Artificial Organs
- 1. ï ï Presented by K Ajith B pharmacy 4th yr 256513881040 St Pauls College of pharmacy Guided by Kiran Kumar Sir Asst Professor Dept of Pharmaceutics St Pauls College of Pharmcy
- 2. ï Introduction ï Different parts of body ï Why to use artificial organs? ï Statistics About organ loss? ïķ Artificial Heart ïķ Artificial Lungs ïķ Artificial Kidneys ïķ Artificial Tongue ïķ What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Organs ïķ Health Risks ïķ References
- 3. âAn artificial organ is a man-made device that is implanted or integrated into a human to replace a natural organ, for the purpose of restoring a specific function or a group of related functions so the patient may return to a normal life as soon as possible.â ï Usually made out of stem cells from the patient. ï Human made device designed to replace, duplicate or augment, functionally or cosmetically a missing, diseased or otherwise incompetent part of the body, either temporarily or permanently and which requires a non-biologic material interface with the living tissue.
- 4. ï 1885 M. von Frey and M. Gruber (Leipzig) build and use the first artificial heart-lung apparatus for organ perfusion studies. ï 1925 G. Haas (Germany) performs first clinical hemodialysis of 5 patients, using a modification of the Hopkins artificial kidney. ï 1939 W. Thalheimer (New York) performs the first hemodialysis of a dog using cellophane membrane and heparin anticoagulation. ï 1943 W. Kolff (Kampen, The Netherlands) develops a rotating drum artificial kidney and later the Kolff-Brigham dialyzer (designed and constructed in Boston), which becomes the standard throughout the 1950s. ï And all the development leads to the 21st century inventions of modern artificial organs used in the body.
- 6. ï There are many reasons to use of artificial organs o They are used for the replacement of vital functions of organs in body o They can be used as different models of organs, which can be used for research o More over every strive of a scientist is to increase the compliance of the humans and for their welfare o By use of artificial organs people can live their normal life o Many people lose their organs or damage them due to different reasons âĒ Diseases, Accidents, lack of proper health care, infections etc
- 7. ï 1. Artificial organs can replace diseased or damaged organs, thereby, providing the ailing patient with an opportunity to lead a healthy and normal life. ï 2. Artificial organs can meet the huge demand of healthy donor organs. There is a huge list of patients who are in urgent need of healthy organs but are unable to find a suitable willing donor. ï 3. A major stumbling block in the form of organ rejection can be solved due to artificial organs. As artificial organs are created by taking the stem cells of the same person and of the same organ, the possibility of rejection has been reduced significantly. ï 4.With the help of regenerative medicine or artificial organ therapy, burn victims can even have a new skin.
- 8. ï A major concern is the possible presence of the disease in the base tissue which is used to create the organ. ï The entire cost of growing and transplanting an artificial organ is prohibitive, and thus, limit the scope of its application to the general public. ï There are high chances of organ failure, and the body may even take some time to adapt to the new organ
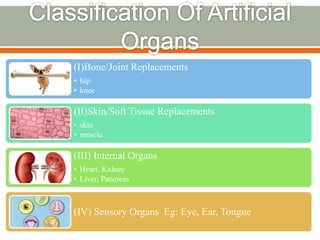
- 10. (I)Bone/Joint Replacements âĒ hip âĒ knee (II)Skin/Soft Tissue Replacements âĒ skin âĒ muscle (III) Internal Organs âĒ Heart, Kidney âĒ Liver, Pancreas (IV) Sensory Organs Eg: Eye, Ear, Tongue