Culture in practice
- 2. Culture in Practice collects the academic and political writings from the 1960s through the 1990s of anthropologist Marshall Sahlins. More than a compilation, Culture in Practice unfolds as an intellectual autobiography. The book opens with Sahlins's early general studies of culture, economy, and human nature. It then moves to his reportage and reflections on the war in Vietnam and the antiwar movement, the event that most strongly affected his thinking about cultural specificity. Finally, it offers his more historical and globally aware works on indigenous peoples, especially those of the Pacific islands. http://www.zonebooks.org/titles/SAHL_CUL.html
- 3. • Part I Culture between 60s-70s Consceptual exercises and comparisons between cultures • Part II Practice US War in Vietnam – Antiwar movements • Part III Culture in practice More historical and more grounded ethnographically. * Cultural integrity of the indigenous peoples. http://www.zonebooks.org/titles/SAHL_CUL.html
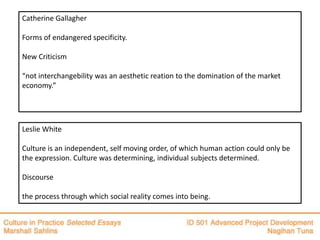
- 4. Catherine Gallagher Forms of endangered specificity. New Criticism “not interchangebility was an aesthetic reation to the domination of the market economy.” Leslie White Culture is an independent, self moving order, of which human action could only be the expression. Culture was determining, individual subjects determined. Discourse the process through which social reality comes into being.
- 5. White; The symbol is the origin and the basis of human behaviour. Ferdinand de Saussure and John Locke Ideas determine how people classify and relate to objects in different ways. White was a convinced technological determinist. He advocates that when the people hold an axe a simple social order is formed. However here an axe turn into a symbolic phenomenon, so; Sybolicity < Technological determination
- 6. A comparison between American and Britsh anthropologists; Structural functionalists, Culture is the expressive and customary means by which a social system is maintained. Social antropologists, Cultural phenomena is only contingent in relation to the systematic character of the social structures. Radcliffe Brown, Culture is an abstraction. It is without emprical presence or effects. Brown and White, Culture concept encompasses any kinds of human practice, everything organized symbolically.
- 7. However, for too many culture still has predominantly aesthetic or intellectual signification. White didn’t agree with them because there are contradictiıns between the material and symbolic. The problem was the superstracture included the economic basis. Lévi Strauss, Everything could be reduced to behavior, utilitarian behavior, symbolism was lost. Levi-Strauss (The Savage Mind) with due homages to Marx; there is always a mediator between praxis and practice, namely the conceptual scheme by the operation of which matter and form, neither with any independent existence, are realized as structures, that is as entities which are both empirical and intelligible (1966:130)
- 8. In 1950s and 1960s there was an ongoin anthropological positivism. In the chain of this lawful generalizations , one culture can only be an instance, Sahlins says. Boas, He also oppose these arguements. Cosmography, A multivalent distinction that invoke venerable oppositions to science and history, objectivity and subjectivity, classicisim and romanticism. Cosmographic disposition, anthropology came to know as cultural relativism. Relativizm, The practices must be placed in their own context and positional values in order to be understood.
- 9. Vietnam War, Antiwar movement in University of Michigan in 1965. Transformed a cultural physicist to a cosmographer. Teach in, Instead of holding classes outside of the university, teach out, they occupy the buildings all nght in order to discuss the war. The social formation doesn’t determine the individuality of the leaders it gives itself, thus their individuality determine powers over its own destiny.
- 10. According to Shlins the rest ( after 70s) is history. Cultures are relative and historical forms of life with particular validity without some universal necessity. Anthropology uses its objects as its methods and it is a different science because it examines the reasons behind human things, not causes. Anthropologist recapitulates symbolic operations by which customs are produced. Method recapitulates truths, here is identity as a human translation of a material process.
- 11. In conclusion, In his introduction, Sahlins evaluates the notion of culture historically, and covers the movements that affect culture approaches from1960s to 1990s. He examine the concept of culture through social sciences according to anthropologists and sociologists. The role of individual is questioned. History, societies and specificity of cultures are evaluated in relation to eachother.