PROTOZOAN part 2
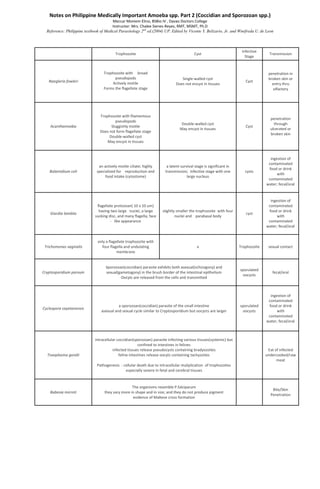
- 1. Notes on Philippine Medically Important Protozoans Part 2 (Coccidian and Sporozoan) Meccar Moniem Elino, BSBio IV , Davao Doctors College Instructor: Mrs. Chalee Sienes-Reyes, RMT, MSMT, Ph.D Reference: Philippine textbook of Medical Parasitology 2nd ed.(2004) UP. Edited by Vicente Y. Belizario, Jr. and Winifreda U. de Leon Infective Trophozoite Cyst Transmission Stage Trophozoite with broad penetration in pseudopods Single-walled cyst broken skin or Naegleria fowleri Actively motile Cyst Does not encyst in tissues entry thru Forms the flagellate stage olfactory Trophozoite with filamentous penetration pseudopods Double-walled cyst through Acanthamoeba Sluggishly motile Cyst May encyst in tissues ulcerated or Does not form flagellate stage broken skin Double-walled cyst May encyst in tissues ingestion of contaminated an actively motile ciliate; highly a latent survival stage is significant in food or drink Balantidium coli specialized for reproduction and transmission; infective stage with one cysts with food intake (cytostome) large nucleus contaminated water; fecal/oral ingestion of flagellate protozoan( 10 x 10 um) contaminated having two large nuclei, a large slightly smaller the trophozoite with four food or drink Giardia lamblia cyst sucking disc, and many flagella; face nuclei and parabasal body with - like appearance contaminated water; fecal/oral only a flagellate trophozoite with Trichomonas vaginalis four flagella and undulating x Trophozoite sexual contact membrane Sporozoan(coccidian) parasite exhibits both asexual(schizogony) and sporulated Cryptosporidium parvum sexual(gametogony) in the brush border of the intestinal epithelium fecal/oral oocysts Oocyts are released from the cells and transmitted ingestion of contaminated a sporozoan(coccidian) parasite of the small intestine sporulated food or drink Cyclospora cayetanensis asexual and sexual cycle similar to Cryptosporidium but oocysts are larger oocysts with contaminated water; fecal/oral intracellular coccidian(sporozoan) parasite infecting various tissues(systemic) but confined to intestines in felines infected tissues release pseudocysts containing bradyozoites Eat of infected Toxoplasma gondii feline intestines release oocyts containing tachyzoites undercooked/raw meat Pathogenesis : cellular death due to intracellular muliplication of trophozoites especially severe in fetal and cerebral tissues The organisms resemble P.falciparum Bite/Skin Babesia microti they vary more in shape and in size; and they do not produce pigment Penetration evidence of Maltese cross formation