World War One and in Africa
- 1. WORLD WAR ONE AND/IN AFRICA Brett Shadle Department of History Virginia Tech
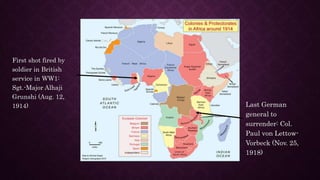
- 2. First shot fired by soldier in British service in WW1: Sgt.-Major Alhaji Grunshi (Aug. 12, 1914) Last German general to surrender: Col. Paul von Lettow- Vorbeck (Nov. 25, 1918)
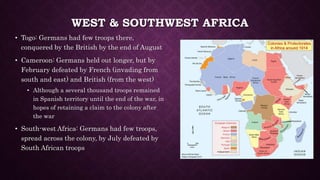
- 3. WEST & SOUTHWEST AFRICA âĒ Togo: Germans had few troops there, conquered by the British by the end of August âĒ Cameroon: Germans held out longer, but by February defeated by French (invading from south and east) and British (from the west) âĒ Although a several thousand troops remained in Spanish territory until the end of the war, in hopes of retaining a claim to the colony after the war âĒ South-west Africa: Germans had few troops, spread across the colony, by July defeated by South African troops
- 4. EAST AFRICA âĒ British largely distracted with Cameroon for first part of the war âĒ German commander von Lettow- Vorbeck more concerned with tying up Allied troops than retaining the colony or preventing African rebellion
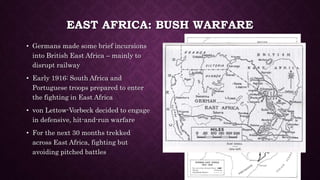
- 5. EAST AFRICA: BUSH WARFARE âĒ Germans made some brief incursions into British East Africa â mainly to disrupt railway âĒ Early 1916: South Africa and Portuguese troops prepared to enter the fighting in East Africa âĒ von Lettow-Vorbeck decided to engage in defensive, hit-and-run warfare âĒ For the next 30 months trekked across East Africa, fighting but avoiding pitched battles
- 6. EAST AFRICA: CIVILIANS IN WARFARE âĒ Living off the land â for Germans and Allies âĒ Requisition of food and cattle âĒ British official, December 1916, on Dodoma: âĒ âThe whole district has been ransacked for cattle.â âĒ Germans had taken 26,000 head of cattle, British in five months took 5,600 head and 100,000 kilograms of flour âĒ November 1917 rains failed, as many as 30,000 people died
- 7. EAST AFRICA: CIVILIANS IN WARFARE âĒ Living off the land â for Germans and Allies âĒ September 15, 1918, diary of German Dr. Ludwig Deppe âĒ âBehind us we leave destroyed fields, ransacked magazines and, for the immediate future, starvation. âĒ We are no longer agents of culture; our track is marked by death, plundering and evacuated villages, just like the progress of our own and enemy armies in the Thirty Years War.â
- 8. EAST AFRICA: CIVILIANS IN WARFARE âĒ Living off the land â for Germans and Allies âĒ British official, 1916, after Belgians went through Tabora region: âĒ âIt is like proceeding through a deserted plague stricken land.â
- 9. EAST AFRICA: CIVILIANS IN WARFARE âĒ Transportation and supplies âĒ Railways? âĒ Roads? âĒ Animals? âĒ People. âĒ Poor record keeping, informal recruitment, means number of porters ultimately uncertain âĒ Possible numbers: âĒ At the peak (March 1916), Germans used 45,000 âĒ Allies used over the course of the war 500,000 to 1,000,000
- 10. PORTERSâ EXPERIENCES âĒ According to one source, fewer than 400 employed by the British died in action âĒ More deadly: âĒ Disease âĒ new disease environments (malaria) or contaminated water (dysentery) âĒ Malnutrition (either not enough or poorly prepared food) âĒ Climate âĒ Exhaustion âĒ Execution for attempted desertion âĒ Belgian officer: Another two portersâ corpses on the road! Shot by the soldiers detailed to guard them. Not a day passes without one or more of these unfortunates paying with their lives for their love of freedom.
- 11. PORTERSâ EXPERIENCES âĒ According to one source, fewer than 400 employed by the British died in action âĒ Official British figure for deaths in Carrier Corps: 44, 911 âĒ Likely underestimate âĒ Second half of 1917: recorded deaths reached 2% per month, while âwastageâ (loss of manpower through illness, desertion, etc.) was 15% per month âĒ One scholar estimates at least 100,000 Africa porters died, perhaps 2- 3 times that number
- 12. MEMORIES OF THE PORTERS âĒ At least in Kenya and Tanganyika, when word of a new war first began circulating in the late 1930s, many young men deserted their jobs, some went into hiding, for fear of being caught up in a new Carrier Corps
- 13. AFRICAN SOLDIERS âĒ Despite some hesitation of using African troops in a white manâs war, all the combatants made use of them âĒ British, Germans, employed them only in Africa âĒ French envisioned the colonies as an almost limitless source of manpower for the war in Europe âĒ Had used them extensively in their conquest of West Africa
- 14. FRENCH WEST AFRICA âĒ At first, French desired African soldiers mainly as garrison troops to allow French soldiers to go to front âĒ After major losses in first two years of the war, decided instead to put African (and other colonial) troops in the front lines âĒ Eventually around 140,000 from French West Africa fought in France âĒ 29,000 from Senegal âĒ 2.4% of the population
- 15. FRENCH WEST AFRICA âĒ Recruiting soldiers âĒ Through 1917, very few volunteers âĒ Instead, each chief (many of whom had little legitimacy) required to fulfill their quota âĒ Those most likely to be brought forward âĒ Youth from marginal families âĒ Orphans âĒ Younger children âĒ Children of secondary wives in polygamous families
- 16. FRENCH WEST AFRICA âĒ Recruiting soldiers âĒ Compared to slave raids âĒ Thousands fled âĒ At times, number of those fleeing equal to number conscripted âĒ Armed resistance in areas farthest from French centers of control âĒ Called âtax in bloodâ
- 17. FRENCH WEST AFRICA âĒ In France âĒ Africans often used as âshock troopsâ ahead of white units âĒ Lt. Col. Debieuvre, April 1917: âĒ [The Senegalese are] above all superb attack troops permitting the saving of the lives of whites, who behind them exploit their success and organize the positions they conquer.
- 18. âTHE WAR FOR RIGHTSâ âĒ Blaise Diagne, representative for Four Communes, negotiated new rights for soldiers in exchange for new recruitment campaign âĒ Veterans to be exempt from corvÃĐe (unpaid communal labor), indigÃĐnat (âlawâ that could be enforced by French officials without recourse to the courts), given preference in government jobs âĒ More volunteers came forward
- 19. THE SIGNIFICANCE OF WORLD WAR ONE âĒ Death and destruction in Africa, death and debilitating injuries for many soldiers âĒ Impact of colonialism felt in many areas that had had only limited contact with European rule âĒ New political map (with German colonies becoming âMandatesâ under the League of Nations, ruled by Britain, France, South Africa, and Belgium) âĒ New political ideas in circulation in some areas













![FRENCH WEST AFRICA
âĒ In France
âĒ Africans often used as âshock
troopsâ ahead of white units
âĒ Lt. Col. Debieuvre, April 1917:
âĒ [The Senegalese are] above all
superb attack troops permitting
the saving of the lives of whites,
who behind them exploit their
success and organize the positions
they conquer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/worldwaroneand-inafrica-141118090333-conversion-gate02/85/World-War-One-and-in-Africa-17-320.jpg)

