Powerpoint presentation of jelmarie
Download as pptx, pdf2 likes1,835 views
Soil erosion occurs naturally through processes like water and wind but is exacerbated by human activities like deforestation, overgrazing, overcropping, agricultural disturbance, logging, farming, cattle ranching, surface mining, strip mining, and urbanization. The effects of soil erosion include the deterioration of agricultural lands, increased flooding, reduced water supply, destruction of infrastructure, and the depletion of wildlife and natural resources. While advances in soil management have helped maintain crop yields, soil erosion remains a significant problem that often only becomes apparent when property is damaged and productive soil is lost.
1 of 12
Downloaded 28 times











Ad
Recommended
Soil erosion
Soil erosionBigyan Thapa
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, including its definition, causes, effects, and methods to control it. Soil erosion is the loss of topsoil from land by water or wind. It is caused by both natural processes like water flowing downhill and human activities such as overgrazing, deforestation, and overcropping. This accelerated erosion degrades soil quality and reduces crop yields. Control methods center around maintaining ground cover through practices like mulching, cover crops, and crop rotation, as well as using barriers like terraces and contour ploughing to prevent topsoil loss from water runoff. Overall, controlling erosion sustains agricultural productivity and environmental quality.Soils erosion
Soils erosionVeeshalla100
Ěý
Soil erosion is the removal of topsoil from the land, primarily due to human mismanagement. There are three main types of erosion: sheet erosion caused by moving water, gully erosion from water in steep areas, and wind erosion in dry bare areas. Some key causes are overgrazing, cultivation on steep slopes, overcropping, and deforestation. To conserve soils, proper land management techniques can be used, including terracing, strip cropping, crop rotation, contour ploughing, reforestation, and windbreaks. These practices help reduce runoff and protect soil from heavy rainfall and winds.Soil erosion conservation
Soil erosion conservationAnkit Gupta
Ěý
Soil erosion is the displacement of topsoil caused by various natural and human factors, leading to significant ecological impacts, including reduced crop productivity and increased land degradation. Key causes include rainfall, wind, agricultural practices, deforestation, and mining, which exacerbate erosion rates. To prevent soil erosion, methods such as increasing vegetative cover, terracing, and adopting sustainable agricultural techniques are essential to maintain soil health and prevent desertification.Soil erosion by water
Soil erosion by waterMoudud Hasan
Ěý
This document discusses different types of soil erosion, factors that affect erosion, and conservation practices to reduce erosion. It describes geological erosion as natural soil-forming processes, while accelerated erosion is soil loss due to human activities. Water erosion is divided into raindrop, sheet, rill, gully, and stream channel erosion. Major factors affecting erosion by water are climate, soil properties, vegetation, and topography. Conservation practices discussed include contouring, strip cropping, and tillage management.Soil erosion
Soil erosionJishna V V
Ěý
Soil erosion is a naturally occurring process that affects all landforms and can occur slowly over time or rapidly, causing serious topsoil loss. There are four main types of erosion: sheet erosion, gully erosion, channel erosion, and rill erosion. Soil erosion is caused by both natural processes like wind and water flowing downhill, as well as human activities such as overcropping, deforestation, and overgrazing. Problems from soil erosion include loss of topsoil, damage to fields, decreased plant productivity, and desertification. Remedies include avoiding overgrazing, conserving wetlands, terracing, and encouraging water infiltration.Soil erosion
Soil erosionMoocs Engine
Ěý
Soil erosion is the removal of the top layer of soil due to wind and water, which can lead to barren land and hinder crop growth. It accelerates when human activities, such as poor farming practices, remove vegetation that protects the soil. Prevention strategies include planting windbreaks, contour ploughing, and maintaining plant cover to enhance soil stability.15 Evapotranspiration
15 EvapotranspirationAboutHydrology şÝşÝߣs
Ěý
The document explores the concept of evapotranspiration, encompassing both evaporation and transpiration processes that involve the phase change of water from liquid to vapor. It discusses factors affecting evaporation, such as energy balance, temperature, vapor content, wind, and water availability, along with various principles and laws governing these phenomena. Additionally, it highlights educational goals for understanding the dynamics of evapotranspiration in relation to environmental conditions.Land subsidence: what is it and why do we care?
Land subsidence: what is it and why do we care?EMA-tucson
Ěý
The document discusses land subsidence, which is the sinking or settling of land caused by underground water withdrawal. It notes that groundwater overdraft is the principal cause of subsidence, and it has impacted over 1,200 square miles in Arizona, with up to 20 feet of subsidence measured. The document outlines how subsidence occurs, where it is located nationally and in Arizona, its impacts such as damage to infrastructure and earth fissures, monitoring techniques, and potential mitigation strategies.Soil conservation
Soil conservationSaad Farooqi
Ěý
The document discusses various agronomic measures for soil conservation. Some key measures mentioned include contour cultivation, strip cropping, use of cover crops, mulching, addition of manure and fertilizers, construction of bench terraces, use of vegetative barriers, and maintaining soil pH and salinity levels. Soil conservation is important to prevent erosion and destruction of soil. Various farming practices can be employed to effectively conserve soil on agricultural lands.Soil erosion
Soil erosionRishi Rajput
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion including its causes, types, and agents. It defines soil erosion as the detachment, transportation, and deposition of soil particles by forces like wind and water. The two main types of erosion are geologic erosion, which is the natural, balanced process of soil formation and loss, and accelerated erosion, which exceeds the natural rate due to human and natural causes. Water and wind are the primary agents of soil erosion. Factors like vegetation removal, improper land use, and slope steepness can increase soil erosion and negatively impact crop production, waterways, and infrastructure.land degradation
land degradation abhisha prabheesh
Ěý
Land degradation is the temporary or permanent lowering of land productivity caused by soil degradation, impacts on water resources, deforestation, and other factors. Key factors responsible for land degradation include loss of vegetation from deforestation, unsustainable extraction of fuel and fodder, shifting cultivation, encroachment into forests, overgrazing, failure to implement soil conservation measures, improper crop rotation, misuse of agrochemicals, poor management of irrigation systems, excessive groundwater extraction, open access to resources, and poverty among agriculture-dependent communities.Soil erosion2
Soil erosion2manishj007
Ěý
Soil erosion is a major problem in India caused by various natural and human factors. The key causes are heavy rainfall, deforestation, overgrazing, and poor agricultural practices. This strips away topsoil, especially on steep slopes. Regions highly impacted include Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Himalayan foothills. To control erosion, methods such as terracing, contour plowing, afforestation, and constructing dams have been used. Preventing further environmental degradation and switching to sustainable farming techniques are important to reduce soil loss.Soil erosion kvg
Soil erosion kvgkaushal gadariya
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, focusing on its mechanics, types, agents, and factors affecting it, such as climate and soil properties. It elaborates on various erosion types including geological and accelerated erosion, and specific forms like rain splash and gully erosion, with a mention of the historical 'Black Sunday' event. Additionally, it outlines methods for soil conservation, such as terrace farming, contour ploughing, and planting shelter belts.Land Pollution
Land PollutionStudent
Ěý
Land pollution is caused by waste in liquid or solid form from uncontrolled garbage disposal, sewage, and toxic and nuclear waste. It results in changes to soil color, fertility, and structure. Deforestation can also cause land pollution as the absence of tree roots makes the ground loose and prone to erosion. Soil contamination leads to diseases spreading through pests and damage to soil quality and plant growth. Environmental education and awareness campaigns can help address the problem by teaching people about protecting the environment.Soil erosion
Soil erosionAshiMirzaa
Ěý
Soil erosion is the displacement of the upper layer of soil, primarily accelerated by human activity, leading to a loss of fertile topsoil and degradation of land. It occurs through various processes such as water and wind erosion, with factors like overgrazing, lack of vegetation, and steep slopes contributing to its severity. Prevention strategies include maintaining permanent vegetation, using cover crops, and implementing conservation practices to reduce runoff and protect soil integrity.Soil erosion
Soil erosionammaranayab
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, definining it as the removal of topsoil caused by natural forces and human activities. It outlines the composition of soil, the types of erosion, and its on-site and off-site impacts, such as decreased agricultural productivity and sedimentation of waterways. Solutions for preventing soil erosion include careful tilling, implementing water control measures, and increasing knowledge about sustainable farming practices.Land pollution
Land pollutionAkthar1998
Ěý
Land pollution is caused by the disposal of waste in liquid or solid form, which can change the color, fertility and cause erosion of land. The main causes are uncontrolled garbage disposal, sewage, deforestation, overuse of pesticides, mining and inadequate waste treatment. This leads to effects like loss of forest cover and rainfall, which affect climate and can cause problems like acid rain, global warming and bioaccumulation of non-biodegradable substances in the food chain. Land pollution prevention methods include proper waste disposal through separation and decomposition, recycling, use of biodegradable products, growing more trees, efficient use of resources and judicious use of oil and petrol.Soil degradation
Soil degradationAtif Nauman
Ěý
The document discusses soil degradation, which is the decline in soil quality caused by improper use that reduces its ability to support plant growth. There are three main types of soil degradation: chemical, through loss of nutrients and increased acidity/salinity; physical, such as compaction and waterlogging; and biological, through reduced microbial activity. Soil degradation is caused by unsustainable land management practices like deforestation, overuse of nutrients, and cultivation on steep slopes. Its impacts include reduced food production, water shortages, lower incomes, and forced migration. Sustainable soil management aims to maintain soil organic matter, minimize tillage, and keep nitrogen and organic matter levels balanced through practices like cover cropping. In Pakistan,characteristics and morphological change of the river.ppt
characteristics and morphological change of the river.pptAmanuel Beza
Ěý
1) The document provides information about river engineering and sediment transport. It discusses river characteristics such as catchment areas, stream ordering, longitudinal profiles, and flow types.
2) River hydraulics concepts are explained, including laminar and turbulent flow, boundary layers, velocity profiles, and shear stress. Different flow layers and classifications of flow based on roughness are also covered.
3) Types of rivers are classified based on variables such as discharge patterns, location, and planform. Perennial, non-perennial, flashy, mountainous, meandering, and braided rivers are some of the types described.Soil erosion (IGKV RAIPUR, C.G)
Soil erosion (IGKV RAIPUR, C.G)Rahul Raj Tandon
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion, including its definition, causes, types, and extent. It defines soil erosion as the wearing away of land by forces like water, wind, or human activity. The main types of erosion are water erosion and wind erosion. Water erosion includes splash erosion, sheet erosion, rill erosion, gully erosion, and stream-bank erosion. Wind erosion occurs through surface creep, saltation, and suspension. The document also notes that approximately 45% of India's land is affected by serious soil erosion.Soil Erosion
Soil Erosionjbgruver
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion, its causes, impacts, and methods for measuring and addressing it. It provides context on the development of the Universal Soil Loss Equation to quantitatively predict erosion. While useful, the USLE does not capture extreme weather events that cause most erosion. Direct measurements are most accurate but also most resource-intensive. The document outlines various on-site and off-site impacts of erosion and early efforts to address the problem through the Soil Conservation Service and projects like Coon Creek Watershed.Floods in bangladesh
Floods in bangladeshHanif Bhuian
Ěý
The presentation discusses the issue of floods in Bangladesh, outlining various types and causes, including heavy rainfall and dam failures. Historical floods have resulted in significant loss of life and damage, with severe events occurring in 1974, 1988, and 1998 among others. It emphasizes the negative impact of floods on agriculture, infrastructure, and public health, and suggests preventative measures and management strategies to mitigate their effects.Offsite and onsite
Offsite and onsiteSantosh pathak
Ěý
Soil erosion, primarily caused by water and wind, results in significant on-site and off-site consequences, including the loss of valuable soil nutrients and organic matter, increased water runoff, and degradation of soil structure. It leads to environmental issues like water pollution, eutrophication, and habitat destruction, affecting both agriculture and aquatic ecosystems. The document emphasizes the necessity for collective action to combat soil erosion to mitigate its detrimental effects.Impact of drought on economy of a country
Impact of drought on economy of a country university of gujrat
Ěý
The document discusses drought in several contexts:
1) It defines drought and describes three main types: meteorological, hydrological, and agricultural.
2) It outlines the consequences of drought including environmental, economic, and social impacts such as famine, habitat damage, and conflict over resources.
3) Several examples of historical droughts are provided, including those that affected ancient Egypt, the Maya civilization, the 1930s Dust Bowl in the US, and droughts in China and the Northern Great Plains in the 1980s-90s.Soil erosion
Soil erosionshivacivil1401
Ěý
The document discusses the various types and causes of soil erosion, distinguishing between geological and accelerated erosion caused by human activities. It outlines the mechanisms of erosion, including splash, rill, gully, and sheet erosion, along with their impacts such as loss of nutrients, land degradation, and increased flooding risks. Factors contributing to accelerated erosion include land preparation, deforestation, and poor watershed management.Seminar on frost action
Seminar on frost actionShruthi NP
Ěý
The document discusses frost action and its effects on pavements. Frost action refers to frost heave, frost melting/thawing, and the alternating freezing and thawing cycles. Frost heave occurs when frozen soil expands and lifts the pavement surface due to water absorption. As temperatures rise, the frozen soil thaws and becomes soft, which can cause frost boils and damage pavement. Factors like soil type, temperature, water supply, and drainage influence frost action. Proper drainage systems, layered pavement design, and soil stabilization can prevent damage from frost action.Soil conservation
Soil conservationRafiullah Utmani
Ěý
The document discusses various soil conservation practices aimed at preventing soil erosion and enhancing soil fertility. Key methods include contour farming, terrace farming, no-till farming, organic farming, restoring wetlands, planting vegetation cover, and implementing proper waste management. These practices collectively help to protect soil integrity by managing water flow, reducing chemical use, and preventing contamination.DESIGN OF SUBSURFACE DRAINAGE SYSTEM
DESIGN OF SUBSURFACE DRAINAGE SYSTEMNamitha M R
Ěý
This document discusses the design of subsurface drainage systems. It describes different types of subsurface drainage methods like tile drains, mole drains and drainage wells. It also covers investigations required for planning subsurface drainage like topographic maps and groundwater studies. The key aspects of designing a tile drainage system are discussed in detail, including layout, depth and spacing of drains, size and grade of tiles, installation methods and use of a multiple well system.Role of Textiles in Soil Erosion Control ppt
Role of Textiles in Soil Erosion Control pptAshutosh Shukla
Ěý
Textiles play an important role in soil erosion control. Geotextiles like biaxially oriented process nets, erosion control meshes, and erosion control blankets can be used to reinforce soils and control erosion. They protect soil surfaces from water and wind forces, helping to establish vegetation. Geogrids also reinforce soils by improving tensile strength. Fibre-reinforced sands add flexibility like plant roots. Together, geosynthetics and natural fibers provide cost-effective soil stabilization and erosion prevention.Shore protection copy
Shore protection copyHamid Hussain
Ěý
This document discusses coastal erosion, its causes, impacts, and various mitigation approaches. It identifies key physical parameters that contribute to coastal erosion like waves, tides, and vegetation. Approaches to mitigate erosion include hard engineering methods like seawalls, breakwaters, and groynes, as well as soft engineering methods like beach nourishment, relocating structures, planting mangroves, and growing coral reefs. Hard structures provide direct protection but can have negative environmental impacts. Soft methods aim to work with natural coastal processes but have challenges with feasibility and cost. Overall management requires consideration of engineering and environmental factors.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Soil conservation
Soil conservationSaad Farooqi
Ěý
The document discusses various agronomic measures for soil conservation. Some key measures mentioned include contour cultivation, strip cropping, use of cover crops, mulching, addition of manure and fertilizers, construction of bench terraces, use of vegetative barriers, and maintaining soil pH and salinity levels. Soil conservation is important to prevent erosion and destruction of soil. Various farming practices can be employed to effectively conserve soil on agricultural lands.Soil erosion
Soil erosionRishi Rajput
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion including its causes, types, and agents. It defines soil erosion as the detachment, transportation, and deposition of soil particles by forces like wind and water. The two main types of erosion are geologic erosion, which is the natural, balanced process of soil formation and loss, and accelerated erosion, which exceeds the natural rate due to human and natural causes. Water and wind are the primary agents of soil erosion. Factors like vegetation removal, improper land use, and slope steepness can increase soil erosion and negatively impact crop production, waterways, and infrastructure.land degradation
land degradation abhisha prabheesh
Ěý
Land degradation is the temporary or permanent lowering of land productivity caused by soil degradation, impacts on water resources, deforestation, and other factors. Key factors responsible for land degradation include loss of vegetation from deforestation, unsustainable extraction of fuel and fodder, shifting cultivation, encroachment into forests, overgrazing, failure to implement soil conservation measures, improper crop rotation, misuse of agrochemicals, poor management of irrigation systems, excessive groundwater extraction, open access to resources, and poverty among agriculture-dependent communities.Soil erosion2
Soil erosion2manishj007
Ěý
Soil erosion is a major problem in India caused by various natural and human factors. The key causes are heavy rainfall, deforestation, overgrazing, and poor agricultural practices. This strips away topsoil, especially on steep slopes. Regions highly impacted include Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Himalayan foothills. To control erosion, methods such as terracing, contour plowing, afforestation, and constructing dams have been used. Preventing further environmental degradation and switching to sustainable farming techniques are important to reduce soil loss.Soil erosion kvg
Soil erosion kvgkaushal gadariya
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, focusing on its mechanics, types, agents, and factors affecting it, such as climate and soil properties. It elaborates on various erosion types including geological and accelerated erosion, and specific forms like rain splash and gully erosion, with a mention of the historical 'Black Sunday' event. Additionally, it outlines methods for soil conservation, such as terrace farming, contour ploughing, and planting shelter belts.Land Pollution
Land PollutionStudent
Ěý
Land pollution is caused by waste in liquid or solid form from uncontrolled garbage disposal, sewage, and toxic and nuclear waste. It results in changes to soil color, fertility, and structure. Deforestation can also cause land pollution as the absence of tree roots makes the ground loose and prone to erosion. Soil contamination leads to diseases spreading through pests and damage to soil quality and plant growth. Environmental education and awareness campaigns can help address the problem by teaching people about protecting the environment.Soil erosion
Soil erosionAshiMirzaa
Ěý
Soil erosion is the displacement of the upper layer of soil, primarily accelerated by human activity, leading to a loss of fertile topsoil and degradation of land. It occurs through various processes such as water and wind erosion, with factors like overgrazing, lack of vegetation, and steep slopes contributing to its severity. Prevention strategies include maintaining permanent vegetation, using cover crops, and implementing conservation practices to reduce runoff and protect soil integrity.Soil erosion
Soil erosionammaranayab
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, definining it as the removal of topsoil caused by natural forces and human activities. It outlines the composition of soil, the types of erosion, and its on-site and off-site impacts, such as decreased agricultural productivity and sedimentation of waterways. Solutions for preventing soil erosion include careful tilling, implementing water control measures, and increasing knowledge about sustainable farming practices.Land pollution
Land pollutionAkthar1998
Ěý
Land pollution is caused by the disposal of waste in liquid or solid form, which can change the color, fertility and cause erosion of land. The main causes are uncontrolled garbage disposal, sewage, deforestation, overuse of pesticides, mining and inadequate waste treatment. This leads to effects like loss of forest cover and rainfall, which affect climate and can cause problems like acid rain, global warming and bioaccumulation of non-biodegradable substances in the food chain. Land pollution prevention methods include proper waste disposal through separation and decomposition, recycling, use of biodegradable products, growing more trees, efficient use of resources and judicious use of oil and petrol.Soil degradation
Soil degradationAtif Nauman
Ěý
The document discusses soil degradation, which is the decline in soil quality caused by improper use that reduces its ability to support plant growth. There are three main types of soil degradation: chemical, through loss of nutrients and increased acidity/salinity; physical, such as compaction and waterlogging; and biological, through reduced microbial activity. Soil degradation is caused by unsustainable land management practices like deforestation, overuse of nutrients, and cultivation on steep slopes. Its impacts include reduced food production, water shortages, lower incomes, and forced migration. Sustainable soil management aims to maintain soil organic matter, minimize tillage, and keep nitrogen and organic matter levels balanced through practices like cover cropping. In Pakistan,characteristics and morphological change of the river.ppt
characteristics and morphological change of the river.pptAmanuel Beza
Ěý
1) The document provides information about river engineering and sediment transport. It discusses river characteristics such as catchment areas, stream ordering, longitudinal profiles, and flow types.
2) River hydraulics concepts are explained, including laminar and turbulent flow, boundary layers, velocity profiles, and shear stress. Different flow layers and classifications of flow based on roughness are also covered.
3) Types of rivers are classified based on variables such as discharge patterns, location, and planform. Perennial, non-perennial, flashy, mountainous, meandering, and braided rivers are some of the types described.Soil erosion (IGKV RAIPUR, C.G)
Soil erosion (IGKV RAIPUR, C.G)Rahul Raj Tandon
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion, including its definition, causes, types, and extent. It defines soil erosion as the wearing away of land by forces like water, wind, or human activity. The main types of erosion are water erosion and wind erosion. Water erosion includes splash erosion, sheet erosion, rill erosion, gully erosion, and stream-bank erosion. Wind erosion occurs through surface creep, saltation, and suspension. The document also notes that approximately 45% of India's land is affected by serious soil erosion.Soil Erosion
Soil Erosionjbgruver
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion, its causes, impacts, and methods for measuring and addressing it. It provides context on the development of the Universal Soil Loss Equation to quantitatively predict erosion. While useful, the USLE does not capture extreme weather events that cause most erosion. Direct measurements are most accurate but also most resource-intensive. The document outlines various on-site and off-site impacts of erosion and early efforts to address the problem through the Soil Conservation Service and projects like Coon Creek Watershed.Floods in bangladesh
Floods in bangladeshHanif Bhuian
Ěý
The presentation discusses the issue of floods in Bangladesh, outlining various types and causes, including heavy rainfall and dam failures. Historical floods have resulted in significant loss of life and damage, with severe events occurring in 1974, 1988, and 1998 among others. It emphasizes the negative impact of floods on agriculture, infrastructure, and public health, and suggests preventative measures and management strategies to mitigate their effects.Offsite and onsite
Offsite and onsiteSantosh pathak
Ěý
Soil erosion, primarily caused by water and wind, results in significant on-site and off-site consequences, including the loss of valuable soil nutrients and organic matter, increased water runoff, and degradation of soil structure. It leads to environmental issues like water pollution, eutrophication, and habitat destruction, affecting both agriculture and aquatic ecosystems. The document emphasizes the necessity for collective action to combat soil erosion to mitigate its detrimental effects.Impact of drought on economy of a country
Impact of drought on economy of a country university of gujrat
Ěý
The document discusses drought in several contexts:
1) It defines drought and describes three main types: meteorological, hydrological, and agricultural.
2) It outlines the consequences of drought including environmental, economic, and social impacts such as famine, habitat damage, and conflict over resources.
3) Several examples of historical droughts are provided, including those that affected ancient Egypt, the Maya civilization, the 1930s Dust Bowl in the US, and droughts in China and the Northern Great Plains in the 1980s-90s.Soil erosion
Soil erosionshivacivil1401
Ěý
The document discusses the various types and causes of soil erosion, distinguishing between geological and accelerated erosion caused by human activities. It outlines the mechanisms of erosion, including splash, rill, gully, and sheet erosion, along with their impacts such as loss of nutrients, land degradation, and increased flooding risks. Factors contributing to accelerated erosion include land preparation, deforestation, and poor watershed management.Seminar on frost action
Seminar on frost actionShruthi NP
Ěý
The document discusses frost action and its effects on pavements. Frost action refers to frost heave, frost melting/thawing, and the alternating freezing and thawing cycles. Frost heave occurs when frozen soil expands and lifts the pavement surface due to water absorption. As temperatures rise, the frozen soil thaws and becomes soft, which can cause frost boils and damage pavement. Factors like soil type, temperature, water supply, and drainage influence frost action. Proper drainage systems, layered pavement design, and soil stabilization can prevent damage from frost action.Soil conservation
Soil conservationRafiullah Utmani
Ěý
The document discusses various soil conservation practices aimed at preventing soil erosion and enhancing soil fertility. Key methods include contour farming, terrace farming, no-till farming, organic farming, restoring wetlands, planting vegetation cover, and implementing proper waste management. These practices collectively help to protect soil integrity by managing water flow, reducing chemical use, and preventing contamination.DESIGN OF SUBSURFACE DRAINAGE SYSTEM
DESIGN OF SUBSURFACE DRAINAGE SYSTEMNamitha M R
Ěý
This document discusses the design of subsurface drainage systems. It describes different types of subsurface drainage methods like tile drains, mole drains and drainage wells. It also covers investigations required for planning subsurface drainage like topographic maps and groundwater studies. The key aspects of designing a tile drainage system are discussed in detail, including layout, depth and spacing of drains, size and grade of tiles, installation methods and use of a multiple well system.Viewers also liked (6)
Role of Textiles in Soil Erosion Control ppt
Role of Textiles in Soil Erosion Control pptAshutosh Shukla
Ěý
Textiles play an important role in soil erosion control. Geotextiles like biaxially oriented process nets, erosion control meshes, and erosion control blankets can be used to reinforce soils and control erosion. They protect soil surfaces from water and wind forces, helping to establish vegetation. Geogrids also reinforce soils by improving tensile strength. Fibre-reinforced sands add flexibility like plant roots. Together, geosynthetics and natural fibers provide cost-effective soil stabilization and erosion prevention.Shore protection copy
Shore protection copyHamid Hussain
Ěý
This document discusses coastal erosion, its causes, impacts, and various mitigation approaches. It identifies key physical parameters that contribute to coastal erosion like waves, tides, and vegetation. Approaches to mitigate erosion include hard engineering methods like seawalls, breakwaters, and groynes, as well as soft engineering methods like beach nourishment, relocating structures, planting mangroves, and growing coral reefs. Hard structures provide direct protection but can have negative environmental impacts. Soft methods aim to work with natural coastal processes but have challenges with feasibility and cost. Overall management requires consideration of engineering and environmental factors.Coastal Erosion And Its Control
Coastal Erosion And Its Controlpartha sharma
Ěý
The document provides an overview of coastal erosion, outlining its causes, processes, impacts, and various prevention methods. It discusses factors such as wind, water, tides, and human activities that contribute to erosion and the potential hazards it poses to urban development and marine life. Additionally, it highlights structural and non-structural measures for mitigating coastal erosion, including the use of sea walls, groins, and the development of coastal vegetation.Preventing soil erosion 02 20-12
Preventing soil erosion 02 20-12gevsln
Ěý
Humans must work to prevent soil erosion through responsible stewardship of the earth. Key methods include terracing, contour plowing, and strip cropping to slow water runoff and preserve soil minerals. Reforestation helps stabilize soil with tree roots, while educating farmers on sustainable practices can discourage activities like kaingin that damage the land over time. Together, these farming techniques and education can reduce erosion and protect the soil for future generations.soil erosion
soil erosioncheergalsal
Ěý
Soil erosion is caused by both natural processes like wind and water, as well as human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, monoculture farming, and removing windbreaks. This accelerated erosion decreases soil fertility and crop production. Several methods can limit soil erosion, including terracing to hold soil and water, contour ploughing across slopes, planting shelter belts to protect soil, using strip farming to minimize bare soil, and installing stone lines along contours to reduce runoff.Soil Erosion and Conservation
Soil Erosion and ConservationAisling O Connor
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion, its causes, effects, and methods for prevention. It covers:
- Natural and human-caused soil erosion, with the latter including overcropping, overgrazing, and deforestation.
- Problems from erosion like loss of topsoil and declining plant productivity.
- A case study on erosion and desertification in Africa's Sahel region exacerbated by climate change.
- Conservation methods like windbreaks, contour plowing, stubble planting, terraces, and stone walls.Ad
Similar to Powerpoint presentation of jelmarie (20)
SOIL EROSION
SOIL EROSIONthanianu92
Ěý
Soil erosion is the displacement of topsoil from its original location. It occurs naturally but can be exacerbated by certain human activities like deforestation, farming practices, lack of vegetation, and wind. The erosion process involves three steps: detachment of topsoil, movement of topsoil to another area, and deposition of topsoil in the new area. Major causes of soil erosion include rain and rainwater runoff, farming, slope of the land, lack of vegetation, and wind. Effects of soil erosion are loss of fertile topsoil, soil compaction, reduced organic and fertile matter, and issues with plant reproduction. Solutions to soil erosion include careful tilling, crop rotation, strip farming, shelter belts, contour plSOIL EROSION.pptx
SOIL EROSION.pptxtushar575020
Ěý
Soil erosion is the natural process of topsoil removal caused by wind and water, influenced by both natural occurrences and human activities, particularly poor farming practices. Key factors include strong winds, climate change, heavy rainfall, and wildfires, which can exacerbate erosion. Types of soil erosion include water erosion, which occurs after rainfall or flooding, and is categorized further based on the severity and causes.Soil erosion
Soil erosionTaseerBaloch1
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, its causes, types, and effects. It defines soil erosion as the process by which soil is removed by agents like wind and water. The main causes are identified as deforestation, running water, overgrazing, faulty agriculture practices like improper plowing, over irrigation, and wind. The types of erosion are wind erosion, where soil particles are removed and transported by wind, and water erosion, where rain and runoff remove soil. Key effects listed are loss of arable land, water and air pollution, damage to infrastructure and aquatic systems, and desertification.soil erosion and its causes .pptx
soil erosion and its causes .pptxSanskriti Kumari
Ěý
Sanskriti Kumari presented on the topic of soil erosion and its causes. She discussed the different types of soil erosion including water erosion, wind erosion, and mass movement. Water erosion can occur through splash erosion, sheet erosion, rill erosion, gully erosion, ravine erosion, and more. Wind erosion moves soil particles through surface creep, saltation, and suspension. Mass movement includes processes like creep, landslides, debris flows, and mudflows. The causes of soil erosion include soil erodibility, slope, climate, rainfall, deforestation, farming practices, and more. Long-term soil erosion degrades soil fertility and productivity by reducing topsoil thickness, rooting depth, and soil nutrient levels.Soil Erosion Defination causes effects .pptx
Soil Erosion Defination causes effects .pptxNarayanRimal2
Ěý
Soil erosion is the process by which the top layer of soil is worn away by water, wind, or tillage. It occurs naturally but human activities like agriculture, grazing, logging, and mining have accelerated the process. Soil erosion reduces soil fertility and can lead to loss of arable land, pollution of waterways, air pollution, and desertification if left unchecked. Methods to prevent soil erosion include planting trees, adding mulch, using fibre logs, and improving drainage systems.Soil Erosion
Soil Erosion KristinaClarke6
Ěý
This document discusses soil erosion, defining it as the process by which soil particles are carried away from one area and deposited in another by water or wind. It differentiates between natural soil erosion, which occurs in undisturbed environments due to running water, landslides, winds, or waves, and accelerated erosion caused by human activities like burning vegetation, overgrazing, deforestation, mining, unsuitable farming practices, and over-weeding. Specific types of erosion caused by water and wind are described, as well as their effects like loss of topsoil, silting of waterways, and alluvial deposits.Soil Erosion FOR EARTH SCIENCE EEEYY.pptx
Soil Erosion FOR EARTH SCIENCE EEEYY.pptxJohnCarloCerico
Ěý
The document outlines the causes, effects, and types of soil erosion, detailing both natural and human-induced factors that contribute to this environmental issue. It discusses various erosion types, including water, wind, and glacial erosion, and emphasizes the significant impacts on soil fertility, water quality, and food security. Solutions for mitigating soil erosion, such as conservation practices and land management strategies, are also presented, alongside the importance of education and policy in promoting sustainable practices.CAUSES OF SOIL EROSIONxnxx xhamster pornhub bangbross naughtyamerica.pptx
CAUSES OF SOIL EROSIONxnxx xhamster pornhub bangbross naughtyamerica.pptxSuvendu Rinku
Ěý
Soil erosion is the process of detachment, transportation, and deposition of soil particles, primarily caused by wind and water. It can be classified into geological and accelerated erosion, with various agents such as water, wind, and gravity contributing to the phenomenon. Factors affecting soil erosion include deforestation, overgrazing, and climatic conditions, making it a complex problem that requires careful management.soil-erosion.pptx pls read this thank ii
soil-erosion.pptx pls read this thank iitpsskzjyvr
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, defining it as the natural process where topsoil is removed by wind and water, exacerbated by human activities like agriculture and deforestation. It outlines the causes of soil erosion, including rainfall, construction, and agricultural practices, and highlights its detrimental effects such as loss of arable land, pollution, and desertification. Prevention methods are also suggested, including tree planting and proper drainage systems to mitigate erosion impacts.Soil erosion-History, distribution, identification, forms, impact of soil ero...
Soil erosion-History, distribution, identification, forms, impact of soil ero...Annappa N N
Ěý
The document discusses the history and distribution of soil erosion globally and in India. It describes common forms of soil erosion such as water erosion, wind erosion, and mass movement. Key indicators for identifying soil erosion are mentioned, such as eroded soil, gullies, sedimentation, and loss of topsoil. The impacts of soil erosion include reduced soil fertility, increased flooding, and water pollution. Strategies to control erosion include terracing, contour plowing, cover cropping, check dams, and reforestation.Erosion
ErosionEclud Sugar
Ěý
Erosion is the process through which Earth's surface is worn down by natural forces like water, wind, and ice, with human activities exacerbating the issue significantly. Both water and wind erosion can be accelerated by factors like soil structure, vegetation cover, and slope gradient, leading to various types of soil degradation, including gully and bank erosion. Preventive measures, such as planting vegetation, using matting, and constructing retaining walls, can help mitigate soil erosion and maintain soil health.soil erosion.pptx
soil erosion.pptxChandu471547
Ěý
This document discusses the causes and effects of soil erosion. The main causes are rainfall, agriculture, grazing, logging, mining, construction, and wind. Intense rainfall causes four types of erosion: rill, gully, sheet, and splash. Farming, grazing, deforestation, and mining disturb soil structures. Effects include loss of arable land, pollution of waterways, air pollution, desertification, and damaged infrastructure. Preventing soil erosion requires planting vegetation, adding mulch and rocks, using matting, and installing drainage systems.Soil Erosion, Agents_Favorite report.pptx
Soil Erosion, Agents_Favorite report.pptxjersondeligero26
Ěý
Soil erosion is the displacement of the upper soil layer caused by natural agents such as water, air, and human activities, particularly through farming and land clearing. It leads to decreased fertility, increased pollution, and can cause flooding due to degraded lands. Preventative methods include replanting trees, using protective materials in vulnerable areas, and stopping illegal logging and mining.Soil revitalization.pptx
Soil revitalization.pptxSumitBhatia69
Ěý
This document discusses soil revitalization and soil erosion. It defines soil and describes its composition and textures. It then lists the major causes of soil erosion, including rainfall, agriculture, grazing, logging, construction, rivers and streams, and wind. The effects of soil erosion are outlined as the loss of arable land, air pollution, desertification, and destruction of infrastructure. Methods for preventing soil erosion include planting trees, adding mulch and rocks, using matting and fibre logs, and improving drainage systems.Eroded soil
Eroded soilKaminiKumari13
Ěý
Eroded soils and their reclamation is discussed. Soil erosion is defined as the detachment and transportation of soil mass from one place to another through the action of wind, water, or rain drops. In India, 86.9% of soil erosion is caused by water and 17.7% by wind. Erosion reduces soil nutrients and crop yields. Various types of erosion like sheet, rill, gully and stream bank erosion are explained. Best management practices to control erosion include crop rotation, contour cultivation, strip cropping, terraces, grassed waterways, and no-till planting.Geography grade 11 soil erosion presentation
Geography grade 11 soil erosion presentationsiyamkhonza08
Ěý
The document discusses soil erosion, defined as the removal of the fertile top layer of soil due to water, wind, or ice. It outlines various causes including water erosion, wind erosion, mass wasting, overgrazing, and deforestation, along with the impacts such as poor soil quality, pollution, and habitat loss. Additionally, it suggests management strategies like afforestation to combat soil erosion.Erosion definition and types of erosion .ppt
Erosion definition and types of erosion .pptAfnanAhmad53
Ěý
Erosion is the process of soil particles being removed by natural forces such as water and wind, which decreases soil productivity. Human activities like agriculture and deforestation accelerate erosion, leading to ecological deterioration and topsoil loss. There are several types of erosion, including splash or raindrop erosion, gully erosion, sheet erosion, and rill erosion, each with distinct characteristics.A research paper on soil erosion, including definition, types, causes, effect...
A research paper on soil erosion, including definition, types, causes, effect...elizabethnarinemiaic
Ěý
This PowerPoint presentation explores the topic of Soil Erosion, focusing on its causes, types, effects, and prevention methods. It provides a clear explanation of how natural elements like water and wind contribute to the wearing away of topsoil, as well as how human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, and poor farming practices speed up the process. The presentation also highlights the environmental and economic impacts of soil erosion, particularly in agriculture and land degradation. Solutions such as reforestation, contour plowing, and sustainable land management practices are also discussed. This presentation aims to raise awareness and promote strategies to reduce soil erosion and protect our natural resources.A research paper on soil erosion, including definition, types, causes, effect...
A research paper on soil erosion, including definition, types, causes, effect...elizabethnarinemiaic
Ěý
Ad
Powerpoint presentation of jelmarie
- 1. The Soil ErosionJelmarie Cerillo VelacruzAb English Language II
- 2. What is Soil Erosion?Loss and displacement of earths fertile topsoilSoil is naturally removed by the action of water or wind: such 'background' (or 'geological') soil erosion has been occurring for some 450 million years
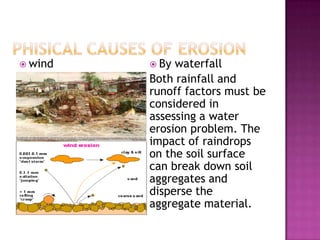
- 3. Phisical Causes of ErosionwindBy waterfallBoth rainfall and runoff factors must be considered in assessing a water erosion problem. The impact of raindrops on the soil surface can break down soil aggregates and disperse the aggregate material.
- 4. Manifestation of Human ActsCausing Soil ERosionDeforestionOvergazingOver cropping
- 5. Principal Effect Of Soil ErosionDeterioration of agricultural lands.Increase of flood occurence.Reduce Water supplySintatics of reservoirs canals and rivers.Destruction of blags roads, and public works.Depletion of wild life and other natural resources.
- 6. Activities Of ManContributing to soil Erosion and disruption of earth surface
- 9. Urbanization
- 10. Disruption of LandscapeSurface MiningStrip mining
- 11. ConclusionBecause of continued advances in soil management and crop production technology that have maintained or increased yields in spite of soil erosion, others have not been aware of the increasing problem on farmland. Awareness usually occurs only when property is damaged and productive areas of soil are lost.
- 12. Additional KnowledgeThe implications of soil erosion extend beyond the removal of valuable topsoil. Crop emergence, growth and yield are directly affected through the loss of natural nutrients and applied fertilizers with the soil.Soil quality, structure, stability and texture can be affected by the loss of soil