IT Talks The approach for solving impossible tasks (dynamic programming)
- 1. ąöąĖąĮą░ą╝č¢čćąĮąĄ ą┐čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ ąöąĖąĮą░ą╝č¢čćąĮąĄ ą┐čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ ŌĆō čåąĄ ą║ąŠą╗ąĖ čā čö ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćą░ čÅą║čā ąĮąĄ ąĘčĆąŠąĘčāą╝č¢ą╗ąŠ čÅą║ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłčāą▓ą░čéąĖ č¢ ą▓ąŠąĮą░ čĆąŠąĘą▒ąĖą▓ą░čöčéčīčüčÅ ąĮą░ ą▒ą░ą│ą░č鹊 ą╝ąĄąĮčłąĖčģ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć, čÅą║č¢ č鹥ąČ ąĮąĄąĘčĆąŠąĘčāą╝č¢ą╗ąŠ čÅą║ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłčāą▓ą░čéąĖ (ąÉ. ąÜčāą╝ąŠą║)
- 2. ą¤ąĄčĆąĄą▓ą░ą│ąĖ ą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝č¢čćąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ: Ō¢¬ ą¤ąŠčłčāą║ ą│ą░čĆą░ąĮč鹊ą▓ą░ąĮąŠ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąĖčģ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮčī. Ō¢¬ ą¤ąŠčłčāą║ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąĖčģ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮčī ą┤ą╗čÅ ą▓čüč¢čöčŚ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ čéą░ ą┐ąŠą▓ąĮąŠą│ąŠ ąĮą░ą▒ąŠčĆčā ą┐čĆąŠą╝č¢ąČąĮąĖčģ ą┐č¢ą┤ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć. Ō¢¬ ą×ą┐čéąĖą╝č¢ąĘą░čåč¢čÅ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčüčā ąŠą▒čćąĖčüą╗ąĄąĮčī (ąĘą╝ąĄąĮčłąĄąĮąĮčÅ čüą║ą╗ą░ą┤ąĮąŠčüčéč¢ ąĘąĮą░čģąŠą┤ąČąĄąĮąĮčÅ čĆąŠąĘą▓`čÅąĘą║čā ą┤ąŠ ą┐ąŠą╗č¢ąĮąŠą╝č¢ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčŚ/ą╗ąŠą│ą░čĆąĖčäą╝č¢čćąĮąŠčŚ). Ō¢¬ ą£ąŠąČą╗ąĖą▓č¢čüčéčī ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ čłąĖčĆąŠą║ąŠą│ąŠ ą║ą╗ą░čüčā ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć ąĄą║ąŠąĮąŠą╝č¢ą║ąŠ-ą╝ą░č鹥ą╝ą░čéąĖčćąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄą╗čÄą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ. Ō¢¬ ąÆč¢ą┤čüčāčéąĮč¢čüčéčī ą░ą╗čīč鹥čĆąĮą░čéąĖą▓ąĮąĖčģ ą▓ąĖčüąŠą║ąŠąĄč乥ą║čéąĖą▓ąĮąĖčģ ą╝ąĄč鹊ą┤č¢ą▓ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć.
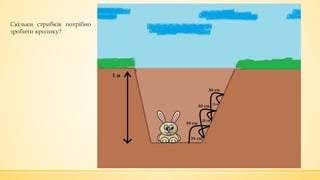
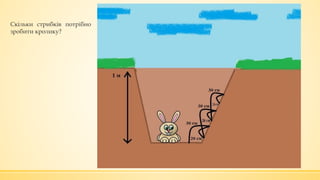
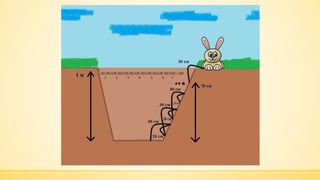
- 4. ąĪą║č¢ą╗čīą║ąĖ čüčéčĆąĖą▒ą║č¢ą▓ ą┐ąŠčéčĆč¢ą▒ąĮąŠ ąĘčĆąŠą▒ąĖčéąĖ ą║čĆąŠą╗ąĖą║čā?
- 5. ąĪą║č¢ą╗čīą║ąĖ čüčéčĆąĖą▒ą║č¢ą▓ ą┐ąŠčéčĆč¢ą▒ąĮąŠ ąĘčĆąŠą▒ąĖčéąĖ ą║čĆąŠą╗ąĖą║čā?
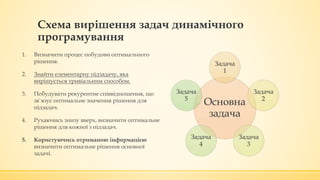
- 7. ąĪčģąĄą╝ą░ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć ą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝č¢čćąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ 1. ąÆąĖąĘąĮą░čćąĖčéąĖ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčü ą┐ąŠą▒čāą┤ąŠą▓ąĖ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ. 2. ąŚąĮą░ą╣čéąĖ ąĄą╗ąĄą╝ąĄąĮčéą░čĆąĮčā ą┐č¢ą┤ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćčā, čÅą║ą░ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłčāčöčéčīčüčÅ čéčĆąĖą▓č¢ą░ą╗čīąĮąĖą╝ čüą┐ąŠčüąŠą▒ąŠą╝. 3. ą¤ąŠą▒čāą┤čāą▓ą░čéąĖ čĆąĄą║čāčĆąĄąĮčéąĮąĄ čüą┐č¢ą▓ą▓č¢ą┤ąĮąŠčłąĄąĮąĮčÅ, čēąŠ ąĘą▓`čÅąĘčāčö ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąĄ ąĘąĮą░č湥ąĮąĮčÅ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ą┤ą╗čÅ ą┐č¢ą┤ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć. 4. ąĀčāčģą░čÄčćąĖčüčī ąĘąĮąĖąĘčā ą▓ą▓ąĄčĆčģ, ą▓ąĖąĘąĮą░čćąĖčéąĖ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąĄ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ą┤ą╗čÅ ą║ąŠąČąĮąŠčŚ ąĘ ą┐č¢ą┤ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć. 5. ąÜąŠčĆąĖčüčéčāčÄčćąĖčüčī ąŠčéčĆąĖą╝ą░ąĮąŠčÄ č¢ąĮč乊čĆą╝ą░čåč¢čöčÄ ą▓ąĖąĘąĮą░čćąĖčéąĖ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąĄ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ąŠčüąĮąŠą▓ąĮąŠčŚ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢. ą×čüąĮąŠą▓ąĮą░ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 1 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 2 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 3 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 4 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 5
- 8. ąóąĖą┐ąĖ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć, čēąŠ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłčāčÄčéčīčüčÅ ą£ąöą¤: Ō¢¬ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ (ąĮą░ą╣ą║ąŠčĆąŠčéčłąŠą│ąŠ, ąĮą░ą╣ą┤ąĄčłąĄą▓čłąŠą│ąŠ, ą┐ąŠą▓ąĮąŠą│ąŠ) čłą╗čÅčģčā. Ō¢¬ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ąĄą║ąŠąĮąŠą╝č¢čćąĮąŠčŚ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝č¢ąĘą░čåč¢čŚ. Ō¢¬ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā (ąĮą░ą╣ą╝ąĄąĮčłąŠčŚ, ąĮą░ą╣ą▒č¢ą╗čīčłąŠčŚ) ą║č¢ą╗čīą║ąŠčüčéč¢ ą╝ąŠąČą╗ąĖą▓ąĖčģ ą║ąŠą╝ą▒č¢ąĮą░čåč¢ą╣. Ō¢¬ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą░ąĮą░ą╗č¢ąĘčā č鹥ą║čüč鹊ą▓ąĖčģ čéą░ čćąĖčüą╗ąŠą▓ąĖčģ ą┤ą░ąĮąĖčģ (ą┐ąŠčĆč¢ą▓ąĮčÅąĮąĮčÅ čĆčÅą┤ą║č¢ą▓, ą┐ąĄčĆąĄčéą▓ąŠčĆąĄąĮąĮčÅ ą┐ąŠčüą╗č¢ą┤ąŠą▓ąĮąŠčüč鹥ą╣ ą┤ąŠ čöą┤ąĖąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą▓ąĖą│ą╗čÅą┤čā, ą┐ąŠčłčāą║ ą┐ąŠą╗č¢ąĮą┤čĆąŠą╝č¢ą▓ čéą░ ą┐č¢ą┤ą┐ąŠą╗č¢ąĮą┤čĆąŠą╝č¢ą▓). Ō¢¬ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą┐ą╗ą░ąĮčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ čéą░ ą┐čĆąŠą│ąĮąŠąĘčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ ą╝ą░ą╣ą▒čāčéąĮčīąŠą│ąŠ. Ō¢¬ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ čĆąŠąĘčĆąŠą▒ą║ąĖ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ ą╝ą░čüąŠą▓ąŠą│ąŠ ąŠą▒čüą╗čāą│ąŠą▓čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ čéą░ ą▒ą░ą│ą░č鹊ą┐ąŠč鹊čćąĮąŠčŚ ąŠą▒čĆąŠą▒ą║ąĖ ą┤ą░ąĮąĖčģ.
- 9. ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ čłą╗čÅčģčā ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ą▓ąĖčģąŠą┤čā ąĘ ą╗ą░ą▒č¢čĆąĖąĮčéčā┬╗, ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ čłą╗čÅčģčā┬╗, ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą║ąŠą╝č¢ą▓ąŠčÅąČąĄčĆą░┬╗, ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┤ą▓ąŠčģ ą║ąŠą╝č¢ą▓ąŠčÅąČąĄčĆč¢ą▓┬╗
- 10. ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ą▓ąĖčģąŠą┤čā ąĘ ą╗ą░ą▒č¢čĆąĖąĮčéčā
- 11. ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ą▓ąĖčģąŠą┤čā ąĘ ą╗ą░ą▒č¢čĆąĖąĮčéčā
- 17. ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ čłą╗čÅčģčā
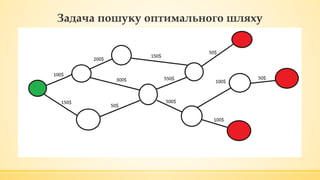
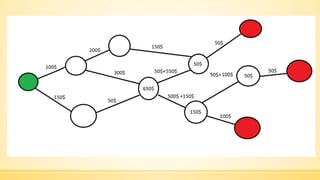
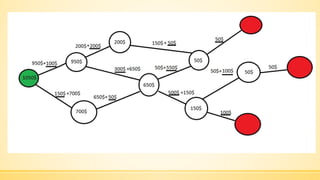
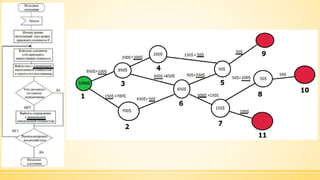
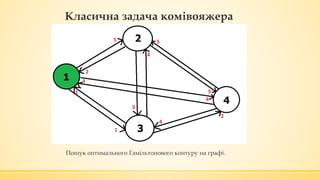
- 21. ąÜą╗ą░čüąĖčćąĮą░ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą║ąŠą╝č¢ą▓ąŠčÅąČąĄčĆą░ ą¤ąŠčłčāą║ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ ąōą░ą╝č¢ą╗čīč鹊ąĮąŠą▓ąŠą│ąŠ ą║ąŠąĮčéčāčĆčā ąĮą░ ą│čĆą░čäč¢.
- 22. Ō¢¬ ą¤ąŠą▓ąĮąĖą╣ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą▒č¢čĆ (ą┤ą╗čÅ 15 č鹊č湊ą║ ŌĆō 43 589 145 600, 18 ą╝č¢čüčé ŌĆō > 177 čéčĆąĖą╗čīą╣ąŠąĮč¢ą▓) Ō¢¬ ąÆąĖą┐ą░ą┤ą║ąŠą▓ąĖą╣ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą▒č¢čĆ Ō¢¬ ą¢ą░ą┤ąĮč¢ ą░ą╗ą│ąŠčĆąĖčéą╝ąĖ Ō¢¬ ą£ąĄč鹊ą┤ ą▓č¢č鹊ą║ čéą░ ą│čĆą░ąĮąĖčåčī Ō¢¬ ą£ąĄč鹊ą┤ ąĄą╗ą░čüčéąĖčćąĮąŠčŚ ą╝ąĄčĆąĄąČč¢ (ą£ąöą¤) (ą┤ą╗čÅ 30 č鹊č湊ą║ ŌĆō 1000 č¢č鹥čĆą░čåč¢ą╣) ąÉą╗ą│ąŠčĆąĖčéą╝ąĖ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢
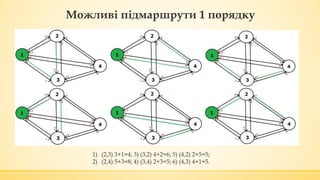
- 23. ą£ąŠąČą╗ąĖą▓č¢ ą┐č¢ą┤ą╝ą░čĆčłčĆčāčéąĖ 1 ą┐ąŠčĆčÅą┤ą║čā 1) (2,3) 3+1=4; 3) (3,2) 4+2=6; 5) (4,2) 2+5=5; 2) (2,4) 5+3=8; 4) (3,4) 2+3=5; 6) (4,3) 4+1=5.
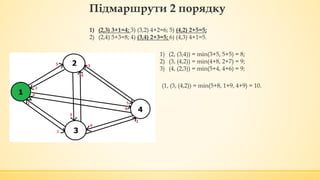
- 24. ą¤č¢ą┤ą╝ą░čĆčłčĆčāčéąĖ 2 ą┐ąŠčĆčÅą┤ą║čā 1) (2, (3,4)) = min(3+5, 5+5) = 8; 2) (3, (4,2)) = min(4+8, 2+7) = 9; 3) (4, (2,3)) = min(5+4, 4+6) = 9; 1) (2,3) 3+1=4; 3) (3,2) 4+2=6; 5) (4,2) 2+5=5; 2) (2,4) 5+3=8; 4) (3,4) 2+3=5; 6) (4,3) 4+1=5. (1, (3, (4,2)) = min(5+8, 1+9, 4+9) = 10.
- 25. ąÉą╗ą│ąŠčĆąĖčéą╝ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą║ąŠą╝č¢ą▓ąŠčÅąČąĄčĆą░ ą╝ąĄč鹊ą┤ąŠą╝ ą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝č¢čćąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ:
- 26. ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ąĄą║ąŠąĮąŠą╝č¢čćąĮąŠčŚ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝č¢ąĘą░čåč¢čŚ ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐čĆąŠ ą│čĆąŠčłč¢┬╗, ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐čĆąŠ čĆą░ąĮąĄčåčī┬╗, ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐čĆąŠ čĆąŠąĘą┐ąŠą┤č¢ą╗ ą║ą░ą┐č¢čéą░ą╗čā┬╗, ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ č¢ąĮą║ą░čüą░čåč¢čŚ┬╗, ┬½ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ą┐ąŠčłčāą║čā ą╝ą░ą║čüąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┤ąŠą▒čāčéą║čā┬╗
- 27. ążąŠčĆą╝čāą╗čÄą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą┐čĆąŠ ą│čĆąŠčłč¢ ąæą░ąĮą║ąŠą╝ą░čé ą╝ą░čö ąĮą░ą▒č¢čĆ ą║čāą┐čÄčĆ čĆč¢ąĘąĮąĖčģ ąĮąŠą╝č¢ąĮą░ą╗č¢ą▓ (2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100) ą║č¢ą╗čīą║č¢čüčéčī ą▒ą░ąĮą║ąĮąŠčé ąŠą▒ą╝ąĄąČąĄąĮą░. ąÆ ąĘą░ą╗ąĄąČąĮąŠčüčéč¢ ą▓č¢ą┤ ąĮą░čÅą▓ąĮąŠčüčéč¢ ą║čāą┐čÄčĆ ą║ąŠąČąĮąŠą│ąŠ čéąĖą┐čā ą▓ąĖąĘąĮą░čćąĖčéąĖ ą╝č¢ąĮč¢ą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮčā čŚčģ ą║č¢ą╗čīą║č¢čüčéčī ąĮąĄąŠą▒čģč¢ą┤ąĮčā ą┤ą╗čÅ č乊čĆą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ ąĘą░ą┐ąĖčéčāą▓ą░ąĮąŠčŚ čüčāą╝ąĖ ą░ą▒ąŠ č鹥, čēąŠ čüčāą╝čā čüč乊čĆą╝čāą▓ą░čéąĖ ąĮąĄ ą╝ąŠąČąĮą░.
- 28. ąĀąŠąĘą▓`čÅąĘąŠą║ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢ ą£ą░čÄčćąĖ ąĮą░ą▒č¢čĆ: 2 (10), 5 (0), 10 (3), 15(1), 20 (10), 50 (1), 100(1) ą▓ąĖąĘąĮą░čćąĖčéąĖ ą╝č¢ąĮč¢ą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮčā ą║č¢ą╗čīą║č¢čüčéčī ą║čāą┐čÄčĆ ą┤ą╗čÅ č乊čĆą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ čüčāą╝ąĖ ą▓ 175 ąŠą┤ ą░ą▒ąŠ ą▓ą║ą░ąĘą░čéąĖ, čēąŠ čéą░ą║čā čüčāą╝čā ąĘč¢ą▒čĆą░čéąĖ ąĮąĄą╝ąŠąČą╗ąĖą▓ąŠ. ąØąĄčģą░ą╣ S[i] ŌĆō č湥čĆą│ąŠą▓ą░ ą┐č¢ą┤čüčāą╝ą░, čÅą║čā ą┐ąŠčéčĆč¢ą▒ąĮąŠ ąĘč¢ą▒čĆą░čéąĖ, ą┤ąĄ i ŌĆō čüčāą╝ą░, ą░ S[i] ŌĆō ą║č¢ą╗čīą║č¢čüčéčī ąŠą┤ąĖąĮąĖčåčī. ąóąŠą┤č¢ S[1], S[0], S[-1], S[-2]ŌĆ” = ├ś; S[175] = stop. ąĀč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ: S[2] => 2 = 1; S[3] => S[1] + S[2] = ├ś; S[4] => (S[3] + S[1]), (S[2]+S[2]) = 2; S[5] => (S[2] + S[2] + S[1]), (S[3]+S[2]), (5) = 1; S[6] => (S[3] + S[3]), (S[2]+S[2]+S[2]), (S[5], S[1]) = 3; ŌĆ”.. S[175] => (S[10] + S[15] + S[50] + S[100]) = 4;
- 29. ąĪčģąĄą╝ą░ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć ą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝č¢čćąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ 1. ąŚąĮą░ą╣čéąĖ ąĄą╗ąĄą╝ąĄąĮčéą░čĆąĮčā ą┐č¢ą┤ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćčā, čÅą║ą░ ą▓ąĖčĆč¢čłčāčöčéčīčüčÅ čéčĆąĖą▓č¢ą░ą╗čīąĮąĖą╝ čüą┐ąŠčüąŠą▒ąŠą╝. 2. ą¤ąŠą▒čāą┤čāą▓ą░čéąĖ čĆąĄą║čāčĆąĄąĮčéąĮąĄ čüą┐č¢ą▓ą▓č¢ą┤ąĮąŠčłąĄąĮąĮčÅ, čēąŠ ąĘą▓`čÅąĘčāčö ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąĄ ąĘąĮą░č湥ąĮąĮčÅ čĆąŠąĘą▓`čÅąĘą║čā ą┤ą╗čÅ ą┐č¢ą┤ąĘą░ą┤ą░čć. 3. ąÜąŠčĆąĖčüčéčāčÄčćąĖčüčī ąŠčéčĆąĖą╝ą░ąĮąŠčÄ č¢ąĮč乊čĆą╝ą░čåč¢čöčÄ ą▓ąĖąĘąĮą░čćąĖčéąĖ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąĄ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ąŠčüąĮąŠą▓ąĮąŠčŚ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢. ą×čüąĮąŠą▓ąĮą░ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćą░ ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 1 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 2 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 3 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 4 ąŚą░ą┤ą░čćą░ 5
- 31. ą¤čĆąĖąĮčåąĖą┐ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéč¢ ąæąĄą╗ą╗ą╝ą░ąĮą░ Ō¢¬ Bellman's optimality principle - ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮą░ ą┐ąŠą▓ąĄą┤č¢ąĮą║ą░ ą╝ą░čö čéčā ą▓ą╗ą░čüčéąĖą▓č¢čüčéčī, čēąŠ, čÅą║č¢ ą▒ ąĮąĄ ą▒čāą╗ąĖ ą┐ąŠčćą░čéą║ąŠą▓ąĖą╣ čüčéą░ąĮ č¢ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ (č鹊ą▒č鹊 ┬½čāą┐čĆą░ą▓ą╗č¢ąĮąĮčÅ┬╗), ąĮą░čüčéčāą┐ąĮč¢ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ ą┐ąŠą▓ąĖąĮąĮč¢ čüą║ą╗ą░ą┤ą░čéąĖ ąŠą┐čéąĖą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮčā ą┐ąŠą▓ąĄą┤č¢ąĮą║čā ą▓č¢ą┤ąĮąŠčüąĮąŠ čüčéą░ąĮčā, čēąŠ ą▓ąĖčģąŠą┤ąĖčéčī ą▓ čĆąĄąĘčāą╗čīčéą░čéč¢ ą┐ąĄčĆčłąŠą│ąŠ čĆč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ. Ō¢¬ ą”ąĄą╣ ą┐čĆąĖąĮčåąĖą┐ ą╝ąŠąČąĮą░ ą▓ąĖčĆą░ąĘąĖčéąĖ č¢ čĆąŠąĘą╝č¢čĆą║ąŠą▓čāčÄčćąĖ ą▓č¢ą┤ ą┐čĆąŠčéąĖą╗ąĄąČąĮąŠą│ąŠ: čÅą║čēąŠ ąĮąĄ ą▓ąĖą║ąŠčĆąĖčüč鹊ą▓čāą▓ą░čéąĖ ąĮą░ą╣ą║čĆą░čēąĖą╝ čćąĖąĮąŠą╝ č鹥, čēąŠ ą╝ąĖ ą╝ą░čöą╝ąŠ ąĘą░čĆą░ąĘ, č鹊 č¢ ąĮą░ą┤ą░ą╗č¢ ąĮąĄ ą▓ą┤ą░čüčéčīčüčÅ ąĮą░ą╣ą║čĆą░čēąĖą╝ čćąĖąĮąŠą╝ čĆąŠąĘą┐ąŠčĆčÅą┤ąĖčéąĖčüčÅ čéąĖą╝, čēąŠ ą╝ąĖ ą╝ąŠą│ą╗ąĖ ą▒ ą╝ą░čéąĖ.













![ąĀąŠąĘą▓`čÅąĘąŠą║ ąĘą░ą┤ą░čćč¢
ą£ą░čÄčćąĖ ąĮą░ą▒č¢čĆ: 2 (10), 5 (0), 10 (3), 15(1), 20 (10), 50 (1), 100(1)
ą▓ąĖąĘąĮą░čćąĖčéąĖ ą╝č¢ąĮč¢ą╝ą░ą╗čīąĮčā ą║č¢ą╗čīą║č¢čüčéčī ą║čāą┐čÄčĆ ą┤ą╗čÅ č乊čĆą╝čāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅ čüčāą╝ąĖ ą▓ 175 ąŠą┤ ą░ą▒ąŠ
ą▓ą║ą░ąĘą░čéąĖ, čēąŠ čéą░ą║čā čüčāą╝čā ąĘč¢ą▒čĆą░čéąĖ ąĮąĄą╝ąŠąČą╗ąĖą▓ąŠ.
ąØąĄčģą░ą╣ S[i] ŌĆō č湥čĆą│ąŠą▓ą░ ą┐č¢ą┤čüčāą╝ą░, čÅą║čā ą┐ąŠčéčĆč¢ą▒ąĮąŠ ąĘč¢ą▒čĆą░čéąĖ, ą┤ąĄ i ŌĆō čüčāą╝ą░, ą░ S[i] ŌĆō ą║č¢ą╗čīą║č¢čüčéčī
ąŠą┤ąĖąĮąĖčåčī. ąóąŠą┤č¢ S[1], S[0], S[-1], S[-2]ŌĆ” = ├ś; S[175] = stop.
ąĀč¢čłąĄąĮąĮčÅ:
S[2] => 2 = 1;
S[3] => S[1] + S[2] = ├ś;
S[4] => (S[3] + S[1]), (S[2]+S[2]) = 2;
S[5] => (S[2] + S[2] + S[1]), (S[3]+S[2]), (5) = 1;
S[6] => (S[3] + S[3]), (S[2]+S[2]+S[2]), (S[5], S[1]) = 3;
ŌĆ”..
S[175] => (S[10] + S[15] + S[50] + S[100]) = 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-160628094926/85/IT-Talks-The-approach-for-solving-impossible-tasks-dynamic-programming-28-320.jpg)



