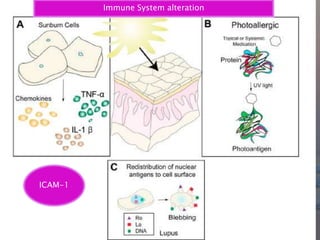
Sunlight and Skin Cancer
- 1. Karen Zapata Montenegro Dermatology and Dermatology surgery CSS
- 3. ïķ Introduction ïķUV Radiation ïķConcept ïķUV radiation damage ïķPhotoprotection
- 10. Concept
- 11. âĒ Isaac Newton. âĒ âColors phenomenonâ1666 âĒWilliam Herschel. âĒInfrared radiation 1800 âĒJohann Ritter. âĒ Ultraviolet radiation1801 Diffey B. Methods. 2002; 28: 4-13
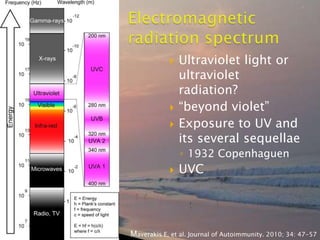
- 12. ï― Ultraviolet light or ultraviolet radiation? ï― âbeyond violetâ ï― Exposure to UV and its several sequellae âĶ 1932 Copenhaguen ï― UVC Maverakis E, et al. Journal of Autoimmunity. 2010; 34: 47-57
- 14. Less than 9% UV
- 15. Elliptical orbit âĶ 3.4 % perihelion (January 3) âĶ Aphelion (July 5) âĶ 7% UVR variation UV radiation
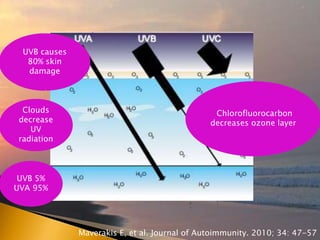
- 17. UVB 5% UVA 95% UVB causes 80% skin damage Clouds decrease UV radiation Chlorofluorocarbon decreases ozone layer Maverakis E, et al. Journal of Autoimmunity. 2010; 34: 47-57
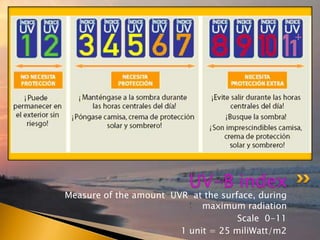
- 18. Measure of the amount UVR at the surface, during maximum radiation Scale 0-11 1 unit = 25 miliWatt/m2 UV-B index
- 19. Snow Desert area 90% 5% 15-30%
- 22. Elevates mood and improves energy
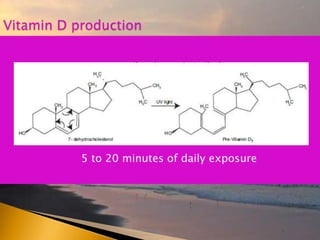
- 23. 5 to 20 minutes of daily exposure Vitamin D production
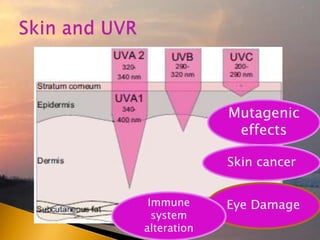
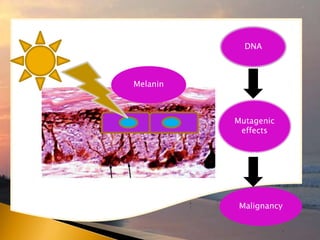
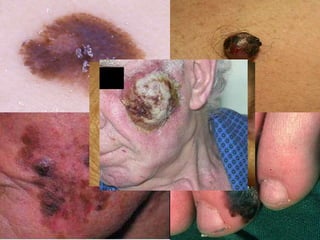
- 24. Skin cancer
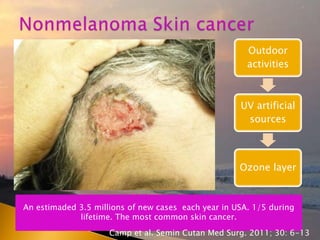
- 29. An estimaded 3.5 millions of new cases each year in USA. 1/5 during lifetime. The most common skin cancer. Outdoor activities UV artificial sources Ozone layer Camp et al. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011; 30: 6-13
- 30. ï― Most common cancer in humans ï― 3-8% of annual increase since 1960 ï― Firm association with UV exposure ï― 40 -50% recurrent CBC ï― 80% older than 60 year Madan V, Lear J, Szeimies R. Lancet. 2010; 375:373-85
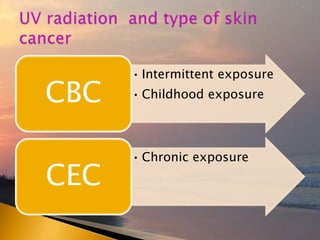
- 31. âĒ Intermittent exposure âĒ Childhood exposureCBC âĒ Chronic exposure CEC
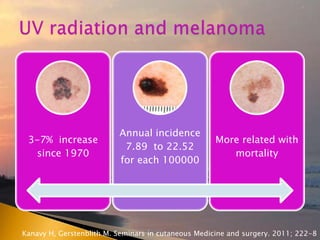
- 32. 3-7% increase since 1970 Annual incidence 7.89 to 22.52 for each 100000 More related with mortality Kanavy H, Gerstenblith M. Seminars in cutaneous Medicine and surgery. 2011; 222-8
- 34. Melanoma geographical distribution is bigger next to this area. 1% decrease in ozone layer increase melanoma mortality 1-2%. Kanavy H, Gerstenblith M. Seminars in cutaneous Medicine and surgery. 2011; 222-8
- 35. Chronic and intermittent Indoor tanning Skin cancer risk factor since 2009
- 36. High-altitude regions tend to have a higher melanoma rate that may be related to the higher UV fluences (J/cm2) noted at these sites
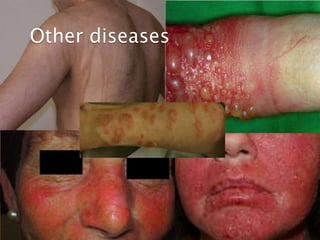
- 37. Other diseases
- 38. Key points
- 39. Gilaberte Y, GonzÃĄlez S. Actas Dermo-SifiliogrÃĄficas. 2010; 101: 659-72
- 40. Gilaberte Y, GonzÃĄlez S. Actas Dermo-SifiliogrÃĄficas. 2010; 101: 659-72
- 41. ï― Sunscreens are photochemical systems that absorb or reflect UV radiation. ï― Frequently use of sunscreens is the best photoprotection strategy. ï― The first sunscreen was marketed in 1930 ï― Actually there are 28 chemical filters in Australia, 26 in Europe and 14 in USA. Kockler J, Oelgemoller M, Robertson S, Glass B. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. 2012; 1-17
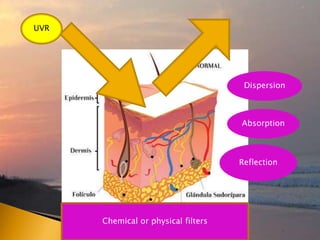
- 42. Absorption Dispersion UVR Chemical or physical filters Reflection
- 43. ï― La capacidad de eritema depende âĶ Longitud de onda de radiaciÃģn âĶ Fotosensibilidad del individuo âĶ DEM uso estudios observacionales SPF = ---------------- MED protected MED unprotected Kockler J, Oelgemoller M, Robertson S, Glass B. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. 2012; 1-17
- 44. ï― La capacidad de eritema depende âĶ Longitud de onda de radiaciÃģn âĶ Fotosensibilidad del individuo âĶ DEM uso estudios observacionales UVA FP = ---------------- MPD protected MPD unprotected DPM: dosis de pigmento mÃnima Kockler J, Oelgemoller M, Robertson S, Glass B. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. 2012; 1-17
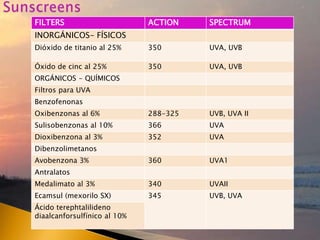
- 45. FILTERS ACTION SPECTRUM INORGÃNICOS- FÃSICOS DiÃģxido de titanio al 25% 350 UVA, UVB Ãxido de cinc al 25% 350 UVA, UVB ORGÃNICOS - QUÃMICOS Filtros para UVA Benzofenonas Oxibenzonas al 6% 288-325 UVB, UVA II Sulisobenzonas al 10% 366 UVA Dioxibenzona al 3% 352 UVA Dibenzolimetanos Avobenzona 3% 360 UVA1 Antralatos Medalimato al 3% 340 UVAII Ecamsul (mexorilo SX) 345 UVB, UVA Ãcido terephtalilideno diaalcanforsulfÃnico al 10%
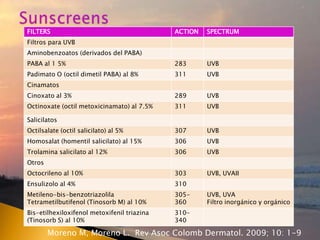
- 46. FILTERS ACTION SPECTRUM Filtros para UVB Aminobenzoatos (derivados del PABA) PABA al 1 5% 283 UVB Padimato O (octil dimetil PABA) al 8% 311 UVB Cinamatos Cinoxato al 3% 289 UVB Octinoxate (octil metoxicinamato) al 7.5% 311 UVB Salicilatos Octilsalate (octil salicilato) al 5% 307 UVB Homosalat (homentil salicilato) al 15% 306 UVB Trolamina salicilato al 12% 306 UVB Otros Octocrileno al 10% 303 UVB, UVAII Ensulizolo al 4% 310 Metileno-bis-benzotriazolila Tetrametilbutifenol (Tinosorb M) al 10% 305- 360 UVB, UVA Filtro inorgÃĄnico y orgÃĄnico Bis-etilhexiloxifenol metoxifenil triazina (Tinosorb S) al 10% 310- 340 Moreno M, Moreno L. Rev Asoc Colomb Dermatol. 2009; 10: 1-9
- 47. 20 min before and 2 - 3 hours ï― SPF 30 (97.5 UVB) âĶ 370nm ï― High UVA protection SPF 30 UVA high protection
- 48. 50- 80% solar damage is before 18 Correct solar protection Walker D. Journal of Pediatric nursing. 2011 Article in press
- 49. UPF higher than 40 Dark colors, nylon and polyester
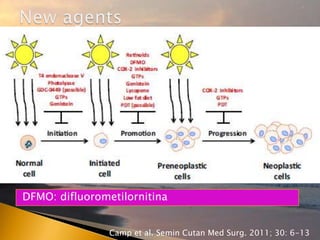
- 50. DFMO: difluorometilornitina Camp et al. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011; 30: 6-13