Ecg interpretation
- 1. ECG Rhythm Interpretation Module IV a Sinus Rhythms and Premature Beats
- 2. Course Objectives ? To recognize the normal rhythm of the heart - ˇ°Normal Sinus Rhythm.ˇ± ? To recognize the 13 most common rhythm disturbances. ? To recognize an acute myocardial infarction on a 12-lead ECG.
- 3. Learning Modules ? ECG Basics ? How to Analyze a Rhythm ? Normal Sinus Rhythm ? Heart Arrhythmias ? Diagnosing a Myocardial Infarction
- 4. Arrhythmias ? Sinus Rhythms ? Premature Beats ? Supraventricular Arrhythmias ? Ventricular Arrhythmias ? AV Junctional Blocks
- 5. Sinus Rhythms ? Sinus Bradycardia ? Sinus Tachycardia
- 6. Rhythm #1 ? Rate? 30 bpm ? Regularity? regular ? P waves? normal ? PR interval? 0.12 s ? QRS duration? 0.10 s Interpretation? Sinus Bradycardia
- 7. Sinus Bradycardia ? Deviation from NSR - Rate < 60 bpm
- 8. Sinus Bradycardia ? Etiology: SA node is depolarizing slower than normal, impulse is conducted normally (i.e. normal PR and QRS interval).
- 9. Rhythm #2 ? Rate? 130 bpm ? Regularity? regular ? P waves? normal ? PR interval? 0.16 s ? QRS duration? 0.08 s Interpretation? Sinus Tachycardia
- 10. Sinus Tachycardia ? Deviation from NSR - Rate > 100 bpm
- 11. Sinus Tachycardia ? Etiology: SA node is depolarizing faster than normal, impulse is conducted normally. ? Remember: sinus tachycardia is a response to physical or psychological stress, not a primary arrhythmia.
- 12. Premature Beats ? Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs) ? Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
- 13. Rhythm #3 ? Rate? 70 bpm ? Regularity? occasionally irreg. ? P waves? 2/7 different contour ? PR interval? 0.14 s (except 2/7) ? QRS duration? 0.08 s Interpretation? NSR with Premature Atrial Contractions
- 14. Premature Atrial Contractions ? Deviation from NSR ¨C These ectopic beats originate in the atria (but not in the SA node), therefore the contour of the P wave, the PR interval, and the timing are different than a normally generated pulse from the SA node.
- 15. Premature Atrial Contractions ? Etiology: Excitation of an atrial cell forms an impulse that is then conducted normally through the AV node and ventricles.
- 16. Teaching Moment ? When an impulse originates anywhere in the atria (SA node, atrial cells, AV node, Bundle of His) and then is conducted normally through the ventricles, the QRS will be narrow (0.04 - 0.12 s).
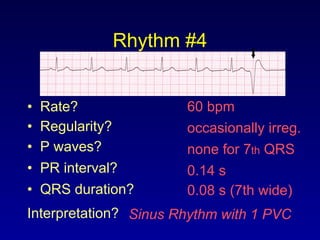
- 17. Rhythm #4 ? Rate? 60 bpm ? Regularity? occasionally irreg. ? P waves? none for 7th QRS ? PR interval? 0.14 s ? QRS duration? 0.08 s (7th wide) Interpretation? Sinus Rhythm with 1 PVC
- 18. PVCs ? Deviation from NSR ¨C Ectopic beats originate in the ventricles resulting in wide and bizarre QRS complexes. ¨C When there are more than 1 premature beats and look alike, they are called ˇ°uniformˇ±. When they look different, they are called ˇ°multiformˇ±.
- 19. PVCs ? Etiology: One or more ventricular cells are depolarizing and the impulses are abnormally conducting through the ventricles.
- 20. Teaching Moment ? When an impulse originates in a ventricle, conduction through the ventricles will be inefficient and the QRS will be wide and bizarre.
- 21. Ventricular Conduction Normal Abnormal Signal moves rapidly Signal moves slowly through the ventricles through the ventricles
- 22. End of Module IV a Sinus Rhythms and Premature Beats Proceed to Module IV a Practice Quiz on your iROCKET Course