The progressive era_(1)
- 2. The first modern reform movement ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ Womenâs suffrage Child labor laws Prohibition Conservation Trust busting Shorter working hours Voting reforms Graduated income tax Social welfare reforms
- 3. Change: Immigration After the depression of the 1890s, immigration jumped from a low of 3.5 million in that decade to a high of 9 million in the first decade of the new century. After the 1880s, immigrants increasingly came from Eastern and Southern European countries, Asia, Canada, and Latin America. New Immigration 1880-1920s
- 4. Change: Urbanization Reformer Jacob Riis documented poor immigrants in the slums on the lower east side in NYC in How the Other Half Lives
- 5. Change: Industrialization Lewis Hine documented poor laborers, especially children, working long hours under harsh conditions.
- 6. Other changes T. Roosevelt ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ W. Wilson ïĻ Technological changes that impact communication/transportation Development of modern social sciences New styles of presidential leadership New role of US as a power in world affairs Great White Fleet 1907
- 7. Middle Class Concerns ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ Economic power concentrating in the hands of a few industrialists Rising power of big business Increasing gap between rich and poor Violent conflicts between labor and capital Dominance of corrupt political machines in the cities Minorities: racist, Jim Crow laws in the South Political reform and greater democracy William âBossâ Tweed
- 8. Who were the progressives? Middle class ïĻ Educated ïĻ Residents of cities ïĻ Protestants ïĻ Optimistic about human nature ïĻ Women found a public role in reform ïĻ Ida Tarbell & Florence Kelley
- 9. Who were the progressives? ïĻ ïĻ Fought for social reform and believed government power could be used to achieve it Believed that cleaning up an environment would improve the people living in itâ(saloons, movie houses, temperance, prostitution, city beautiful movement) Carry Nation & Lincoln Steffens
- 10. Who were the progressives? ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ Feared immigration (Jane Addams an exception) Wanted to humanize big business, not eliminate it Believed in the virtue of efficiency Jane Addams & Frederick Taylor
- 11. Influences Susan B. Antony & Elizabeth C. Stanton ïĻ ïĻ Horace Mann Reformers (1840s) Populism (1890s) Grimke Sisters W. J. Bryan Mary Lease Dorothea Dix
- 12. Influences ïĻ ïĻ Pragmatism--practical. From John Dewey and William James. Pragmatists believed that people should take a pragmatic or practical approach to morals, ideals, and knowledge. They should experiment with ideas and laws and test them in action until they found something that seemed to work well for the better ordering of society William James (top), John Dewey (bottom)
- 13. Influences ïĻ Scientific Managementâefficiency. From Frederick Taylor. Businesses and governments should organize in the most efficient manner possible. Time and motion studiesï efficiency
- 14. Influences ïĻ Gladden Rauschenbusch ïĻ Social GospelâChristians have social responsibility (Washington Gladden, Walter Rauschenbusch) Goals of the movement were ending child labor, a weekly day off, a living wage, improved working conditions for women, and religious/moral education for the poor. Because they stressed Godâs love for all over damnation, it was known as a âchurch of love.â
- 15. Influences ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ Professionalismâgrowth of professions and professional organizations. American Medical Association American Bar Association American Federation of Teachers
- 16. Influences ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ Civic organizations National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Society of American Indians (1911) An 1890 photo of Carlos Montezuma, a member of the Society of American Indians
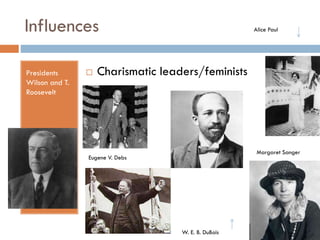
- 17. Influences Presidents Wilson and T. Roosevelt ïĻ Alice Paul Charismatic leaders/feminists Margaret Sanger Eugene V. Debs W. E. B. DuBois
- 18. Influences Ida Tarbell Lincoln Steffens Upton Sinclair Ray S. Baker S. S. McClure David G. Phillips ïĻ Writers (i.e. Muckrakers)
- 19. Influences William Glackens George Bellows Robert Henri John Sloan George Luks ïĻ Artists (i.e. Ashcan School)
- 20. Influences Booker T. Washington & Tuskegee Inst. Niagara Movement
- 21. Influences IWW ïĻ Labor leaders & unions Knights of Labor AF of L American Railway Union S. Gompers E. Debs Bill Haywood