IranOUG_Oracle_Multitenant
- 1. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«ž¦┘å┘łž¦ž»┌»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½ž║┘üž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ćž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž¦ž”┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łžČ┘łž╣ŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘éž»┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼Oracle Multitenant ŌĆ½ž¬ž¦ž▒█īž«ŌĆ¼:█ČŌĆ½ž¬█īž▒ŌĆ¼█▒█│█╣█Ė
- 2. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘ć┘åž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž¦ž”┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž©ž¦ž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž▒┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ć┘åž»ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž┤┘垦ž│█īŌĆ¼ŌĆōŌĆ½ž┤┘ģž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž¦žŁž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¦┘ä┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž▓ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘åž┤┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž¦█ī┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦┘ć┌®ž¦ž▒┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž┤ž¬█īž©ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž┤ž¦┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž¦█ī┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž│ž╣┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘é█ī┘éŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž«ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»█īž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž¼┘ć█īž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦█īž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž▒┌®ž¬ŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž¦█ī┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦┘ć┌®ž¦ž▒┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓┘ģ█ī┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘ł┘䞬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓┘ģž¦┘å┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«žĄ┘łžĄ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž▒┌®ž¬┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž┤ž¦┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž«žĄžĄ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣┘ģž▒ŌĆ¼:█ĄŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘äŌĆ¼
- 3. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Šž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž¦ž”┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łžČ┘łž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘éž»┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼Oracle Multitenan
- 4. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Šž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘ä█īž¬ŌĆ¼MultitenantŌĆ½ž©ž▓ž▒┌»ž¬ž▒█ī┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž║█ī█īž▒ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž¦ž▒█īž«ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘üž¦┘ć█ī┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ł█ī┌ś┌»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åŌĆ¼CDBŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣ž▒┘ü█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼
- 5. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½█īž╣┘å█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘垬█ī┘åž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ”¤æć¤æć
- 6. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Šž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ł█ī┌ś┌»█īŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž¦ž┤ž¬ž▒ž¦┌®█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘垦ž©ž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž║ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž▒ž¦┌®┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘ä█īž¬ŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬┘łž▒ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž▒█īž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»█īž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ä┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žó┘ģž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼SQL ’üČŌĆ½ž│ž▒█īž╣ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘łž▓ž▒ž│ž¦┘å█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┌åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž»█īž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ä┌»┘ł┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½┘ģž¬┘ģž▒┌®ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĄ┘łž▒ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¬ž╣ž»ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»█īž▒█īž¬ŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘垦ž©ž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»█īž▒█īž¬ŌĆ¼Pluggable
- 7. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Šž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘łž©ž¦ž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌垦┘äž┤█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Š┘ä█ī┌®█īž┤┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓█īž¦ž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣ž»ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž┤ž¬ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«█ī┘ä█īŌĆ¼┬½ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼┬╗ŌĆ½┘ģž©┘垦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž«ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼Oracle RDBMSŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒┘åž»ŌĆ¼: ’üČŌĆ½┌®┘å┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Š█īž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘ł█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž«ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒žĄž»ŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ģž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘鞬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åž»ž¦ž▒┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓█īž¦ž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž│█īž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š█ī┌å█īž»┌»█īŌĆ¼┬½ŌĆ½┘ł┘鞬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž»┘ģ█ī┘åŌĆ¼┬╗ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž┤ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█īž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█īž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘Š┘ä█ī┌®█īž┤┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘łž▓ž▒ž│ž¦┘å█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█īž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┌åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ć█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓┘ģž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ’üČŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©█īž┤ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁ┘łž¦ž│ž┤┘ł┘åŌĆ¼instanceŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓█īž¦ž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣ž»ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒┘üž¬┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘éž▒ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž░ž«█īž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘üžČž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼┬½ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼┬╗ŌĆ½ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ł█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘å┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼┘ä┘ł┌»█īž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž░ž«█īž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ü█īž▓█ī┌®█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž▒┘łž▒ŌĆ¼
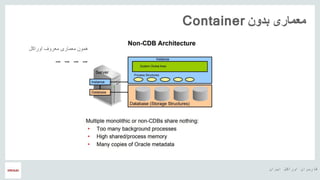
- 9. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž»┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼Container ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣ž▒┘ł┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ģ┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ Ō×Ī’ĖÅ Ō×Ī’ĖÅ Ō×Ī’ĖÅ Ō×Ī’ĖÅ
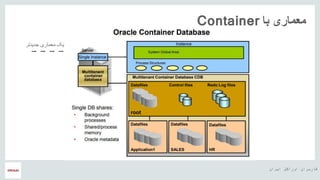
- 10. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼Container ŌĆ½ž¼ž»█īž»ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ Ō×Ī’ĖÅŌ×Ī’ĖÅŌ×Ī’ĖÅŌ×Ī’ĖÅ
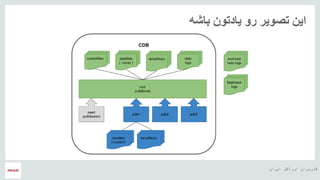
- 11. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█īž¦ž»ž¬┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žĄ┘ł█īž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åŌĆ¼
- 12. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼CDBŌĆ½┌å█īž│ž¬ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘垬█ī┘åž▒ŌĆ¼(CDB) ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘éž▒█īž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦█īž¼ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž©█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«█ī┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž│┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĖž¦┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž«ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒█īž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž┤┘垦█ī█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘枦ž┤ŌĆ¼ (controlfiles, datafiles, undo, tempfiles, redo logsŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž║█īž▒┘ćŌĆ¼) ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘垬█ī┘åž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█ī┌®ž┤┘åž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¬ž╣┘éŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█ī█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž©ž¼┌®ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘垬█ī┘åž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█ī█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž¬█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┘Šž░█īž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒┘ł█īž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬┘åž»ŌĆ¼
- 13. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼PDB ŌĆóŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦┘ä┌»ž©┘äŌĆ¼(PDB) ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ł┘åž¼ž¦█ī█īŌĆ¼CDBžīŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž«ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©█īž┤ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼pdbŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█īž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ü┘éžĘŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž«žĄ┘łžĄŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž┤ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½┘å█īž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┌»ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█īž│ž¬ŌĆ¼controlfiles, redo logsŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼undoŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž║█īž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤█īž»ŌĆ¼.
- 14. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘å█īž¦█īŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóPDBŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĄž▒┘üž¦ŌĆ¼datafilesŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼tempfilesŌĆ½ž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž«ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž©ž¼┌®ž¬┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ć┘åž»┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆó┘ŗŌĆ½ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘éžĘž╣ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»█ī┌®ž┤┘åž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž¦┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž«ž¬žĄž¦žĄ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ć┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž¦┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž©ž¦ž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█ī█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž©ž¼┌®ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž«žĄ┘łžĄŌĆ¼PDB ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼12.2ŌĆ½█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž©ž╣ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž©ž¬┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦█īž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž¬┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼local undo tablespaceŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž┤ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½┘ģž«žĄ┘łžĄŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž©ž¼┌®ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘垬█ī┘åž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž▒ž¦█īž¼ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž©ž¼┌®ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©█ī┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█ī┌®ž┤┘åž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘åž»█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘éž│█ī┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ žī ŌĆ½ž»█ī┌®ž┤┘åž▒█īŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┘ģ█īž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘å┘垬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¦┘䞬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘ä█īž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░█īž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž╣žĘž¦┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž╣ž½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž»ž¦ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½┘ģ┘ć┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž│█īž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ žī
- 15. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼PDBžīŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»█ī┌®ž┤┘åž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©█ī┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š█ī┘ł┘åž»ŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž»█ī┌®ž┤┘åž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┘Šž│ŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½┘ģ█īž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžŁž│┘łž©ŌĆ¼ PDBŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģ┘ł┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž©█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«█ī┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©žĘ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ģ┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█īž╣┘å█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž»┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ containerŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóžīŌĆ½┘ģž½ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ł█ī┘ł┘枦█īŌĆ¼DBA_%ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ALL_%ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒┘ł┘åŌĆ¼pdbŌĆ½ž║█īž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž½┘äŌĆ¼CDB ŌĆ½ž▒ž│┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»█ī┌»┘ćŌĆ¼
- 16. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åž»┘üž╣┘ćŌĆ¼OMFŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼Multitenant ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž│žĘŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘üž¦█ī┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»█īž▒█īž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘ä█īž¬ŌĆ¼(OMF)ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘ä█īž¬ŌĆ¼Oracle MultitenantŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘ć┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘łž│ž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒┘åž»ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž»┘ģ█ī┘å┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼OMFŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘å┌»ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼MultitenantŌĆ½┘Š█īž┤┘å┘枦ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼žīŌĆ½┘ģ█ī┌®┘å┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž╣ž½ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž«ž¬┘ä┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣┘ģ┘ä┌®ž▒ž»┘枦█īŌĆ¼MultitenantŌĆ½┘ģ█īž┤┘ćŌĆ¼.ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼OMF žīŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘äž▓ž¦┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒┌®ž▒ž»┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž«█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦█īž¼ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ł┘éž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž½ž¦┘äŌĆ¼Application ContainersŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ 12.2
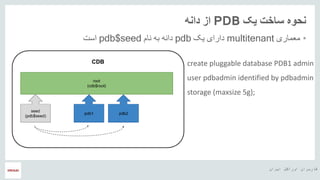
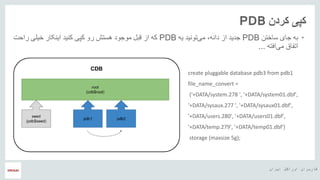
- 17. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž«ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åžŁ┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼multitenantŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼pdbŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘å┘ćŌĆ¼pdb$seedŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ create pluggable database PDB1 admin user pdbadmin identified by pdbadmin storage (maxsize 5g);
- 18. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘Š█īŌĆ¼PDB ŌĆóŌĆ½ž¼ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž«ž¬┘åŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž»█īž»ŌĆ¼žīŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ł┘å█īž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┌®┘Š█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž¼┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘éž©┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž«█ī┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘å┌®ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘å█īž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦žŁž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž¬┘üž¦┘éŌĆ¼... create pluggable database pdb3 from pdb1 file_name_convert = ('+DATA/system.278 ', '+DATA/system01.dbf', '+DATA/sysaux.277 ', '+DATA/sysaux01.dbf', '+DATA/users.280', '+DATA/users01.dbf', '+DATA/temp.279', '+DATA/temp01.dbf') storage (maxsize 5g);
- 19. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘Š█īŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½ž▒█ī┘ģ┘łž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ä█ī┘å┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ü┘éžĘŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘äž▓┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦žŁž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«█ī┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åŌĆ¼ CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb1new FROM pdb1@clone_link;
- 20. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž│ž¬┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘åž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»┘å█īž¦█īŌĆ¼PDBŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½█ī┌®█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ł█ī┌ś┌»█ī┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘éž»ž▒ž¬┘ģ┘åž»ž¬ž▒█ī┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘å┘垬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¦┘䞬█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘å┘Šž¦┘ä┌»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘垦█ī█īŌĆ¼ žīPDBŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼CDBŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¼ž»ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦┘ä┌»ŌĆ¼CDBŌĆ½ž»█ī┌»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼. ŌĆóŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ä┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž©ž┤┘ł┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦ž©ž¼ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž│┘ł┘å█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┌®ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»█īž¬ž¦ž©█īž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘å┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█ī┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█ī┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣█ī┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž░ž¦ž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž«ž¬█īž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž│ž«┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘łž▓ž▒ž│ž¦┘å█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┌åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦█ī┌»ž▓█ī┘åŌĆ¼.
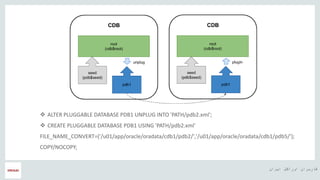
- 21. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ’üČ ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE PDB1 UNPLUG INTO 'PATH/pdb2.xml'; ’üČ CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE PDB1 USING 'PATH/pdb2.xml' FILE_NAME_CONVERT=('/u01/app/oracle/oradata/cdb1/pdb2/','/u01/app/oracle/oradata/cdb1/pdb5/'); COPY/NOCOPY;
- 22. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž▒ž¦ž¼ž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘垦ž©ž╣ŌĆ¼ ’üČ mghaffari.blog.ir ’üČ oracle-base.com ’üČ Oracle Course: Managing Multitenant Architecture https://www.linkedin.com/in/mahdighaffari/
- 23. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼
- 24. ŌĆ½ž¦█īž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćŌČ─¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž©ž▓ž¬ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁžČ┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž┤┌®ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼