Hypothesis Testing Template
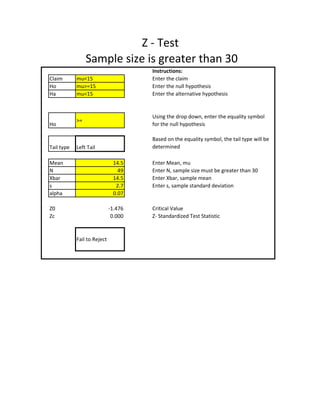
- 1. Z - Test Sample size is greater than 30 Instructions: Claim mu<15 Enter the claim Ho mu>=15 Enter the null hypothesis Ha mu<15 Enter the alternative hypothesis Using the drop down, enter the equality symbol >= Ho for the null hypothesis Based on the equality symbol, the tail type will be Tail type Left Tail determined Mean 14.5 Enter Mean, mu N 49 Enter N, sample size must be greater than 30 Xbar 14.5 Enter Xbar, sample mean s 2.7 Enter s, sample standard deviation alpha 0.07 Z0 -1.476 Critical Value Zc 0.000 Z- Standardized Test Statistic Fail to Reject
- 2. T - Test Sample size is less than 30 Claim mu > 95 Ho mu <= 95 Ha mu > 95 <= Ho Tail type Right Tail Mean 95 N 7 Xbar 100 s 42.5 alpha 0.01 To 3.143 Tc 0.311 Fail to Reject
- 3. T - Test mple size is less than 30 Instructions: Enter the claim Enter the null hypothesis Enter the alternative hypothesis Using the drop down, enter the equality symbol for the null hypothesis Based on the equality symbol, the tail type will be determined Enter Mean, mu Enter N, sample size must be less than 30 Enter Xbar, sample mean Enter s, sample standard deviation Critical Value T- Standardized Test Statistic
- 4. = <= >=