
- 12. NEUROCHEMISTRY ’āÆ Dopamine ’āÆ Serotonin ’āÆ Glutamate ’āÆ GABA ’āÆ Nor Epinephrine
- 13. BIOLOGICAL FACTORS ’āÆ Abnormal DST ’āÆ Decreased LH/FSH ’āÆ Blunted response to Prolactin/GH ’āÆ Autoimmune pathology ’āÆ IL-2 decrease ’āÆ Decreased peripheral lymphocytes ’āÆ Retroviral infection ’āÆ Eye movement dysfunction
- 14. BIOLOGICAL FACTORS ’āÆ Winter births ’āÆ Birth complications ’āÆ Influenza epidemic in 2nd trimester ’āÆ Maternal starvation ’āÆ Rh incompatibility
- 15. PSYCHOSOCIAL THEORIES ’āÆ Sigmund Freud: ’āē early fixation leading to intrapsychic conflicts and ego defect ’āÆ Magret Mahler: ’āē distortion of reciprocal relationship between mother& infant ’āÆ Learning theory: ’āē Children learn irrational reaction& abnormal ways of thinking by imitating parents
- 16. PSYCHOSOCIAL THEORIES ’āÆ Adolf Meyer: ’āē reaction to adverse life events ’āÆ Double blind theory: ’āē Gregory Bateson& Donald Jackson-conflicting parental messages about their behaviour, attitudes, and feelings ’āÆ Expressed Emotions
- 17. SOCIAL FACTORS ’āÆ 40%- alcohol abuse ’āÆ 90%- Nicotine ’āÆ Cannabis 6 times risk ’āÆ Population density> I million ’āÆ Increased economical burden
- 18. SIGNS & SYMPTOMS ’āÆ Impaired sleep ’āÆ Impaired appetite ’āÆ Impaired personal care ’āÆ Unprovoked irritability ’āÆ Self talking/Muttering ’āÆ Self laughing ’āÆ Poor social interaction ’āÆ Difficulty in concentration
- 19. SIGNS& SYMPTOMS ŌĆó Suspiciousness ŌĆó Fearfulness ŌĆó Irrelevant talk ŌĆó Irregular job pattern ŌĆó Hoarding behavior ŌĆó Wandering tendency ŌĆó Suicidal tendency ŌĆó Abusiveness/destructiveness
- 20. SIGNS& SYMPTOMS ’āÆ Thought echo/insertion/ withdrawal/broadcasting ’āÆ Delusions of control/influence/passivity ŌĆó Running commentary/ 3rd person AH/hallucinatory voices from body ’āÆ Bizarre delusions ’āÆ Other Hallucinations ’āÆ Neologisms ’āÆ Catatonic behaviour ’āÆ NegativeŌĆó symptoms
- 21. SIGNS& SYMPTOMS ŌĆó Depressive/euphoric mood changes ŌĆó Anhedonia ŌĆó Autistic thinking ŌĆó Affective flattening ŌĆó Association loosening ŌĆó Ambivalence ŌĆó Avolition ŌĆó Attentional disturbances
- 22. MANAGEMENT ’āÆ Hospitalization ’āē Confirm diagnosis ’āē Safety of the patient ’āē Initiation &Stabilization of medication ’āē Care of basic needs ’āē Psycho education ’āē Effective association with community ’āÆ Improve Quality of Life ’āÆ Employment ’āÆ Social relationship
- 23. MANAGEMENT ’āÆ Acute stage ’āē Antipsychotics ’āē BZD ’āÆ Maintenance stage ’āē Improve level of function ’āē Prevent psychotic relapse ’āē Manage Non compliance ’āē Manage side effects ’āē Health monitoring
- 24. MANAGEMENT ’āÆ Psychological interventions ’āē Psycho education ’āē Social skills training ’āē Cognitive Behavior Therapy ’āē Individual Psychotherapy ’āē Vocational Therapy ’āē Managing Expressed Emotions ’āē Family oriented therapy
- 25. Ó┤¬ÓĄüÓ┤©Ó┤░Ó┤¦Ó┤┐Ó┤ĄÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĖÓ┤é ’āÆ Ó┤ĄÓ┤»Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤┐Ó┤ČÓĄüÓ┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ĄÓ┤é Ó┤¬ÓĄüÓ┤▓Ó┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żl, Ó┤¬Ó┤ŠÓ┤ÜÓ┤ĢÓ┤é, Ó┤£ Ó┤ŠÓ┤▓Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄü Ó┤£Ó┤¬Ó┤ŠÓ┤Ģl Ó┤żÓĄŹÓĄüÓ┤¤Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ÖÓ┤┐Ó┤» Ó┤”ÓĄłÓ┤©Ó┤éÓĄłÓ┤┐Ó┤© Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤ĄÓĄāÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹ Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤»Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĖÓ┤«Ó┤©ÓĄüÓ┤ŁÓ┤ĄÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤ĄÓ┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤é Ó┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤▓ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤Ģ’éĢ. ’āÆ Ó┤åÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤«Ó┤ĄÓ┤┐Ó┤ČÓ┤ĄÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĖÓ┤é Ó┤ĄÓĄĆÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄåÓ┤¤ÓĄüÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹ Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤«Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤ÓĄŹÓ┤¤ ÓĄĆÓ┤ĄÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤é Ó┤©Ó┤»Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤Šn Ó┤¬ÓĄüÓ┤░Ó┤©Ó┤¦Ó┤┐Ó┤ĄÓ┤ŠÓ┤Ė Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤ĄÓ┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤©Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤Ö’éĢ’ĆĀ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤ĖÓ┤╣Ó┤ŠÓ┤»Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄü. ’āÆ Ó┤ĖÓ┤ŠÓ┤«ÓĄéÓ┤╣Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ĄÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ŠÓ┤┤Ó┤┐Ó┤▓ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤ĄÓĄüÓ┤«Ó┤ŠÓ┤» Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ČÓĄĆÓ┤▓Ó┤©Ó┤é Ó┤©Ó┤▓ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤żÓĄŹÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤ģÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐Ó┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤ŁÓ┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤«Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹ.
- 26. Ó┤¬ÓĄüÓ┤©Ó┤░Ó┤¦Ó┤┐Ó┤ĄÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĖÓ┤é ’āÆ Ó┤¬Ó┤ŻÓ┤é Ó┤ÄÓ┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ÖÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤© Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤»Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĘÓ┤«Ó┤«Ó┤ŠÓ┤»Ó┤┐ Ó┤ēÓ┤¬Ó┤£Ó┤»Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤é, Ó┤£ Ó┤ŠÓ┤▓Ó┤┐ Ó┤ÄÓ┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ÖÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤© Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤»Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĖÓ┤é Ó┤ĢÓĄéÓ┤¤Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤żÓĄŹ Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤ÜÓ┤»ÓĄŹÓ┤ŠÓ┤é Ó┤ÄÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤©Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤Ģ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹ Ó┤ēÓ┤¬Ó┤£ÓĄłÓ┤ČÓ┤é Ó┤©Ó┤▓ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄü. ’āÆ Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ŠÓ┤┤Ó┤┐l Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ČÓĄĆÓ┤▓Ó┤©Ó┤£Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤Ó┤ŠÓ┤¤Ó┤é Ó┤©Ó┤▓Ó┤▓Ó┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤ĢÓĄå Ó┤é Ó┤«Ó┤©Ó┤ĖÓĄŹÓ┤ĖÓ┤┐l Ó┤ŖÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤┐Ó┤»ÓĄüÓĄåÓ┤¤Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤│ Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤ČÓ┤«Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ÖÓĄåÓ┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĄÓ┤ČÓ┤»Ó┤é.
- 27. TIPS TO CARE TAKERS ’āÆ Ó┤ĖÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤£Ó┤ĖÓ┤ŠÓ┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤░ÓĄĆÓ┤©Ó┤┐Ó┤» Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄå Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤ ÓĄĆÓ┤ĄÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤┐Ó┤▓Ó┤ĄÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤é Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤«Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤Ó┤¤ÓĄüÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐l Ó┤ģÓ┤ĄÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤░ Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤ĄÓ┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹ Ó┤ĄÓĄåÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤░ Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤¦Ó┤ŠÓ┤©Ó┤«Ó┤ŠÓ┤» Ó┤¬Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓĄåÓĄŹ. ’āÆ Ó┤åÓ┤ČÓĄüÓ┤¬Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐ Ó┤ĄÓ┤┐ÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄŹ Ó┤ĄÓĄĆÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤┐Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤▓Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤© Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤ĄÓ┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹ Ó┤ł Ó┤ģÓ┤ĖÓĄüÓ┤¢Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ż Ó┤ĢÓĄüÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓĄŹ Ó┤ĄÓ┤»Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤«Ó┤ŠÓ┤» Ó┤¦Ó┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤Ż Ó┤ēÓĄåÓ┤ŠÓ┤»Ó┤┐Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓ┤é. ’āÆ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤ĄÓĄĆÓĄåÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤¬Ó┤┤Ó┤» Ó┤ģÓ┤ĄÓ┤ĖÓĄŹÓ┤źÓ┤»Ó┤┐Ó┤£Ó┤▓Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹ Ó┤«Ó┤¤Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ÖÓ┤┐Ó┤£Ó┤¤Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤│ Ó┤ĖÓ┤ŠÓ┤¦Ó┤»Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤ĢÓĄüÓĄåÓ┤»ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤│ Ó┤ĄÓ┤┤Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄåÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓĄŹ Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤Ģr Ó┤ģÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤×ÓĄŹÓ┤×Ó┤┐Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓ┤é.
- 28. TIPS TO CARE TAKERS ’āÆ Ó┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ĖÓ┤»Ó┤┐l Ó┤¬Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄåÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤© Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓĄĆÓ┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤ĢÓ┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹ Ó┤ĄÓĄåÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤░ Ó┤ĄÓ┤▓Ó┤┐Ó┤» Ó┤¬Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄüÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤│Ó┤żÓĄŹ. ’āÆ Ó┤«Ó┤░ÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤ĢÓĄāÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤»Ó┤ĖÓ┤«Ó┤»Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹ Ó┤©Ó┤▓ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤«Ó┤░ÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤ĢÓ┤┤Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤▓Ó┤▓Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤┐l Ó┤ēÓĄåÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĄÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤© Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤ČÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ÖÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄåÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓĄŹ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤¬ÓĄåÓ┤×ÓĄŹÓ┤×ÓĄüÓ┤«Ó┤©Ó┤ĖÓĄŹÓ┤ĖÓ┤┐Ó┤▓Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓĄĆÓ┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤Ģr Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤ČÓ┤”ÓĄŹÓ┤¦Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓ┤é. ’āÆ Ó┤åÓ┤ČÓĄüÓ┤¬Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐ Ó┤ĄÓ┤┐ÓĄŹÓ┤¤ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤«Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐Ó┤»Ó┤ŠÓ┤» Ó┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤Ė Ó┤▓Ó┤ŁÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄåÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄŹ Ó┤ēÓĄåÓ┤¤ Ó┤ĄÓ┤░ÓĄüÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤żÓĄŹÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤ĄÓĄåÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤░ Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤¦Ó┤ŠÓ┤©Ó┤«Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹ.
- 29. TIPS TO CARE TAKERS ’āÆ Ó┤«Ó┤░ÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤©Ó┤┐Ó┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄåÓ┤»ÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤© Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤▓ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤żÓĄŹÓĄüÓ┤¤Ó┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ĖÓ┤»ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄü Ó┤£Ó┤¬Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤ĄÓ┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤▓ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤ŠÓ┤ĄÓ┤ĖÓĄŹÓ┤ź Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤Ü Ó┤ĄÓ┤£Ó┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤é. ’āÆ Ó┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤Ė Ó┤żÓĄŹÓĄüÓ┤¤Ó┤░Ó┤Šn Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤£Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤¤Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓĄŹ Ó┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ĖÓ┤»Ó┤┐l Ó┤ĖÓ┤╣Ó┤ŠÓ┤»Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤┐Ó┤▓ÓĄéÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤ Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤ĢÓ┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄŹ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄå Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤ ÓĄĆÓ┤ĄÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤é Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤«Ó┤ÜÓĄŹÓ┤ÜÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤Ó┤¤ÓĄüÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤ŠÓ┤©Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤é.
- 30. TIPS TO CARE TAKERS ’āÆ Ó┤ŖÓ┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤£ÓĄŹÓ┤£Ó┤ĖÓ┤ĄÓ┤▓Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤£Ó┤»Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤ ÓĄĆÓ┤ĄÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤Šn Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤Ģr Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤£Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤¤Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓ┤é ’āÆ Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤Ģr ÓĄłÓ┤»Ó┤»ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤ČÓ┤”ÓĄŹÓ┤¦Ó┤»ÓĄüÓ┤«ÓĄüÓ┤│ÓĄŹÓ┤│Ó┤ĄÓ┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓ┤é ’āÆ Ó┤«Ó┤░ÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤ĢÓĄāÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤»Ó┤«Ó┤ŠÓ┤»Ó┤┐ Ó┤ĢÓ┤┤Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤Šn Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤£Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤¤Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓ┤é
- 31. TIPS TO CARE TAKERS ’āÆ Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄåÓ┤┐l Ó┤åÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤«Ó┤╣Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤»Ó┤ŠÓ┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤ĄÓ┤ŻÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤»ÓĄüÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤ Ó┤ÄÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤▓ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤ĖÓĄéÓ┤ÜÓ┤©Ó┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄüÓ┤ĢÓ┤»Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤ŻÓ┤ÖÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤┐l Ó┤ģÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤»Ó┤é Ó┤ēÓ┤¤Ó┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤© Ó┤ÜÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤┐Ó┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ĖÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤© Ó┤£ Ó┤ŠÓ┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤ģÓĄåÓ┤┐Ó┤»Ó┤┐Ó┤£Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄåÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤ŠÓ┤ŻÓĄŹ. ’āÆ Ó┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤ÜÓ┤ŠÓ┤░Ó┤Ģr Ó┤£Ó┤░Ó┤ŠÓ┤ŚÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄå Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤¤ Ó┤©Ó┤▓Ó┤▓ Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤ĄÓĄāÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤┐Ó┤ĢÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤ÓĄå Ó┤ģÓ┤ŁÓ┤┐Ó┤©Ó┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤”Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤ĢÓ┤»ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤ģÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤░Ó┤é Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤ĄÓĄāÓ┤żÓĄŹÓ┤żÓ┤┐Ó┤Ģ’éĢ Ó┤żÓĄŹÓĄüÓ┤¤Ó┤░ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄŹÓ┤©ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤ÜÓ┤»ÓĄŹÓ┤Šn Ó┤ģÓ┤ĄÓ┤ŻÓĄŹÓ┤¤Ó┤░ Ó┤£Ó┤¬ÓĄŹÓ┤¬Ó┤░Ó┤┐Ó┤¤Ó┤┐Ó┤ĢÓĄŹÓ┤ĢÓĄüÓ┤ĢÓ┤»ÓĄüÓ┤é Ó┤£Ó┤ĄÓ┤ŻÓ┤é.
- 32. TIPS TO CARE TAKERS ’āÆ ’éĆn’üŹ’üÖ’āü’ééAVm ’āÆ B’é▒j’éäieL ’üĢ’āŗ’éć’āē’üŹ’éä’éĆ ’āÆ eeVKARiK aTu’éŹm’ĆĀ’ĆĀ ’āÆ Vi’üŹr’éåNj’éĢ ’āÆ ’ü»’āģ’üÉAl’üōA’üłNm ’āÆ ’āģ’üÉAr’ü╣N ’āÆ d’üŹ ’āÆ am’üć’āüKARm
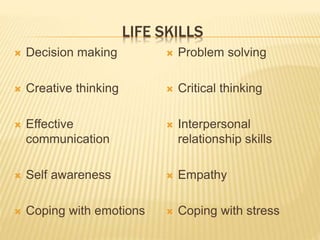
- 33. LIFE SKILLS ’āÆ Decision making ’āÆ Creative thinking ’āÆ Effective communication ’āÆ Self awareness ’āÆ Coping with emotions ’āÆ Problem solving ’āÆ Critical thinking ’āÆ Interpersonal relationship skills ’āÆ Empathy ’āÆ Coping with stress
- 34. S]MXP-P ]┬”M-FN┬»W ’üČ Xt┬▒i `c-W-tI-{╬╝-┬¦├ä ’üČ aX-t-Xm-┬Ī├ä ’üČ k┬Č-┬▓-tk-mw-K-┬¦├ä IpSpw-_{io Ab├é┬Īq┬½w km┬Ż-cXm {]h├Ć┬»-I├Ć XpS-┬¦n-b-h├Ć ’üČ hnZym├Ć┬░n-I├ä
- 36. ŌĆ£Education is not the amount of information, that is put into your brain and runs riot there undigestedŌĆØ - Swami Vivekananda
































![S]MXP-P ]┬”M-FN┬»W
’üČ Xt┬▒i `c-W-tI-{╬╝-┬¦├ä
’üČ aX-t-Xm-┬Ī├ä
’üČ k┬Č-┬▓-tk-mw-K-┬¦├ä
IpSpw-_{io
Ab├é┬Īq┬½w
km┬Ż-cXm {]h├Ć┬»-I├Ć XpS-┬¦n-b-h├Ć
’üČ hnZym├Ć┬░n-I├ä](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/livingwithschizophrenia-wmhd2014-141010114208-conversion-gate01/85/Living-with-schizophrenia-WMHD-2014-34-320.jpg)

