Short bowel syndrome
- 1. DR.K.MALANI
- 2. DEFINITION ?It is a malabsorptive state that follows after massive resection of small intestine (i.e.) more than 50%of small intestine is resected or <150cm of remaining small intestine .
- 3. ETIOLOGY PAEDIATRIC GROUP: ?Necrotising enterocolitis ?Intestinal atresia ?Volvulus ADULTS: ?CrohnĄŊs disease ?Mesenteric ischemia ?Radiation enteritis ?Trauma ?Neoplasm
- 4. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY ?About 90% of digestion and absorption of significant macro and micro nutrients are accomplished in the proximal 100-150 cm of jejunum. ?Ileum is the only site for the absorption of vit.B12 and bile salts. ?Colon ĻC increased salt and water absorption, ferments undigested carbohydrates into short chain fatty acids
- 6. ?Symptoms occur due to: ?Loss of small bowel surface area ?Loss of intestinal absorptive capacity ?Rapid intestinal transit ?Gastric hyper secretion and inactivation of digestive enzymes ?Loss of bile salts
- 7. FACTORS DECIDING THE OUTCOME: ?Age ĻC infants tolerate better ?Extent and anatomical site of resection ?Adaptation of small and large bowel ?Presence or absence of ileocaecal valve ?Additional colectomy increases the morbidity, retained jejunum-Ą°net absorbersĄą and Ą°net secretorsĄą.
- 8. ADAPTATIONS 1) Acute phase - immediately after resection and may last up to 3-4 months. 2) Adaptation phase ĻC 2-4 days after resection to 12-18 months. 3) Maintenance phase ĻC absorptive capacity of GIT is at its maximum.
- 9. CLINICAL FEATURES ?Malabsorption ?Diarrhoea ?Steatorrhea ?Water and electrolyte imbalance ?Recurrent bacterial enteritis ?Ca , Mg, Iron, Zinc,Fat soluble vit.,Vit B.12 def ?Weight loss
- 10. PHYSICAL SIGNS ?Anaemia ?Dry and flaky skin ?Easy bruising ?Peripheral oedema ?Temporal wasting ?Muscle spasm ?Poor blood clotting ?Bone pain
- 11. COMPLICATIONS ?Peptic ulceration ?Gall stone formation ?Renal stones ?D lactic acidosis ĻC confusion,ataxia,nystagmus ?Nutritional def. ?Bacterial overgrowth
- 12. INVESTIGATIONS ?Haematological: ?CBC ?Plasma albumin and pre albumin level ?AST,ALT ?Electrolytes , vitamin level , BUN ?Blood culture and sensitivity ?Radiological ?Plain x-ray abdomen ?Barium enema ?USG abdomen ?CT abdomen
- 13. TREATMENT ?MEDICAL CARE ?Total parenteral nutritionĄú25-30 kcal/kg/day ?Electrolyte replacement, vit B12 supplementation ?Hydration ?PPI, H2 blockers ,loperamide ?Ocreotide ?Cholestyramine ?Antibiotics
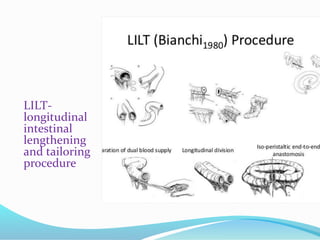
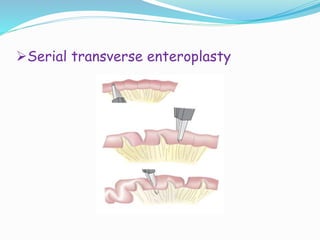
- 14. ?SURGICAL CARE ?Non transplantation procedures: ?Intestinal lengthening ?Segmental reversal of small bowel ?Interposition segment of colon between small intestine ?Construction of small intestinal valves
- 16. Interposition of colon segmental reversal of small bowel
- 18. ?Small bowel transplantation ? INDICATIONS: ?Impending liver failure ?Severe fluid loss despite medical mx ?Frequent sepsis ?Intestinal failure