states_of_matter.ppt
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes4 views
This document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It provides descriptions of each state in terms of the particle arrangement, energy, and distance between particles. Solids have particles that are tightly packed and vibrate in a fixed position. Liquids also have tightly packed particles that can slide over one another. Gas particles are very far apart and move freely. Plasma is an ionized gas that is affected by magnetic fields and is the most common state of matter at extremely high temperatures. Examples of where plasma can be found include flames, lightning, auroras, and inside stars like the Sun.
1 of 20
Download to read offline












Recommended
states_of_matter 1.pptx
states_of_matter 1.pptxMawandaJohn1
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the key properties of each state, including the arrangement and movement of particles. Solids have particles that vibrate in a fixed position, while liquids have particles that can slide past one another. Gas particles are far apart and move freely. Plasma is an ionized gas where particles are electrically charged. Phase changes between the different states are also outlined, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. Examples of where plasmas can be found naturally are given, such as flames, lightning, and auroras.States of matter
States of matterSoha Bedair
╠²
There are four states of matter: solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. In solids, particles are tightly packed in a fixed position and vibrate. Liquids also have tightly packed particles that can slide over one another. Gas particles are far apart and move freely. Plasma is the fourth state of matter where particles are ionized, conduct electricity, and are affected by magnetic fields. Plasma has no definite shape or volume and is found at extremely high temperatures in places like flames, lightning, auroras, and stars like the sun.States of matter
States of matterjayson castrence
╠²
The document describes the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, each defined by particle arrangement, energy, and distance. It outlines the characteristics of each state, such as solids having a definite shape and volume, while gases have neither. Additionally, it details phase changes like melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation, along with the unique properties of plasma as an ionized gas.NLC- Week 5- MATTER.ppt
NLC- Week 5- MATTER.pptFrenzDelaCruz2
╠²
There are four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. The state depends on how close or far apart the particles are and how much they are moving. Solids have particles that vibrate in a fixed position and maintain a definite shape and volume. Liquids have particles that slide over one another and have an indefinite shape but definite volume. Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely, having an indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that is affected by magnetic fields and is the most common state of matter at very high temperatures over 1000┬░C, found in flames, lightning, auroras, and stars like the Sun.Science 8- The State of Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas, Plasma)
Science 8- The State of Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas, Plasma)Jerome Pantig
╠²
The document outlines the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, detailing their particle arrangement, energy, and behavior. It explains how solids have a fixed shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but take an indefinite shape, gases have neither definite shape nor volume, and plasmas are ionized gases that are good conductors of electricity. Additionally, it describes phase changes, including melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation.states_of_matter. composition and classification
states_of_matter. composition and classificationNisbaRani2
╠²
The document outlines the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, describing their particle arrangement, energy, and volume properties. It also explains phase changes between these states, including melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation, highlighting the heat movement involved in each process. Additionally, the document notes that plasma, an ionized gas, displays unique characteristics like conductivity and is commonly found in phenomena such as flames and lightning.States of Matter: The Solid ,Liquid and Gas
States of Matter: The Solid ,Liquid and GasMelodinaAcain2
╠²
The document outlines the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, detailing their particle arrangement, energy, and volume characteristics. It also explains phase changes between these states, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation, as well as the unique properties of plasma. Additionally, it mentions some common occurrences of plasma, like flames and lightning.sdssssssssdeeeeeeedddssddtates_of_matter.ppt
sdssssssssdeeeeeeedddssddtates_of_matter.pptSunnyAmar
╠²
The document outlines the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, describing their particle arrangement, energy, and distances. It explains the kinetic theory of matter, detailing how each state behaves under different conditions and phase changes, like melting and vaporization. Additionally, it highlights characteristics of plasma, including its electrical conductivity and occurrence in natural phenomena like flames and lightning.states_of_matter.GRADE-5.POWERPOINT-----
states_of_matter.GRADE-5.POWERPOINT-----ShefaCapuras1
╠²
The document outlines the four primary states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, along with their characteristics based on particle arrangement, energy, and distance. It describes the kinetic theory of matter and various phase changes like melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation. Lastly, it explains that plasma is an ionized gas and provides examples of where plasma can be found, such as flames and the sun.States of Matter 2020
States of Matter 2020 alexsong2018
╠²
This document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It provides details on the characteristics of each state in terms of particle arrangement, energy, and distance between particles based on the kinetic theory of matter. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and definite shape/volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles that can slide over one another and have indefinite shape but definite volume. Gases have particles far apart that move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields with indefinite shape and volume. Phase changes between these states are also described.states_of_matter.four kinds of matter.ppt
states_of_matter.four kinds of matter.pptJOANBOBIS1
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the characteristics of each state in terms of particle arrangement, energy, and distance between particles. Solids have particles that vibrate in a fixed position and definite shape/volume. Liquids have particles that can slide over one another and have indefinite shape but definite volume. Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that is affected by magnetic fields and has no definite shape or volume. Examples of where plasma can be found include flames, lightning, auroras, and as the main state of the sun.States of Matters.pptx
States of Matters.pptxTesfayeTadesseGebrem
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the key characteristics of each state, including the arrangement and movement of particles. Solids have tightly packed and vibrating particles that give it a definite shape and volume, while liquids have particles that can slide over one another but still have a definite volume. Gas particles are far apart and move freely, resulting in indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is made of ionized gas particles that are affected by magnetic fields. The document also covers phase changes between states in terms of melting, freezing, and the movement of heat.States o matter
States o mattercnc12m
╠²
This document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the characteristics of each state and the phase changes between them. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, with particles tightly packed and vibrating. Liquids have indefinite shapes but fixed volumes, with particles able to slide past one another. Gases have indefinite shapes and volumes, with particles freely moving and far apart. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. The document gives examples of places where plasma is commonly found like flames, lightning, and as the main state of the sun.Phases of matter overview
Phases of matter overviewskaiser4800
╠²
Matter exists in four main states - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma - depending on the arrangement and energy of its particles. In solids, particles are tightly packed in a fixed position and vibrate; in liquids, particles are closely packed but can slide over one another; and in gases, particles are far apart and move freely. Plasma is an ionized gas in which particles are highly energized electrical charges that are affected by magnetic fields. Matter changes between these states through phase changes as it gains or loses heat energy, altering the distance and movement between its particles.Revised states of matter powerpoint
Revised states of matter powerpointMaria Donohue
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the key properties of each state, including how the particles are arranged and how they move. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position. Liquids also have tightly packed particles that can slide past one another. Gas particles are far apart and move freely. Plasma has electrically charged particles with no definite shape or volume. The document also provides links to online resources about phase changes and states of matter.LESSON 1 STATES OF MATTER. matter is often taken to mean anything composed of...
LESSON 1 STATES OF MATTER. matter is often taken to mean anything composed of...mahathersilungan
╠²
The atom is the ŌĆ£building block of matterŌĆØ.
All substances are composed of invisible particles called atoms.
Atoms are the building blocks of matter and are in constant motion.
The combination of atoms leads to millions of materials with different properties.
LETS LEARN ABOUT THE DIFFERENT STATES OF MATTER
LETS LEARN ABOUT THE DIFFERENT STATES OF MATTERMarkChristianPatrici
╠²
The document outlines the five states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensate, emphasizing their particle arrangement and energy. It describes the characteristics of each state, including how particles behave and the unique properties they exhibit. Additionally, the document explains phase changes and the heat movement involved in transitions between states.States of Matter
States of Matter Cicces20
╠²
There are four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. The document then provides details about each state: solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in place, liquids have particles that can slide over one another but maintain a definite volume, gases have particles that are far apart and move freely with indefinite volume and shape. Plasma is described as an ionized gas where particles are electrically charged and affected by magnetic fields with indefinite volume and shape. Examples of places where plasma can be found are flames, lightning, auroras, and as the main state of the sun.Matter and phase changes
Matter and phase changes NeilfieOrit1
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma - and phase changes between states. It describes the particle behavior and properties of each state. Solids have a definite shape and volume, with particles tightly packed in a regular pattern that vibrate in place. Liquids have a definite volume that takes the shape of their container, with particles close together that can slide past one another. Gases have no definite shape or volume, with particles well separated and moving freely at high speeds. Plasma is similar to gas but with electrically charged particles. Phase changes are physical changes between these states that involve the absorption or release of heat energy as particles speed up and move farther apart or slow down and moveStates of matter_def
States of matter_defabascalcursotic
╠²
There are five states of matter: solids, liquids, gases, plasmas, and Bose-Einstein condensates. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and definite shape and volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles, but they can slide over one another and have indefinite shape but definite volume. Gases have particles far apart that move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasmas are ionized gases that conduct electricity and are affected by magnetic fields. Bose-Einstein condensates occur at temperatures near absolute zero where atoms can no longer be distinguished as individuals and must act identically.states_of_matter_ppt__2_.ppt
states_of_matter_ppt__2_.pptSasiLavisetty
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position, while liquids have particles that can slide past one another but maintain a definite volume. Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas with high energy electrical charged particles and no definite shape. Examples of different states of matter are also provided.States of matter
States of matterjdrin001
╠²
There are four main states of matter: solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and have a definite shape and volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles, but they can slide over one another, giving liquids an indefinite shape but definite volume. Gas particles are far apart, move freely, and have indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields, also having indefinite shape and volume. The document then provides examples of each state.Presentation2
Presentation2venilohidas
╠²
There are four main states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and have a definite shape and volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles, but they can slide over one another and only have a definite volume. Gas particles are far apart, move freely, and have indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Matter can change states through melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation which involve the addition or removal of heat.grade_ 6_---states_of_matter_ppt__2_.ppt
grade_ 6_---states_of_matter_ppt__2_.pptShefaCapuras1
╠²
The document explains the concept of matter, which has mass and occupies space, and is made up of atoms. It discusses the four primary states of matterŌĆösolids, liquids, gases, and plasmaŌĆöalong with their properties and phase changes. The document also covers the laws of conservation of matter and mass, emphasizing that matter can change forms but cannot be created or destroyed.States of matter 2013
States of matter 2013sciencenerd42 McCarthy
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the characteristics of each state in terms of particle arrangement, energy, and distance between particles. Solids have a definite shape and volume, with particles in a tight, regular pattern. Liquids have a definite volume but no shape, with particles farther apart than solids but still not moving freely. Gases have no definite shape or volume, with particles much farther apart and moving freely at high speeds. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. It has an indefinite shape and volume like gases. The document provides examples of different phase changes between states of matter and natural occurrences offormative assessment ppt in science 7 first quarter
formative assessment ppt in science 7 first quarterjozettezamora2
╠²
The document contains 5 multiple choice questions about solutions and their components. Question 1 asks about the universal solvent, with water being the answer. Question 2 asks about the term for a solute's ability to dissolve in a solvent, with solubility being the answer. Question 3 asks about the component being dissolved in a solution, with solute being the answer. Question 4 asks about the substance that dissolves other materials, with solvent being the answer. Question 5 asks which description does not apply to a solution, with cannot pass through light being the exception.Types of Solutions Applied Chemistry 9__
Types of Solutions Applied Chemistry 9__jozettezamora2
╠²
This document provides information about solutions, including their components and types. It defines a solution as a homogeneous mixture of two or more components where the particle size is smaller than 1 nm. The main components are the solute, which is being dissolved, and the solvent, which dissolves the other component. Solutions can be classified as gaseous, liquid, or solid depending on the phase of the components. They can also be described as dilute or concentrated based on the relative amounts of the components. Several examples of different types of solutions are provided.ionic bond_transfer of electron_science 9.pptx
ionic bond_transfer of electron_science 9.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The document provides an overview of a lesson on ionic bonding. It includes activities, such as a mystery item activity where students will answer clues to find a hidden item. It discusses how ions are formed through the transfer of electrons from metal to non-metal atoms. Diagrams are used to illustrate ion formation. Tables are included to compare data. The document emphasizes that not all metals and non-metals form ionic bonds, and that electronegativity must be considered. It reviews concepts and includes additional presentation resources like timelines, roadmaps, and matrices.More Related Content
Similar to states_of_matter.ppt (19)
States of Matter: The Solid ,Liquid and Gas
States of Matter: The Solid ,Liquid and GasMelodinaAcain2
╠²
The document outlines the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, detailing their particle arrangement, energy, and volume characteristics. It also explains phase changes between these states, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation, as well as the unique properties of plasma. Additionally, it mentions some common occurrences of plasma, like flames and lightning.sdssssssssdeeeeeeedddssddtates_of_matter.ppt
sdssssssssdeeeeeeedddssddtates_of_matter.pptSunnyAmar
╠²
The document outlines the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, describing their particle arrangement, energy, and distances. It explains the kinetic theory of matter, detailing how each state behaves under different conditions and phase changes, like melting and vaporization. Additionally, it highlights characteristics of plasma, including its electrical conductivity and occurrence in natural phenomena like flames and lightning.states_of_matter.GRADE-5.POWERPOINT-----
states_of_matter.GRADE-5.POWERPOINT-----ShefaCapuras1
╠²
The document outlines the four primary states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, along with their characteristics based on particle arrangement, energy, and distance. It describes the kinetic theory of matter and various phase changes like melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation. Lastly, it explains that plasma is an ionized gas and provides examples of where plasma can be found, such as flames and the sun.States of Matter 2020
States of Matter 2020 alexsong2018
╠²
This document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It provides details on the characteristics of each state in terms of particle arrangement, energy, and distance between particles based on the kinetic theory of matter. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and definite shape/volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles that can slide over one another and have indefinite shape but definite volume. Gases have particles far apart that move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields with indefinite shape and volume. Phase changes between these states are also described.states_of_matter.four kinds of matter.ppt
states_of_matter.four kinds of matter.pptJOANBOBIS1
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the characteristics of each state in terms of particle arrangement, energy, and distance between particles. Solids have particles that vibrate in a fixed position and definite shape/volume. Liquids have particles that can slide over one another and have indefinite shape but definite volume. Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that is affected by magnetic fields and has no definite shape or volume. Examples of where plasma can be found include flames, lightning, auroras, and as the main state of the sun.States of Matters.pptx
States of Matters.pptxTesfayeTadesseGebrem
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the key characteristics of each state, including the arrangement and movement of particles. Solids have tightly packed and vibrating particles that give it a definite shape and volume, while liquids have particles that can slide over one another but still have a definite volume. Gas particles are far apart and move freely, resulting in indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is made of ionized gas particles that are affected by magnetic fields. The document also covers phase changes between states in terms of melting, freezing, and the movement of heat.States o matter
States o mattercnc12m
╠²
This document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the characteristics of each state and the phase changes between them. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, with particles tightly packed and vibrating. Liquids have indefinite shapes but fixed volumes, with particles able to slide past one another. Gases have indefinite shapes and volumes, with particles freely moving and far apart. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. The document gives examples of places where plasma is commonly found like flames, lightning, and as the main state of the sun.Phases of matter overview
Phases of matter overviewskaiser4800
╠²
Matter exists in four main states - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma - depending on the arrangement and energy of its particles. In solids, particles are tightly packed in a fixed position and vibrate; in liquids, particles are closely packed but can slide over one another; and in gases, particles are far apart and move freely. Plasma is an ionized gas in which particles are highly energized electrical charges that are affected by magnetic fields. Matter changes between these states through phase changes as it gains or loses heat energy, altering the distance and movement between its particles.Revised states of matter powerpoint
Revised states of matter powerpointMaria Donohue
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the key properties of each state, including how the particles are arranged and how they move. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position. Liquids also have tightly packed particles that can slide past one another. Gas particles are far apart and move freely. Plasma has electrically charged particles with no definite shape or volume. The document also provides links to online resources about phase changes and states of matter.LESSON 1 STATES OF MATTER. matter is often taken to mean anything composed of...
LESSON 1 STATES OF MATTER. matter is often taken to mean anything composed of...mahathersilungan
╠²
The atom is the ŌĆ£building block of matterŌĆØ.
All substances are composed of invisible particles called atoms.
Atoms are the building blocks of matter and are in constant motion.
The combination of atoms leads to millions of materials with different properties.
LETS LEARN ABOUT THE DIFFERENT STATES OF MATTER
LETS LEARN ABOUT THE DIFFERENT STATES OF MATTERMarkChristianPatrici
╠²
The document outlines the five states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensate, emphasizing their particle arrangement and energy. It describes the characteristics of each state, including how particles behave and the unique properties they exhibit. Additionally, the document explains phase changes and the heat movement involved in transitions between states.States of Matter
States of Matter Cicces20
╠²
There are four states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. The document then provides details about each state: solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in place, liquids have particles that can slide over one another but maintain a definite volume, gases have particles that are far apart and move freely with indefinite volume and shape. Plasma is described as an ionized gas where particles are electrically charged and affected by magnetic fields with indefinite volume and shape. Examples of places where plasma can be found are flames, lightning, auroras, and as the main state of the sun.Matter and phase changes
Matter and phase changes NeilfieOrit1
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma - and phase changes between states. It describes the particle behavior and properties of each state. Solids have a definite shape and volume, with particles tightly packed in a regular pattern that vibrate in place. Liquids have a definite volume that takes the shape of their container, with particles close together that can slide past one another. Gases have no definite shape or volume, with particles well separated and moving freely at high speeds. Plasma is similar to gas but with electrically charged particles. Phase changes are physical changes between these states that involve the absorption or release of heat energy as particles speed up and move farther apart or slow down and moveStates of matter_def
States of matter_defabascalcursotic
╠²
There are five states of matter: solids, liquids, gases, plasmas, and Bose-Einstein condensates. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and definite shape and volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles, but they can slide over one another and have indefinite shape but definite volume. Gases have particles far apart that move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasmas are ionized gases that conduct electricity and are affected by magnetic fields. Bose-Einstein condensates occur at temperatures near absolute zero where atoms can no longer be distinguished as individuals and must act identically.states_of_matter_ppt__2_.ppt
states_of_matter_ppt__2_.pptSasiLavisetty
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position, while liquids have particles that can slide past one another but maintain a definite volume. Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely with indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas with high energy electrical charged particles and no definite shape. Examples of different states of matter are also provided.States of matter
States of matterjdrin001
╠²
There are four main states of matter: solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and have a definite shape and volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles, but they can slide over one another, giving liquids an indefinite shape but definite volume. Gas particles are far apart, move freely, and have indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields, also having indefinite shape and volume. The document then provides examples of each state.Presentation2
Presentation2venilohidas
╠²
There are four main states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Solids have tightly packed particles that vibrate in a fixed position and have a definite shape and volume. Liquids also have tightly packed particles, but they can slide over one another and only have a definite volume. Gas particles are far apart, move freely, and have indefinite shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Matter can change states through melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation which involve the addition or removal of heat.grade_ 6_---states_of_matter_ppt__2_.ppt
grade_ 6_---states_of_matter_ppt__2_.pptShefaCapuras1
╠²
The document explains the concept of matter, which has mass and occupies space, and is made up of atoms. It discusses the four primary states of matterŌĆösolids, liquids, gases, and plasmaŌĆöalong with their properties and phase changes. The document also covers the laws of conservation of matter and mass, emphasizing that matter can change forms but cannot be created or destroyed.States of matter 2013
States of matter 2013sciencenerd42 McCarthy
╠²
The document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. It describes the characteristics of each state in terms of particle arrangement, energy, and distance between particles. Solids have a definite shape and volume, with particles in a tight, regular pattern. Liquids have a definite volume but no shape, with particles farther apart than solids but still not moving freely. Gases have no definite shape or volume, with particles much farther apart and moving freely at high speeds. Plasma is an ionized gas that conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. It has an indefinite shape and volume like gases. The document provides examples of different phase changes between states of matter and natural occurrences ofMore from jozettezamora2 (20)
formative assessment ppt in science 7 first quarter
formative assessment ppt in science 7 first quarterjozettezamora2
╠²
The document contains 5 multiple choice questions about solutions and their components. Question 1 asks about the universal solvent, with water being the answer. Question 2 asks about the term for a solute's ability to dissolve in a solvent, with solubility being the answer. Question 3 asks about the component being dissolved in a solution, with solute being the answer. Question 4 asks about the substance that dissolves other materials, with solvent being the answer. Question 5 asks which description does not apply to a solution, with cannot pass through light being the exception.Types of Solutions Applied Chemistry 9__
Types of Solutions Applied Chemistry 9__jozettezamora2
╠²
This document provides information about solutions, including their components and types. It defines a solution as a homogeneous mixture of two or more components where the particle size is smaller than 1 nm. The main components are the solute, which is being dissolved, and the solvent, which dissolves the other component. Solutions can be classified as gaseous, liquid, or solid depending on the phase of the components. They can also be described as dilute or concentrated based on the relative amounts of the components. Several examples of different types of solutions are provided.ionic bond_transfer of electron_science 9.pptx
ionic bond_transfer of electron_science 9.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The document provides an overview of a lesson on ionic bonding. It includes activities, such as a mystery item activity where students will answer clues to find a hidden item. It discusses how ions are formed through the transfer of electrons from metal to non-metal atoms. Diagrams are used to illustrate ion formation. Tables are included to compare data. The document emphasizes that not all metals and non-metals form ionic bonds, and that electronegativity must be considered. It reviews concepts and includes additional presentation resources like timelines, roadmaps, and matrices.Divergence of Plates.pptx
Divergence of Plates.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
This document discusses divergent plate boundaries and the processes that occur at them. It describes how divergent boundaries form as plates move away from each other, causing rifting and seafloor spreading. This creates mid-ocean ridges and pulls the crust thin, causing it to crack and form new crust. Over millions of years, this spreading causes the separation of land masses and widening of oceans. Common features at divergent boundaries include mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, and volcanic fissures.hyothesis.pptx
hyothesis.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The document provides instructions for an activity to teach students about formulating hypotheses. It involves using a paper boat in a glass of water and adding paper clips to test how many it takes to sink the boat. Students are asked to make hypotheses predicting how many clips it will take based on observations. The document also discusses the scientific method steps and defines a hypothesis as a testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It identifies the three major types of hypotheses and provides examples to help students distinguish between null, alternative, and causal hypotheses.7_percent mass_concentration.pptx
7_percent mass_concentration.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The concentration of a solution refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent. It can be expressed as a percentage by mass by taking the ratio of the mass of the solute to the total mass of the solution and multiplying by 100. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating concentration as a percentage by mass using various masses of solutes and solvents in solutions.science 7_1.pptx
science 7_1.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
Here is a potential scientific investigation following the scientific method to solve the problem of a light bulb not turning on when the switch is flipped:
1. OBSERVATION: I noticed that when I flip the light switch in my room, the light bulb does not turn on.
2. QUESTION: Why does the light bulb not turn on when I flip the switch?
3. HYPOTHESIS: If there is a loose wire connecting the light bulb to the switch, then the light bulb will not receive electricity and not turn on when the switch is flipped.
4. EXPERIMENT: I will check the wiring connecting the light bulb to the switch for any loose or disconnected wires. I will also test theBiomolecules ppt.pptx
Biomolecules ppt.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The document defines biomolecules as organic compounds made by living things that are categorized into four main types: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It provides details on the structure, functions, and examples of each type of biomolecule. Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and include sugars and starches. Lipids, such as fats and oils, contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and are used to store energy. Proteins are made of amino acids and have a variety of structures that determine their functions, such as enzymes. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA contain genetic information and direct protein synthesis.notes-acidsandbases-130210121114-phpapp02.pptx
notes-acidsandbases-130210121114-phpapp02.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
Acids and bases are characterized by their ability to release hydrogen or hydroxide ions in water. Acids release H+ ions and have a sour taste, react with carbonates and metals, and contain hydrogen. Bases release OH- ions and have a bitter taste, feel slippery, and contain hydroxide. The strength of acids and bases is measured by pH, with lower values indicating more H+ ions and higher values indicating more OH- ions. Acid-base indicators change color based on pH and can be used to determine if a solution is acidic or basic. When an acid and base are combined, they neutralize through a reaction that produces a salt and water.particle nature of matter.pptx
particle nature of matter.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms, which are the smallest particles that make up elements and consist of even smaller particles. Democritus originally coined the term "atom" to refer to particles he believed could not be divided further, though we now know atoms can be broken down into other subatomic particles. The document provides a multiple choice quiz about atoms and particle nature of matter.week 5_7CHARGES-AND-MASSES.pptx
week 5_7CHARGES-AND-MASSES.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
This document provides an overview of the subatomic particles that make up atoms, including electrons, protons, and neutrons. It discusses their locations and charges. Key points include:
- Electrons are negatively charged and located outside the nucleus.
- Protons are positively charged and located within the nucleus.
- Neutrons have no charge and are also located within the nucleus.
- Atoms are neutral when they have an equal number of protons and electrons.
The document contains questions to test the reader's understanding of these concepts.percentage composition.pptx
percentage composition.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The document discusses how fireworks produce different colors. Potassium nitrate, sulfur, and charcoal produce gunpowder when mixed and heated, creating an explosion. To produce fireworks, this gunpowder mixture is placed on canes. Originally, potassium nitrate produced a white color, but using different metal salts as cations produces different colors - strontium produces red, iron produces gold, sodium produces yellow, barium produces green, and copper produces blue.covalent.pptx
covalent.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable outer electron configuration. Nonpolar covalent bonds occur when atoms share electrons equally, while polar covalent bonds form when electrons are shared unequally between atoms of different electronegativity. The document discusses how to explain and illustrate the formation of covalent bonds through examples of nonpolar and polar covalent bonds.maater n non matter.pptx
maater n non matter.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The document discusses distinguishing between matter and non-matter. Matter is defined as objects that possess mass and take up physical space, while non-matter refers to concepts and things that do not have mass or occupy space, such as various forms of energy. Readers are tasked with classifying examples as matter or non-matter and identifying properties of matter, such as mass and the space it occupies.Bohr-Diagram-lesson.ppt
Bohr-Diagram-lesson.pptjozettezamora2
╠²
Niels Bohr proposed the Bohr model of the atom in 1913 to explain the unique emission spectra of elements. In the Bohr model, electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed, quantized energy levels. When excited, electrons jump to higher orbits and release energy in the form of light when falling back to lower orbits. The model successfully explained experimental observations but was later replaced by more accurate quantum mechanical models.sci 7 st 4.pptx
sci 7 st 4.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
This document contains a series of multiple choice questions about elements, compounds, and mixtures. It tests the understanding of:
1) The definitions of elements, compounds, and mixtures and whether they can be broken down into simpler substances.
2) Examples of compounds like carbon dioxide, sodium chloride, sugar, and salts.
3) Whether pairs like water (H and O), salt (Na and Cl), carbon dioxide (C and O), and magnesium chloride (Mg and Cl) are correctly identified as compounds or elements.
4) Whether natural gas is a mixture or substance based on its composition of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
5) Methods to separate mixtures like decantation and ways to identify a substance as a7_sept 12_concentration_jupiter.pptx
7_sept 12_concentration_jupiter.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The concentration of a solution refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent. It can be expressed as a percentage by mass by taking the ratio of the mass of solute over the total mass of the solution and multiplying by 100. Examples are provided for calculating the concentration of NaCl in a solution and the percentage composition by mass of a solution containing oxygen and helium.7_sept 12_concentration.pptx
7_sept 12_concentration.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The concentration of a solution refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent. It can be expressed as a percentage by mass by taking the ratio of the mass of the solute to the total mass of the solution and multiplying by 100. Common examples provided calculate the concentration of solutions based on the given masses of solute and solvent/solution.factors affecting solubility.pptx
factors affecting solubility.pptxjozettezamora2
╠²
The document outlines a daily task and lesson plan to teach students about the factors that affect solubility. The teacher will demonstrate how different factors like temperature, pressure, particle size, stirring, and concentration impact solubility. Students will learn through a teacher demonstration, group activities at stations, and a review of concentrations and key questions about what influences solubility.Recently uploaded (20)
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docx
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docxjunefermunez
╠²
Quiz for the topic Digestive System. 4th QaurterGBSN_Unit 3 - Medical and surgical Asepsis
GBSN_Unit 3 - Medical and surgical AsepsisAreesha Ahmad
╠²
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025
Role of Glutamate, glutamine and Alanine in Transport of Ammonia in Tissues
Role of Glutamate, glutamine and Alanine in Transport of Ammonia in TissuesTayyab
╠²
This slide explains the roles of Glutamate, Glutamine, and Alanine in safely transporting toxic ammonia from tissues to the liver and kidneys, where it is detoxified or excreted."The scientific heritage No 162 (162) (2025)
The scientific heritage No 162 (162) (2025)The scientific heritage
╠²
The scientific heritage No 162 (162) (2025)Operationalising OGC Processes with Application Packages in ILIAD: A Service ...
Operationalising OGC Processes with Application Packages in ILIAD: A Service ...Marco Amaro Oliveira
╠²
This contribution presents the integration of the EO Application Package model into the ILIAD Digital Twin of the Ocean architecture, using the OGC API Processes DRU specification. Built on the EOEPCA framework and OGC best practices and specifications, the approach enables standardized, containerized EO applications packaged with CWL to run across a wide range of infrastructures including Kubernetes and HPC. These applications are already in use across several platforms, and in ILIAD they have been applied to models such as oil spill forecasting, aquaculture, wave energy, and ship routing.
The EDITO platform supports OGC API Processes but is currently optimized for simpler workflows using environment variables. To enhance compatibility with EO Application Packages, ILIAD introduces a Kubernetes-based ADES implementation, enabling dynamic execution and integration with EDITO's object store and metadata catalog. The experience is also informing the evolution of the OGC Best Practice, and practical solutions for bridging architectural gaps will be discussed.Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performance
Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performancevschiavoni
╠²
Best Student Paper Award at ACM DEBS 2025.
Paper here:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3701717.3730540
Since blockchains are increasingly adopted in real-world applications, it is of paramount importance to evaluate their performance across diverse scenarios. Although the network infrastructure plays a fundamental role, its impact on performance remains largely unexplored. Some studies evaluate blockchain in cloud environments, but this approach is costly and difficult to reproduce. We propose a cost-effective and reproducible environment that supports both cluster-based setups and emulation capabilities and allows the underlying network topology to be easily modified. We evaluate five industry-grade blockchains ŌĆō Algorand, Diem, Ethereum, Quorum, and Solana ŌĆō across five network topologies ŌĆō fat-tree, full mesh, hypercube, scale-free, and torus ŌĆō and different realistic workloads ŌĆō smart contract requests and transfer transactions. Our benchmark framework, Lilith, shows that full mesh, hypercube, and torus topologies improve blockchain performance under heavy workloads. Algorand and Diem perform consistently across the considered topologies, while Ethereum remains robust but slower.Death in Sleep Apnea: Who and How It Kills
Death in Sleep Apnea: Who and How It KillsRichard Castriotta
╠²
Evaluation of mortality in obstructive sleep apnea.Synthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatin
Synthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatinProfessional Content Writing's
╠²
Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted isatin have attracted significant interest due to their wide-ranging applications in medicinal chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. These compounds exhibit diverse biological activities, making them promising drug candidates, while their unique chemical structures offer potential in designing advanced functional materials. This presentation focuses on the synthesis and characterization of these derivatives through targeted chemical reactions involving various substituents on the isatin and thiazole cores, enabling the fine-tuning of their biological and physical properties. Characterization techniques such as NMR, FT-IR, Mass Spectrometry, and X-ray crystallography are employed to confirm molecular structures and analyze solid-state properties. These methods provide critical insights into the structureŌĆōactivity relationships of the synthesized compounds. Our presentation highlights the synthetic pathways, structural elucidation, and potential applications of thiazole-based N-substituted isatin derivatives, aiming to support ongoing advancements in drug discovery and material development.
About Author:
Noor Zulfiqar is an award-winning chemist, Premium member of American Chemical Society (ACS), certified publisher & peer reviewer, and an experienced academic lecturer. As a professional content creator, she offers top-tier presentation design, research writing, and scientific content development services. Her multidisciplinary expertise spans computational science, chemistry, nanotechnology, environmental studies, socio-economics, human resource management, life sciences, engineering management, medical and pharmaceutical sciences, and business, her work ensures clarity, creativity, and academic excellence. Her services are ideal for those seeking impactful, visually compelling content tailored to diverse academic and research needs.
For collaborations or custom-designed academic content, feel free to reach out!
Contact:
Email: professionalwriter94@outlook.com
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/share/1LgwpoyLDg/
Website: https://professional-content-writings.jimdosite.comHOW TO FACE THREATS FROM THE FORCES OF NATURE EXISTING ON PLANET EARTH.pdf
HOW TO FACE THREATS FROM THE FORCES OF NATURE EXISTING ON PLANET EARTH.pdfFaga1939
╠²
This article aims to present how to deal with localized or global threats to human beings caused by the forces of nature that exist on planet Earth. The threats to human beings caused by the forces of nature that exist on planet Earth include earthquakes and tsunamis that can affect specific areas of the planet, volcanic eruptions that can affect specific areas of the planet or have a global impact, the cooling of the Earth's core and the inversion of the Earth's magnetic poles, both of which have a global impact. Specific measures are proposed to deal with each of the threats, but in addition to these, it is necessary to create a global structure, a World Organization for Defense Against Natural Disasters with global scope linked to the UN (United Nations) that has the capacity to technically coordinate the actions of countries around the world in dealing with these threats. The creation of this body is absolutely necessary because most of the threats from the forces of nature that exist on planet Earth have a global impact. To carry out its functions, this body must have financial resources from a global fund against natural disasters of global scope to be maintained by all countries on the planet and administered by the UN.Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )
Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )aryanxkohli88
╠²
science holiday homework
good for childrenTHE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM GRADE 9 SCIENCE.pptx
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM GRADE 9 SCIENCE.pptxroselyncatacutan
╠²
The Circulatory System Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 1Science Experiment: Properties of Water.pptx
Science Experiment: Properties of Water.pptxmarionrada1985
╠²
Different experiments to know the properties of waterMatt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Matt Ridley is a British independent science popularizer, journalist, entrepreneur, and author of several bestselling books, for which he has received numerous awards. He focuses primarily on the economic, biological, and environmental dimensions of the spontaneous functioning and advancement of human society. Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...
Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...Md. Arif Shahriar
╠²
This presentation was made as a coursework of "Introduction to Biology and Chemistry for Computation" Course under Fatema Tuj Johora ma'am at Daffodil International University.The Emergence of Signatures of AGI: The Physics of Learning
The Emergence of Signatures of AGI: The Physics of LearningCharles Martin
╠²
A talk for the Cybernetic Society
Operationalising OGC Processes with Application Packages in ILIAD: A Service ...
Operationalising OGC Processes with Application Packages in ILIAD: A Service ...Marco Amaro Oliveira
╠²
Synthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatin
Synthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatinProfessional Content Writing's
╠²
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...
Chromatography ║▌║▌▀Żs for the course of Introduction to Biology and Chemistry...Md. Arif Shahriar
╠²
states_of_matter.ppt
- 2. STATES OF MATTER ŌĆóThe Four States of Matter ŌĆó Four States ŌĆó Solid ŌĆó Liquid ŌĆó Gas ŌĆó Plasma
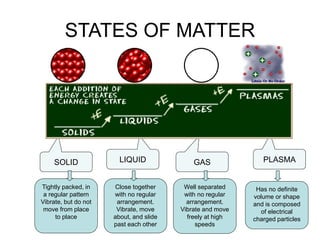
- 3. STATES OF MATTER ’āśBased upon particle arrangement ’āśBased upon energy of particles ’āśBased upon distance between particles
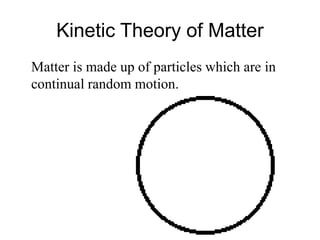
- 4. Kinetic Theory of Matter Matter is made up of particles which are in continual random motion.
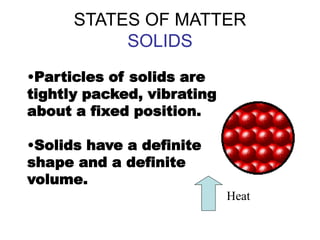
- 5. STATES OF MATTER SOLIDS ŌĆóParticles of solids are tightly packed, vibrating about a fixed position. ŌĆóSolids have a definite shape and a definite volume. Heat
- 6. STATES OF MATTER LIQUID ’é¦ Particles of liquids are tightly packed, but are far enough apart to slide over one another. ’é¦ Liquids have an indefinite shape and a definite volume. Heat
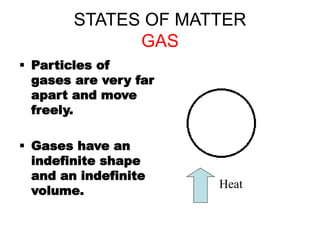
- 8. STATES OF MATTER GAS ’é¦ Particles of gases are very far apart and move freely. ’é¦ Gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume. Heat
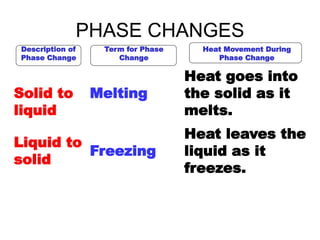
- 9. PHASE CHANGES Description of Phase Change Term for Phase Change Heat Movement During Phase Change Solid to liquid Melting Heat goes into the solid as it melts. Liquid to solid Freezing Heat leaves the liquid as it freezes.
- 10. PHASE CHANGES Description of Phase Change Term for Phase Change Heat Movement During Phase Change Liquid to gas Vaporization, which includes boiling and evaporation Heat goes into the liquid as it vaporizes. Gas to liquid Condensation Heat leaves the gas as it condenses. Solid to gas Sublimation Heat goes into the solid as it sublimates.
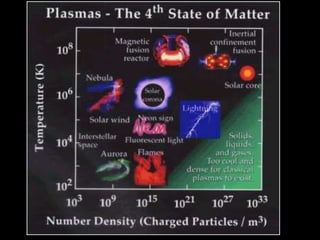
- 11. But what happens if you raise the temperature to super-high levelsŌĆ” between 1000┬░C and 1,000,000,000┬░C ? Will everything just be a gas?
- 12. STATES OF MATTER PLASMA ’é¦ A plasma is an ionized gas. ’é¦ A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. ’é¦ Plasmas, like gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume. ŌĆó Plasma is the common state of matter
- 13. STATES OF MATTER SOLID LIQUID GAS PLASMA Tightly packed, in a regular pattern Vibrate, but do not move from place to place Close together with no regular arrangement. Vibrate, move about, and slide past each other Well separated with no regular arrangement. Vibrate and move freely at high speeds Has no definite volume or shape and is composed of electrical charged particles
- 14. Some places where plasmas are foundŌĆ” 1. Flames
- 15. 2. Lightning
- 16. 3. Aurora (Northern Lights)
- 17. The Sun is an example of a star in its plasma state
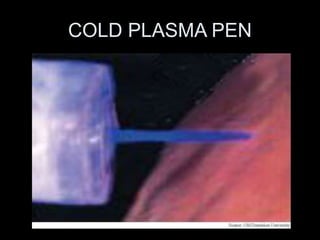
- 19. COLD PLASMA
- 20. COLD PLASMA PEN