Common exam
- 1. StudentBooklet Public Schools of North Carolina State Board of Education Department of Public Instruction Raleigh, North Carolina 27699-6314 Copyright 2013 by the North Carolina Department of Public Instruction. All rights reserved.ã Spring 2013 North Carolina Measures of Student Learning: NC’s Common Exams Grade 6 Science—Form A Released Form R ELEASED
- 2. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 1 Go to the next page. 1 How are earthquakes, sound, and light waves alike? A They transmit energy. B They carry matter. C They travel in space. D They can be seen. 2 What is the relationship between eyesight and light? A Light shines on all objects, allowing people to see them. B Light shines through all objects, allowing people to see them. C Light enters the eye before striking an object, allowing people to see the object. D Light reflects off an object and then enters the eye, allowing people to see the object. 3 Which best explains the relationship between the electromagnetic spectrum and sight? A Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen with the eye. B Ultraviolet light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen with the eye. C Visible light and infrared light are the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen with the eye. D Ultraviolet light and infrared light are the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen with the eye. R ELEASED
- 3. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 2 Go to the next page. 4 Which best explains the relationship between the speed of sound and the medium through which it passes? A Sound travels faster in solids because of the increased distance between solid particles. B Sound travels faster in air because of the decreased distance between air particles. C Sound travels slower in air because of the increased distance between air particles. D Sound travels slower in solids because of the decreased distance between solid particles. 5 Josephine adds thicker strings to her guitar. What does that do? A It prevents the guitar from using air particles to transfer the sound. B It changes the number of strings on the guitar. C It changes the vibrations made by the guitar. D It prevents the guitar from making sounds. 6 Which is composed of matter? A electricity B an atom C light D heat R ELEASED
- 4. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 3 Go to the next page. 7 The diagram below shows two pure iron magnets. N S N S Magnet 1 Magnet 2 Which is true about these two magnets? A They contain different types of atoms but the same elements. B They contain the same types of atoms but different elements. C They contain the same types of atoms and elements. D They contain different types of atoms and elements. 8 How are the atoms in an object affected when the temperature of the object increases? A They join together. B They vibrate faster. C They vibrate slower. D They split apart. 9 In which situation would the atoms in an object begin to move closer together during a phase change? A Heat is removed as a gas turns into a liquid. B Heat is removed as a liquid turns into a gas. C Heat is added as a solid turns into a gas. D Heat is added as a liquid turns into a solid. R ELEASED
- 5. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 4 Go to the next page. 10 Sarah has 100 g of each element listed in the chart below, which also provides the melting point for each element. Melting Point for Elements Element Melting Point copper 1,084°C gold 1,064°C lead 327°C silver 961°C What would happen if she melted only 50 g of each element? A The melting point for each element would double because the mass was changed. B The melting point for each element would decrease by half because the mass was changed. C The melting process would occur more quickly, but the melting points would remain the same. D The melting process would occur more quickly, but the melting points would be decreased by half. 11 How does 250 mL of water compare to 500 mL of water? A They have the same melting point but different boiling points. B They have the same boiling point but different melting points. C They have the same volume but different densities. D They have the same density but different volumes. R ELEASED
- 6. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 5 Go to the next page. 12 During the day, the sand at the beach is very warm; while at night, it is cooler. Why does this occur? A The sand reflects the sun’s energy during the day, causing it to become warmer. B The sand absorbs the sun’s energy during the day, causing it to become warmer. C The sand scatters the sun’s energy during the day, causing it to become warmer. D The sand refracts the sun’s energy during the day, causing it to become warmer. 13 A worker for an electrical company is preparing to fix a power line. Why would he put on rubber gloves before working with any power lines? A Rubber is a poor conductor of heat but a good conductor of electricity. B Rubber is a good conductor of heat but a poor conductor of electricity. C Rubber is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. D Rubber is a good conductor of heat and electricity. 14 Why are some coffee cups composed of ceramic material? A Ceramic materials are conductors that limit heat transfer. B Ceramic materials are insulators that limit heat transfer. C Ceramic materials are conductors that aid heat transfer. D Ceramic materials are insulators that aid heat transfer. R ELEASED
- 7. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 6 Go to the next page. 15 Why does Earth have different seasons? A because of the distance between Earth and the sun B because of the speed of Earth as it rotates on its axis C because of the amount of light blocked by the moon on its axis D because of the tilt of Earth on its axis as it moves around the sun 16 Which best explains why the moon has phases? A The moon’s position changes in relation to the sun and Earth. B The sun’s position changes in relation to the moon and Earth. C The Earth casts a shadow on the moon as it rotates. D The moon rotates along its axis. 17 Which factor makes Earth different from all the other planets in the solar system in its ability to support life? A The Earth is exposed to rays from the sun. B The Earth has only one moon that orbits around it. C The Earth rotates in an elliptical orbit around the sun. D The Earth has a breathable atmosphere. R ELEASED
- 8. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 7 Go to the next page. 18 Which represents information that is gained as a result of space exploration? A weather and climate patterns that occur on Earth B existence of the sun and the moon in the solar system C how to use coal and natural gas as energy resources D location of plates found upon Earth’s surface 19 Which best summarizes the composition of Earth’s core? A It contains a solid outer region surrounding a liquid iron core. B It contains a liquid outer region surrounding a solid iron core. C It contains a semi-liquid rock outer region surrounding a liquid core. D It contains a basalt, semi-liquid outer region surrounding a solid core. 20 Which best describes Earth’s crust? A It is stationary and unable to move. B It is thicker than the mantle and the core. C It is located between the outer and the inner core. D It is composed of continental and oceanic plates. R ELEASED
- 9. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 8 Go to the next page. 21 Which causes the movement of tectonic plates? A gravitational pull between Earth and the moon B convection occurring beneath the Earth’s crust C energy produced by earthquakes within the Earth D rotation of liquid rock found within the core 22 Which most likely occurs when two continental plates are pushed into one another? A The plates will stop moving. B The plates will form a trench. C The plates will form a mountain. D The plates will break into pieces. 23 Which environment would produce soil at a faster rate? A an environment located in warm, wet regions B an environment that consists of many slopes C an environment without any vegetation D an environment with high rates of erosion R ELEASED
- 10. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 9 Go to the next page. 24 A class is conducting an experiment on how different types of soil can affect the growth of a plant. Which are the main factors the class should consider when designing the experiment? A the soil texture and the amount of water it can hold B the types and amounts of sugars found in the soil C the color of the container for the soil and the plant D the shape and color of the seeds planted in the soil 25 How does the anther help with reproduction of a flowering plant? A It develops into a fruit after fertilization occurs. B It moves pollen to the roots of the plant. C It grows the seeds for the plant. D It produces and stores pollen. 26 Which best summarizes the order of energy flow in a food chain? A sun to decomposers to producers to consumers B sun to consumers to decomposers to producers C sun to producers to consumers to decomposers D sun to producers to decomposers to consumers R ELEASED
- 11. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 10 Go to the next page. 27 A plant begins to bend when a tall building is built near it. Why does this occur? A It is adjusting to changes in the temperature. B It is growing away from the light source. C It is adjusting to changes in the soil. D It is growing toward the light source. 28 Why do seeds go through a period of dormancy? A It allows time for the right conditions to occur before the seed germinates. B It allows time for dry soil to accumulate before the seed germinates. C It allows time for sunlight to appear before the seed germinates. D It allows time for pollination to occur before the seed germinates. R ELEASED
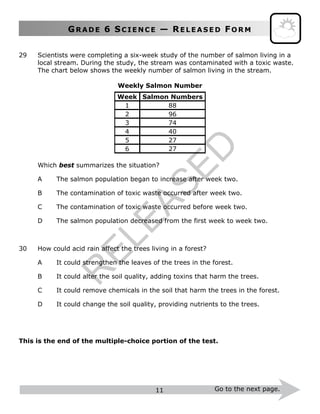
- 12. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 11 Go to the next page. 29 Scientists were completing a six-week study of the number of salmon living in a local stream. During the study, the stream was contaminated with a toxic waste. The chart below shows the weekly number of salmon living in the stream. Weekly Salmon Number Week Salmon Numbers 1 88 2 96 3 74 4 40 5 27 6 27 Which best summarizes the situation? A The salmon population began to increase after week two. B The contamination of toxic waste occurred after week two. C The contamination of toxic waste occurred before week two. D The salmon population decreased from the first week to week two. 30 How could acid rain affect the trees living in a forest? A It could strengthen the leaves of the trees in the forest. B It could alter the soil quality, adding toxins that harm the trees. C It could remove chemicals in the soil that harm the trees in the forest. D It could change the soil quality, providing nutrients to the trees. This is the end of the multiple-choice portion of the test. R ELEASED
- 13. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 12 Go to the next page. The questions you read next will require you to answer in writing. 1. Write your answers on separate paper. 2. Be sure to write your name on each page. 1 Energy can be transferred from one object to another.  How is heat energy transferred by conduction?  Provide an example of how heat is transferred by conduction. 2 Farming uses the land and soil to grow crops.  How can farmers maintain good, healthy soil?  Why is it important that farmers practice good stewardship of their land? 3 Leaves perform many tasks and are important to the survival of plants.  How is transpiration controlled in the leaves of a plant?  Explain why transpiration is important to the survival of the plant. R ELEASED
- 14. GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M 13 This is the end of the Grade 6 Science test. 1. Look back over your answers. 2. Put all of your papers inside your test book and close the test book. 3. Stay quietly in your seat until your teacher tells you that testing is finished. R ELEASED
- 15. Ěý Ěý Ěý 1 GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M Grade 6 Science RELEASED Form Spring 2013 Answer Key Item number Type Key Unifying Concept 1 MC A Forces and Motion 2 MC D Forces and Motion 3 MC A Forces and Motion 4 MC C Forces and Motion 5 MC C Forces and Motion 6 MC B Matter: Properties and Change 7 MC C Matter: Properties and Change 8 MC B Matter: Properties and Change 9 MC A Matter: Properties and Change 10 MC C Matter: Properties and Change 11 MC D Matter: Properties and Change 12 MC B Energy: Conservation and Transfer 13 MC C Energy: Conservation and Transfer 14 MC B Energy: Conservation and Transfer 15 MC D Earth in the Universe 16 MC A Earth in the Universe 17 MC D Earth in the Universe 18 MC A Earth in the Universe 19 MC B Earth Systems, Structures and Processes 20 MC D Earth Systems, Structures and Processes 21 MC B Earth Systems, Structures and Processes 22 MC C Earth Systems, Structures and Processes 23 MC A Earth Systems, Structures and Processes R ELEASED
- 16. Ěý Ěý Ěý 2 GR A D E 6 SC I E N C E — RE L E A S E D FO R M Item number Type Key Unifying Concept 24 MC A Earth Systems, Structures and Processes 25 MC D Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 26 MC C Ecosystems 27 MC D Ecosystems 28 MC A Ecosystems 29 MC B Ecosystems 30 MC B Ecosystems 31 CR Rubric Energy: Conservation and Transfer 32 CR Rubric Earth Systems, Structures and Processes 33 CR Rubric Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Ěý Item Types: MC = multiple choice CR = constructed response Ěý Ěý R ELEASED