Aayan & ehsan two years journey
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes174 views
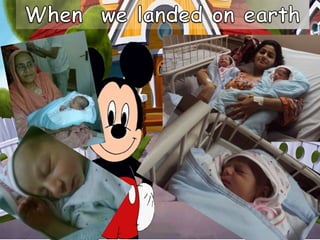
Aayan and Ehsan completed two years of age. The document expresses gratitude to Allah for the twins reaching this milestone. It notes that the twins have now been alive for two years.
1 of 18
Download to read offline

















Recommended
Happy 5th birthday baby boy! slideshow!
Happy 5th birthday baby boy! slideshow! Thiskiss92
╠²
This slideshow celebrates a baby boy turning 5 years old. It includes photos from his life over the past 5 years, from being a sleeping baby to playing soccer and going to preschool graduation. The creator expresses their love for the birthday boy and wishes for him to continue growing into a caring person, saying he is a precious gift and one of a kind.Anne Champagne, Wandsworth Borough Council presentation to the Wandsworth Adv...
Anne Champagne, Wandsworth Borough Council presentation to the Wandsworth Adv...Patrick Torsney
╠²
The Care Act presentation provides an overview of significant reforms in care and support legislation from 1948 to the introduction of the Care Act 2014. This act modernizes over 60 years of care law, establishing a single framework that clarifies entitlements, sets national eligibility criteria, and acknowledges the rights of carers. Key implementation aspects include a focus on well-being, safeguarding provisions, and new funding reforms set to take effect in April 2016.Frances Patterson: Creating a new framework for delivering adult social care
Frances Patterson: Creating a new framework for delivering adult social careThe King's Fund
╠²
The document outlines a project to create a new framework for delivering adult social care in England and Wales. It recommends repealing existing statutes and replacing them with single statutes for each nation. Key recommendations include establishing a "well-being principle" focused on the individual's views, a single duty to assess needs, a mandatory eligibility framework, enforceable duties to meet eligible needs, assessing carers' needs, and statutory safeguarding boards. Next steps include an engagement exercise in 2011, a white paper in 2012, and potential new legislation in 2012.Disability Discrimination Act 1995: 20 years on
Disability Discrimination Act 1995: 20 years onTLT LLP
╠²
This document summarizes key cases related to the Disability Discrimination Act of 1995 and provisions for reasonable adjustments for disabled individuals. It discusses duties for premises managers and landlords to make adjustments to services and facilities. It also outlines requirements for service providers to consider adjustments that prevent substantial disadvantages for disabled customers, as established in cases such as Roads v. Central Trains Limited and Ross v. Ryanair/Stansted Airport. The document concludes with implications for retailers to proactively address accessibility beyond minimal compliance with the Equality Act.P'borough pres
P'borough presBill Badham
╠²
The document discusses the importance of taking a whole family approach when assessing the needs of young carers and their families. It advocates for joint working between children's services, adult services, education, and health to conduct holistic assessments that meet the needs of the entire family. The goal is to ensure young carers are not asked to provide inappropriate levels of care and have the support they need to thrive. Key principles include developing family-oriented assessments and preventing children from caring at levels that impact their development.Managing benefits from projects - the NHS way
Managing benefits from projects - the NHS wayAssociation for Project Management
╠²
The document discusses the importance of benefits management in healthcare projects within the NHS context, emphasizing stakeholder engagement and clear definitions of success. It outlines various approaches and frameworks for effectively measuring and realizing benefits while addressing common pitfalls that lead to project failures. Additionally, it highlights the need for adaptability and continuous improvement in project delivery to foster better patient care and organizational outcomes.What the Equality Act means for you
What the Equality Act means for youEquality and Human Rights Commission
╠²
The Equality Act 2010 consolidates and harmonizes existing equalities legislation into a single act. It protects individuals from discrimination on the basis of nine protected characteristics: age, disability, gender reassignment, marriage/civil partnership, pregnancy/maternity, race, religion/belief, sex, and sexual orientation. The Act applies to sectors like services/public functions, premises, work, and education. It prohibits direct and indirect discrimination as well as harassment and promotes equality of opportunity and good relations between protected groups.Family Law Children Act 1989
Family Law Children Act 1989shummi
╠²
The document provides an overview of parental responsibility under the Children Act 1989. It defines parental responsibility as the rights, duties, powers and authority that parents have regarding their child. It discusses who is considered a parent both biologically and legally. It outlines that several people can have parental responsibility for a child including parents, guardians, those with residence orders, adopters and local authorities in some cases. Parental responsibility is joint and several when shared between multiple individuals.The Principles and the Factors
The Principles and the Factors shummi
╠²
The document discusses the Children Act 1989 and the principles and factors courts consider when making decisions about a child's upbringing. The three principles are: 1) the paramountcy principle where the child's welfare is the top priority; 2) the no order/non-intervention principle where the court only makes orders if necessary; and 3) avoiding delay in decisions. The seven factors courts examine are the child's wishes, needs, potential changes, harm risks, characteristics, parents' capabilities, and available court powers. There is a debate between prioritizing the child's welfare versus autonomy as their rights increase. Overall, the document outlines the framework courtsRight to education act 2009
Right to education act 2009Amrita Sinha
╠²
The Right to Education Act 2009 guarantees free and compulsory education for all children between ages 6-14 as a fundamental right in India. It came into effect in 2010, requiring governments to ensure admission, attendance, and completion of elementary education for all children. The Act lays out duties of governments and parents. It establishes norms for pupil-teacher ratios, infrastructure, curriculum and prohibits corporal punishment and private tuition by teachers. While an important law, implementation faces challenges like shortage of trained teachers, inadequate infrastructure and lack of awareness. Continuous effort is needed from central, state and local governments to fully realize the goals of the Act.NHS Diagrams
NHS DiagramsSocialist Health Association
╠²
The National Health Service (NHS) in England is organized into several levels with NHS England overseeing local clinical commissioning groups that purchase services from hospitals and other providers to deliver healthcare. Key parts of the NHS structure include NHS England, 211 clinical commissioning groups, 146 foundation trusts, and partnerships with public health organizations, local councils, and other social care providers. The devolved health services of Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland each have their own governance and funding structures but similar models of public healthcare delivery.Race relations act
Race relations actCatharine Patay
╠²
The Race Relations Act 1976 and Race Relations Amendment Act 2000 made race discrimination unlawful in employment, education, training and provision of goods, facilities and services in the UK. The acts define direct and indirect discrimination. Direct discrimination occurs when someone is treated less favorably due to their race. Indirect discrimination occurs when a condition or requirement negatively impacts a racial group. The 2000 amendment act requires public authorities to promote racial equality in all activities, including employment practices. It also places duties on public authorities to develop equality schemes, assess policies, monitor impact, and publish results. Both individuals and organizations can be held liable under the acts for discrimination.Equality Act 2010 Presentation
Equality Act 2010 PresentationMohammed (MIDHAL) Dhalech
╠²
The Equality Act 2010 is the most significant overhaul of equality legislation in the UK. It aims to simplify and strengthen discrimination law. The Act consolidates and replaces most previous equality legislation with a single Act. It introduces new protected characteristics and definitions of discrimination. Key areas like employment, services and public functions, and education are covered. The implementation of the Act will take place gradually through 2013, with some provisions coming into force in October 2010 and others being rolled out later. Some aspects of the Act have already proved contentious.Mady's 1st Birthday ║▌║▌▀Żshow
Mady's 1st Birthday ║▌║▌▀Żshowlaurakyates
╠²
This document is a heartfelt photo album chronicling the first year of Madelyn Grace Yates' life, from her birth on April 8, 2008, to her first birthday on April 8, 2009. It captures precious moments with family, milestones in her development, and the overwhelming love her parents feel for her. The narrative reflects on how Madelyn has brought joy and happiness to her family's life throughout the year.Disability awareness pt version
Disability awareness pt versionAccrington & Rossendale college
╠²
This document provides information about a disability awareness course, including its aims, objectives, structure, and assessment methods. The course aims to develop knowledge of disability awareness and covers topics like the meaning of disability, attitudes and barriers faced, and the social model of disability. The qualification is awarded by Education Development International, comprises one unit, and involves flexible workshop and online sessions as well as a final multiple choice assessment.The children act 1989
The children act 1989Nathan Loynes
╠²
The document discusses key aspects of the Children Act 1989 in the UK. It establishes that a child's welfare is the paramount consideration in legal decisions. It defines parental responsibility and outlines the duties of local authorities to investigate child welfare concerns and protect children, including through care and supervision orders if needed. The Act aims to reform laws around protecting children's rights and well-being.Equality and Diversity Presentation
Equality and Diversity PresentationCraig Higham
╠²
This document discusses equality and diversity, providing definitions and perspectives from various sources. Equality refers to equal treatment and opportunities regardless of personal attributes, while diversity acknowledges and respects individual differences. The document outlines relevant UK legislation and how positive action differs from illegal positive discrimination. It provides guidance for organizations to establish equitable policies and procedures regarding recruitment, training, and addressing issues like harassment.Lecture 5 equality and diversity the equality act 2010
Lecture 5 equality and diversity the equality act 2010Newham College University Centre Stratford Newham
╠²
The document discusses the concepts of equality and diversity, defining equality as equal rights and treatment for all individuals, while defining diversity as differences from what is normal or expected. It outlines various types of discrimination prohibited under the Equality Act 2010, including direct, indirect, associative, and perceptive discrimination. The Equality Act 2010 aims to strengthen and streamline anti-discrimination legislation in the UK by protecting individuals from discrimination based on several characteristics.Equality & diversity
Equality & diversityjomortimer
╠²
The document outlines the principles of equality and diversity in the workplace, emphasizing the importance of understanding different types of discrimination and recognizing personal assumptions. It defines equality as equal rights for all and diversity as valuing differences among individuals. The document aims to educate participants on these concepts through definitions, activities, and examples of diverse individuals and roles within society.Person with disability act 1995
Person with disability act 1995Priyanka Chaurasia
╠²
The Persons with Disabilities Act, 1995 aims to ensure equal opportunities for people with disabilities and their rights are protected. It defines disability as a physical or mental impairment of 40% or more. The act mandates reservations in government jobs and access to buildings, transport and services. It also focuses on education, healthcare, rehabilitation and affirmative action to promote the inclusion of people with disabilities.Community Mental Health Services in india At Nmhans Power Point Students.
Community Mental Health Services in india At Nmhans Power Point Students.AIIMS
╠²
The document discusses the history and development of community mental health services in India. It notes that early reports from 1947 and 1964 highlighted a significant shortage of mental health resources and facilities in the country. Several key initiatives helped integrate mental health into primary care starting in the 1970s. These included the National Mental Health Program in 1982 and expanding services to additional districts in the 1990s. The document also outlines the community psychiatry services developed at NIMHANS, including rural clinics and home care services. It discusses the teaching, training, research and roles provided in community mental health.Republic act 10533 presentation
Republic act 10533 presentationReymark Velasco
╠²
This document outlines key provisions of Republic Act No. 10533, also known as the Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013. It establishes an enhanced basic education program in the Philippines consisting of at least one year of kindergarten, six years of elementary education, and six years of secondary education made up of four years of junior high school and two years of senior high school. It aims to develop productive citizens equipped with life-long learning and employment skills through a globally competitive and learner-centered curriculum using research-based approaches including mother tongue instruction in early grades. The act also provides for teacher education and training programs to support the new curriculum as well as hiring specialists and practitioners to address shortage areas.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (14)
The Principles and the Factors
The Principles and the Factors shummi
╠²
The document discusses the Children Act 1989 and the principles and factors courts consider when making decisions about a child's upbringing. The three principles are: 1) the paramountcy principle where the child's welfare is the top priority; 2) the no order/non-intervention principle where the court only makes orders if necessary; and 3) avoiding delay in decisions. The seven factors courts examine are the child's wishes, needs, potential changes, harm risks, characteristics, parents' capabilities, and available court powers. There is a debate between prioritizing the child's welfare versus autonomy as their rights increase. Overall, the document outlines the framework courtsRight to education act 2009
Right to education act 2009Amrita Sinha
╠²
The Right to Education Act 2009 guarantees free and compulsory education for all children between ages 6-14 as a fundamental right in India. It came into effect in 2010, requiring governments to ensure admission, attendance, and completion of elementary education for all children. The Act lays out duties of governments and parents. It establishes norms for pupil-teacher ratios, infrastructure, curriculum and prohibits corporal punishment and private tuition by teachers. While an important law, implementation faces challenges like shortage of trained teachers, inadequate infrastructure and lack of awareness. Continuous effort is needed from central, state and local governments to fully realize the goals of the Act.NHS Diagrams
NHS DiagramsSocialist Health Association
╠²
The National Health Service (NHS) in England is organized into several levels with NHS England overseeing local clinical commissioning groups that purchase services from hospitals and other providers to deliver healthcare. Key parts of the NHS structure include NHS England, 211 clinical commissioning groups, 146 foundation trusts, and partnerships with public health organizations, local councils, and other social care providers. The devolved health services of Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland each have their own governance and funding structures but similar models of public healthcare delivery.Race relations act
Race relations actCatharine Patay
╠²
The Race Relations Act 1976 and Race Relations Amendment Act 2000 made race discrimination unlawful in employment, education, training and provision of goods, facilities and services in the UK. The acts define direct and indirect discrimination. Direct discrimination occurs when someone is treated less favorably due to their race. Indirect discrimination occurs when a condition or requirement negatively impacts a racial group. The 2000 amendment act requires public authorities to promote racial equality in all activities, including employment practices. It also places duties on public authorities to develop equality schemes, assess policies, monitor impact, and publish results. Both individuals and organizations can be held liable under the acts for discrimination.Equality Act 2010 Presentation
Equality Act 2010 PresentationMohammed (MIDHAL) Dhalech
╠²
The Equality Act 2010 is the most significant overhaul of equality legislation in the UK. It aims to simplify and strengthen discrimination law. The Act consolidates and replaces most previous equality legislation with a single Act. It introduces new protected characteristics and definitions of discrimination. Key areas like employment, services and public functions, and education are covered. The implementation of the Act will take place gradually through 2013, with some provisions coming into force in October 2010 and others being rolled out later. Some aspects of the Act have already proved contentious.Mady's 1st Birthday ║▌║▌▀Żshow
Mady's 1st Birthday ║▌║▌▀Żshowlaurakyates
╠²
This document is a heartfelt photo album chronicling the first year of Madelyn Grace Yates' life, from her birth on April 8, 2008, to her first birthday on April 8, 2009. It captures precious moments with family, milestones in her development, and the overwhelming love her parents feel for her. The narrative reflects on how Madelyn has brought joy and happiness to her family's life throughout the year.Disability awareness pt version
Disability awareness pt versionAccrington & Rossendale college
╠²
This document provides information about a disability awareness course, including its aims, objectives, structure, and assessment methods. The course aims to develop knowledge of disability awareness and covers topics like the meaning of disability, attitudes and barriers faced, and the social model of disability. The qualification is awarded by Education Development International, comprises one unit, and involves flexible workshop and online sessions as well as a final multiple choice assessment.The children act 1989
The children act 1989Nathan Loynes
╠²
The document discusses key aspects of the Children Act 1989 in the UK. It establishes that a child's welfare is the paramount consideration in legal decisions. It defines parental responsibility and outlines the duties of local authorities to investigate child welfare concerns and protect children, including through care and supervision orders if needed. The Act aims to reform laws around protecting children's rights and well-being.Equality and Diversity Presentation
Equality and Diversity PresentationCraig Higham
╠²
This document discusses equality and diversity, providing definitions and perspectives from various sources. Equality refers to equal treatment and opportunities regardless of personal attributes, while diversity acknowledges and respects individual differences. The document outlines relevant UK legislation and how positive action differs from illegal positive discrimination. It provides guidance for organizations to establish equitable policies and procedures regarding recruitment, training, and addressing issues like harassment.Lecture 5 equality and diversity the equality act 2010
Lecture 5 equality and diversity the equality act 2010Newham College University Centre Stratford Newham
╠²
The document discusses the concepts of equality and diversity, defining equality as equal rights and treatment for all individuals, while defining diversity as differences from what is normal or expected. It outlines various types of discrimination prohibited under the Equality Act 2010, including direct, indirect, associative, and perceptive discrimination. The Equality Act 2010 aims to strengthen and streamline anti-discrimination legislation in the UK by protecting individuals from discrimination based on several characteristics.Equality & diversity
Equality & diversityjomortimer
╠²
The document outlines the principles of equality and diversity in the workplace, emphasizing the importance of understanding different types of discrimination and recognizing personal assumptions. It defines equality as equal rights for all and diversity as valuing differences among individuals. The document aims to educate participants on these concepts through definitions, activities, and examples of diverse individuals and roles within society.Person with disability act 1995
Person with disability act 1995Priyanka Chaurasia
╠²
The Persons with Disabilities Act, 1995 aims to ensure equal opportunities for people with disabilities and their rights are protected. It defines disability as a physical or mental impairment of 40% or more. The act mandates reservations in government jobs and access to buildings, transport and services. It also focuses on education, healthcare, rehabilitation and affirmative action to promote the inclusion of people with disabilities.Community Mental Health Services in india At Nmhans Power Point Students.
Community Mental Health Services in india At Nmhans Power Point Students.AIIMS
╠²
The document discusses the history and development of community mental health services in India. It notes that early reports from 1947 and 1964 highlighted a significant shortage of mental health resources and facilities in the country. Several key initiatives helped integrate mental health into primary care starting in the 1970s. These included the National Mental Health Program in 1982 and expanding services to additional districts in the 1990s. The document also outlines the community psychiatry services developed at NIMHANS, including rural clinics and home care services. It discusses the teaching, training, research and roles provided in community mental health.Republic act 10533 presentation
Republic act 10533 presentationReymark Velasco
╠²
This document outlines key provisions of Republic Act No. 10533, also known as the Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013. It establishes an enhanced basic education program in the Philippines consisting of at least one year of kindergarten, six years of elementary education, and six years of secondary education made up of four years of junior high school and two years of senior high school. It aims to develop productive citizens equipped with life-long learning and employment skills through a globally competitive and learner-centered curriculum using research-based approaches including mother tongue instruction in early grades. The act also provides for teacher education and training programs to support the new curriculum as well as hiring specialists and practitioners to address shortage areas.Lecture 5 equality and diversity the equality act 2010
Lecture 5 equality and diversity the equality act 2010Newham College University Centre Stratford Newham
╠²
Aayan & ehsan two years journey
- 1. Aayan & Ehsan two years Journey by the grace of Allah our twins baby completed two years -Mashallah
