Wireless sensor network
Download as PPTX, PDF11 likes13,284 views
this will be very useful for those who are seeking a good ppt on wireless sensor network,,have a look
1 of 14
Downloaded 1,878 times









Recommended
Wireless Sensor Networks



Wireless Sensor Networksjuno susi
Ěý
The document discusses wireless sensor networks and their applications. It describes wireless sensor networks as consisting of individual nodes that can interact with their environment by sensing or controlling physical parameters. It then discusses several applications of wireless sensor networks, including disaster relief, environment monitoring, intelligent buildings, facility management, machine maintenance, agriculture, healthcare, and logistics. Finally, it outlines some key requirements and mechanisms needed to implement wireless sensor networks, including communication, energy efficiency, self-configuration, collaboration, data-centric operation, and exploiting tradeoffs between different needs.Wireless Sensor Network



Wireless Sensor NetworkGanesh Khadsan
Ěý
The document summarizes a seminar presentation on wireless sensor networks. It discusses the architecture of WSNs, including sensor nodes, gateways, base stations, and networking topologies. It also covers the advantages and disadvantages of WSNs, their applications in fields like environmental monitoring and medical monitoring, and their future potential to bridge the physical and digital worlds.WSN NETWORK -MAC PROTOCOLS - Low Duty Cycle Protocols And Wakeup Concepts – ...



WSN NETWORK -MAC PROTOCOLS - Low Duty Cycle Protocols And Wakeup Concepts – ...ArunChokkalingam
Ěý
WSN NETWORKING CONCEPTS AND PROTOCOLS
MAC Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks,
Low Duty Cycle Protocols And Wakeup Concepts –
S-MAC,
Transport control protocols for Wireless sensor networks



Transport control protocols for Wireless sensor networksRushin Shah
Ěý
The document discusses traditional transport control protocols and their feasibility for use in wireless sensor networks. It describes how TCP and UDP are generally not suitable for WSNs due to their overhead and lack of features like congestion control that are needed in low power lossy networks. The document then outlines key considerations for designing new transport protocols for WSNs, including performing congestion control and reliable delivery, simplifying connection establishment, avoiding packet loss to reduce energy waste, and providing fairness across nodes. Transport protocols for WSNs need hop-by-hop approaches and mechanisms to reduce buffer usage and packet loss while conserving energy.IEEE 802.11 and Bluetooth



IEEE 802.11 and BluetoothHitesh Mohapatra
Ěý
This document discusses wireless networking technologies including IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi), Bluetooth, and their standards and specifications. It describes the basic concepts of wireless LANs including connecting devices, medium access control, basic service sets, extended service sets, frame formats, and addressing mechanisms. It also discusses Bluetooth standards, layers, and topologies such as piconets and scatternets.WSN-IEEE 802.15.4 -MAC Protocol



WSN-IEEE 802.15.4 -MAC ProtocolArunChokkalingam
Ěý
WSN-IEEE 802.15.4 -MAC Protocol
Low Duty Cycle Protocols And Wakeup Concepts –
S-MAC,
The Mediation Device Protocol
Contention based protocols – PAMAS,
Schedule based protocols – LEACH,
IEEE 802.15.4 MAC protocol,
IS-95 Cdma



IS-95 Cdmayogesh singh
Ěý
IS-95 CDMA is an air interface standard that uses code division multiple access (CDMA). It employs various techniques to improve system capacity and performance, including bandwidth recycling, power control, soft handoffs, diversity combining, and variable rate vocoding. Key aspects of IS-95 include the use of quadrature phase shift keying modulation at a 1.2288 Mcps chip rate, forward error correction coding, and multiple logical channels (pilot, sync, paging, traffic) defined using orthogonal Walsh codes.CS6003 AD HOC AND SENSOR NETWORKS



CS6003 AD HOC AND SENSOR NETWORKSKathirvel Ayyaswamy
Ěý
UNIT IV WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS (WSNS) AND MAC PROTOCOLS 9 Single node architecture: hardware and software components of a sensor node - WSN Network architecture: typical network architectures-data relaying and aggregation strategies -MAC layer protocols: self-organizing, Hybrid TDMA/FDMA and CSMA based MAC- IEEE 802.15.4. Hiperlan



HiperlanThen Murugeshwari
Ěý
HiperLAN was developed as a wireless local area network standard by ETSI to provide higher data rates than early 802.11 standards. HiperLAN Type 1 achieved data rates up to 2 Mbps for ad hoc networking. HiperLAN Type 2 was later developed to provide connection-oriented service up to 54 Mbps, with quality of service guarantees, security, and flexibility. It uses OFDM in the 5 GHz spectrum for robust transmission. While early products only achieved 25 Mbps, the standard provides a framework for higher speeds as technologies advance. HiperLAN is intended to complement wired networks by providing wireless connectivity in hotspot areas like offices, homes, and public places.Spread spectrum



Spread spectrumManish Srivastava
Ěý
Spread spectrum communication uses wideband noise-like signals that are hard to detect, intercept, or jam. It spreads data over multiple frequencies. There are two main techniques: direct sequence spread spectrum multiplies a data signal by a pseudorandom code, and frequency hopping spread spectrum modulates a narrowband carrier that hops between frequencies. Spread spectrum provides benefits like resistance to interference and jamming, better signal quality, and inherent security. It finds applications in wireless networks, Bluetooth, and CDMA cellular systems.TWO STAGE NETWORKS



TWO STAGE NETWORKSAakankshaR
Ěý
This Presentation describes the two stage networks used in the telecommunication switching network applications.wireless sensor network



wireless sensor networkA. Shamel
Ěý
wireless sensor network, the wireless sensor network performance requirement, Mac, medium access control, Mac protocolsRouting Protocols in WSN



Routing Protocols in WSNDarpan Dekivadiya
Ěý
This document discusses power aware routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. It begins by describing wireless sensor networks and how they are used to monitor environmental conditions. It then classifies routing protocols for sensor networks based on their functioning, node participation style, and network structure. Specific examples are provided for different types of routing protocols, including LEACH, TEEN, APTEEN, SPIN, Rumor Routing, and PEGASIS. Chain-based and clustering routing protocols are also summarized.Mac protocols



Mac protocolsjuno susi
Ěý
This document discusses medium access control (MAC) protocols, which regulate access to a shared wireless medium between nodes. It covers key requirements for MAC protocols including throughput efficiency, fairness, and low overhead. It also describes challenges like the hidden terminal problem, exposed terminal problem, and sources of overhead from collisions, overhearing, and idle listening. Finally, it categorizes common MAC protocols as fixed assignment, demand assignment, and random access and notes additional energy conservation requirements for wireless sensor networks.Common protocols



Common protocolsMr SMAK
Ěý
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) allows devices to access the Internet over wireless networks. There are three main categories of protocols for managing shared access to wireless networks: fixed assignment, demand assignment, and random assignment. Fixed assignment divides resources like frequency bands or time slots and allocates them exclusively. Demand assignment allocates resources only to nodes that need them. Random assignment does not preallocate resources and relies on collision detection and retransmission to manage shared access. Common protocols that fall under these categories include FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, ALOHA, and CSMA.Gsm signaling



Gsm signalingKannan Selvam
Ěý
The document discusses GSM signaling and mobile signaling. GSM signaling defines communications between the mobile and network using different protocols across interfaces. Mobile signaling involves the mobile searching for frequencies, synchronizing, downloading information, selecting a network, and signaling to the network by sending a service request when a call is made.Handoff in Mobile Communication



Handoff in Mobile CommunicationNoushad Hasan
Ěý
This document discusses handoff in mobile communication networks. It begins with defining handoff as the transition of signal transmission from one base station to an adjacent one as a user moves. It then discusses various handoff strategies such as prioritizing handoff calls over new calls, monitoring signal strength to avoid unnecessary handoffs, and reserving guard channels for handoff requests. The document also covers types of handoffs, how handoff is handled differently in 1G and 2G cellular systems, challenges like cell dragging, and concepts like umbrella cells to minimize handoffs for high-speed users.Mobile IP



Mobile IPMukesh Chinta
Ěý
This ppt contains information about mobile ip, entities, delivery, mobile ip optimizations, mobile ipv4 vs ipv6IT6601 MOBILE COMPUTING



IT6601 MOBILE COMPUTINGKathirvel Ayyaswamy
Ěý
Unit - I
Mobile Computing – Mobile Computing Vs wireless Networking – Mobile Computing Applications – Characteristics of Mobile computing – Structure of Mobile Computing Application. MAC Protocols – Wireless MAC Issues – Fixed Assignment Schemes – Random Assignment Schemes – Reservation Based Schemes.ZigBee Technology



ZigBee TechnologyNimi T
Ěý
The document introduces ZigBee, a wireless technology standard used for sensor and control networks. ZigBee offers low-cost, low-power wireless connectivity for devices. It uses the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and is intended for applications that require long battery life and secure networking. ZigBee supports mesh networking and can connect thousands of devices together over distances of up to 100 meters. Common applications of ZigBee include wireless light switches, HVAC controls, and other smart home and industrial IoT uses.Cellular network



Cellular networkshreb
Ěý
This document provides an overview of cellular networks. It discusses key concepts like cells, base stations, frequency reuse, and multiple access methods. It describes how location of mobile devices is managed through location updating and paging. It also covers handoff which allows active calls to continue seamlessly as users move between different cells.Channel assignment strategies



Channel assignment strategiesAJAL A J
Ěý
The document discusses different channel assignment strategies for wireless networks, including fixed channel assignment where each cell is predetermined channels and dynamic channel assignment where channels are allocated on request based on factors like channel occupancy. It also describes a partially overlapping channel (FPOC) assignment strategy that aims to increase capacity while minimizing interference through intelligent channel allocation between neighboring nodes.Mobile Network Layer



Mobile Network LayerRahul Hada
Ěý
Mobile Network Layer protocols and mechanisms allow nodes to change their point of attachment to different networks while maintaining ongoing communication. Key concepts include:
- Mobile IP adds mobility support to IP, allowing nodes to use the same IP address even when changing networks. It relies on home agents and care-of addresses.
- Registration allows mobile nodes to inform their home agent of their current location when visiting foreign networks. Tunneling and encapsulation techniques are used to forward packets to mobile nodes' current locations.
- Various routing protocols like DSDV have been developed for mobile ad hoc networks which have no fixed infrastructure and dynamic topologies.Wireless body area network



Wireless body area networkPratik Gondaliya
Ěý
This document discusses wireless body area networks (WBANs), which allow for inexpensive and continuous health monitoring through connecting various medical sensors and appliances located inside and outside the human body via wireless communication. WBANs have a three-tier architecture, consisting of intelligent sensor nodes on the body (Tier 1), a personal server like a cell phone (Tier 2) that interfaces with the sensors, and a medical server (Tier 3) that authenticates users, stores patient data, analyzes sensor data, and can alert emergency services if needed. WBANs allow remote monitoring of patients with chronic conditions and can alert hospitals to health issues even before symptoms occur.Adhoc wireless



Adhoc wirelessIpsita Sharma
Ěý
Ad hoc wireless networks allow devices to connect and communicate with each other without a centralized access point. Nodes in an ad hoc network relay messages through intermediate hops to reach destinations. Examples include Bluetooth networks and wireless mesh networks. Issues in ad hoc networks include medium access control, routing with mobility and bandwidth constraints, and providing quality of service guarantees.WIRELESS ATM BY SAIKIRAN PANJALA



WIRELESS ATM BY SAIKIRAN PANJALASaikiran Panjala
Ěý
The document discusses the emerging field of wireless ATM networks. It notes that both wireless technologies and ATM are still in their infancy, with no standards yet established. The document outlines some key aspects of wireless ATM networks, including using small picocell coverage areas served by base stations connected via a wired ATM backbone. It also discusses challenges like locating mobile units and establishing connections in the network. Overall, the document examines issues in developing protocols for wireless ATM networks to support broadband communications in the future.Manet



ManetPushkar Dutt
Ěý
Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANET) has become an exciting and important technology in recent years because of the rapid proliferation of wireless devices. A mobile adhoc network consists of mobile nodes that can move freely in an open environment. Communicating nodes in a Mobile Adhoc Network usually seek the help of other intermediate nodes to establish communication channels. In such an environment, malicious intermediate nodes can be a threat to the security of conversation between mobile nodes. The security experience from the Wired Network world is of little use in Wireless Mobile Ad hoc networks, due to some basic di_erences between the two Networks. Therefore, some novel solutions are required to make Mobile Adhoc Network secure.Improving coverage and capacity in cellular systems



Improving coverage and capacity in cellular systemsTarek Nader
Ěý
Cellular networks use various techniques to expand coverage and increase capacity as needs change over time, including cell splitting, beam tilting, cell sectoring, microcells, and frequency borrowing. Cell splitting involves dividing larger cells into smaller cells served by lower-power base stations to enable more spatial frequency reuse and greater system capacity, though it increases handoffs and costs. Beam tilting reduces interference between cells by tilting antenna beams downward. Cell sectoring divides cells into wedge-shaped sectors each with their own channels to decrease interference while reducing trunking efficiency. Microcells add capacity in hotspot areas without changing reuse factors. Frequency borrowing assigns congested cells frequencies from adjacent cells dynamically.A Review Paper On Communication Protocols For Wireless Sensor Networks



A Review Paper On Communication Protocols For Wireless Sensor NetworksBria Davis
Ěý
This document reviews communication protocols for wireless sensor networks. It begins by describing the basic components and applications of wireless sensor networks. It then discusses three main classifications of routing protocols for wireless sensor networks: hierarchical, flat, and location-based. Under each classification, several example protocols are described. Factors affecting the design of routing protocols, such as node deployment, energy efficiency, and quality of service, are also discussed. Finally, the document reviews several past studies that have analyzed and compared different routing protocols for wireless sensor networks.Optimized Projected Strategy for Enhancement of WSN Using Genetic Algorithms



Optimized Projected Strategy for Enhancement of WSN Using Genetic AlgorithmsIJMER
Ěý
This document summarizes an optimized projected strategy for enhancing wireless sensor networks using genetic algorithms. It describes a heterogeneous wireless sensor network model with normal, intermediate, and advanced sensor nodes having different initial energy levels. The proposed approach selects cluster heads based on the nodes' battery power and residual energy, giving intermediate and advanced nodes a higher probability of becoming cluster heads to balance energy consumption across the network. The strategy aims to increase the stability period when the first node dies and the overall network lifetime.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Hiperlan



HiperlanThen Murugeshwari
Ěý
HiperLAN was developed as a wireless local area network standard by ETSI to provide higher data rates than early 802.11 standards. HiperLAN Type 1 achieved data rates up to 2 Mbps for ad hoc networking. HiperLAN Type 2 was later developed to provide connection-oriented service up to 54 Mbps, with quality of service guarantees, security, and flexibility. It uses OFDM in the 5 GHz spectrum for robust transmission. While early products only achieved 25 Mbps, the standard provides a framework for higher speeds as technologies advance. HiperLAN is intended to complement wired networks by providing wireless connectivity in hotspot areas like offices, homes, and public places.Spread spectrum



Spread spectrumManish Srivastava
Ěý
Spread spectrum communication uses wideband noise-like signals that are hard to detect, intercept, or jam. It spreads data over multiple frequencies. There are two main techniques: direct sequence spread spectrum multiplies a data signal by a pseudorandom code, and frequency hopping spread spectrum modulates a narrowband carrier that hops between frequencies. Spread spectrum provides benefits like resistance to interference and jamming, better signal quality, and inherent security. It finds applications in wireless networks, Bluetooth, and CDMA cellular systems.TWO STAGE NETWORKS



TWO STAGE NETWORKSAakankshaR
Ěý
This Presentation describes the two stage networks used in the telecommunication switching network applications.wireless sensor network



wireless sensor networkA. Shamel
Ěý
wireless sensor network, the wireless sensor network performance requirement, Mac, medium access control, Mac protocolsRouting Protocols in WSN



Routing Protocols in WSNDarpan Dekivadiya
Ěý
This document discusses power aware routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. It begins by describing wireless sensor networks and how they are used to monitor environmental conditions. It then classifies routing protocols for sensor networks based on their functioning, node participation style, and network structure. Specific examples are provided for different types of routing protocols, including LEACH, TEEN, APTEEN, SPIN, Rumor Routing, and PEGASIS. Chain-based and clustering routing protocols are also summarized.Mac protocols



Mac protocolsjuno susi
Ěý
This document discusses medium access control (MAC) protocols, which regulate access to a shared wireless medium between nodes. It covers key requirements for MAC protocols including throughput efficiency, fairness, and low overhead. It also describes challenges like the hidden terminal problem, exposed terminal problem, and sources of overhead from collisions, overhearing, and idle listening. Finally, it categorizes common MAC protocols as fixed assignment, demand assignment, and random access and notes additional energy conservation requirements for wireless sensor networks.Common protocols



Common protocolsMr SMAK
Ěý
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) allows devices to access the Internet over wireless networks. There are three main categories of protocols for managing shared access to wireless networks: fixed assignment, demand assignment, and random assignment. Fixed assignment divides resources like frequency bands or time slots and allocates them exclusively. Demand assignment allocates resources only to nodes that need them. Random assignment does not preallocate resources and relies on collision detection and retransmission to manage shared access. Common protocols that fall under these categories include FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, ALOHA, and CSMA.Gsm signaling



Gsm signalingKannan Selvam
Ěý
The document discusses GSM signaling and mobile signaling. GSM signaling defines communications between the mobile and network using different protocols across interfaces. Mobile signaling involves the mobile searching for frequencies, synchronizing, downloading information, selecting a network, and signaling to the network by sending a service request when a call is made.Handoff in Mobile Communication



Handoff in Mobile CommunicationNoushad Hasan
Ěý
This document discusses handoff in mobile communication networks. It begins with defining handoff as the transition of signal transmission from one base station to an adjacent one as a user moves. It then discusses various handoff strategies such as prioritizing handoff calls over new calls, monitoring signal strength to avoid unnecessary handoffs, and reserving guard channels for handoff requests. The document also covers types of handoffs, how handoff is handled differently in 1G and 2G cellular systems, challenges like cell dragging, and concepts like umbrella cells to minimize handoffs for high-speed users.Mobile IP



Mobile IPMukesh Chinta
Ěý
This ppt contains information about mobile ip, entities, delivery, mobile ip optimizations, mobile ipv4 vs ipv6IT6601 MOBILE COMPUTING



IT6601 MOBILE COMPUTINGKathirvel Ayyaswamy
Ěý
Unit - I
Mobile Computing – Mobile Computing Vs wireless Networking – Mobile Computing Applications – Characteristics of Mobile computing – Structure of Mobile Computing Application. MAC Protocols – Wireless MAC Issues – Fixed Assignment Schemes – Random Assignment Schemes – Reservation Based Schemes.ZigBee Technology



ZigBee TechnologyNimi T
Ěý
The document introduces ZigBee, a wireless technology standard used for sensor and control networks. ZigBee offers low-cost, low-power wireless connectivity for devices. It uses the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and is intended for applications that require long battery life and secure networking. ZigBee supports mesh networking and can connect thousands of devices together over distances of up to 100 meters. Common applications of ZigBee include wireless light switches, HVAC controls, and other smart home and industrial IoT uses.Cellular network



Cellular networkshreb
Ěý
This document provides an overview of cellular networks. It discusses key concepts like cells, base stations, frequency reuse, and multiple access methods. It describes how location of mobile devices is managed through location updating and paging. It also covers handoff which allows active calls to continue seamlessly as users move between different cells.Channel assignment strategies



Channel assignment strategiesAJAL A J
Ěý
The document discusses different channel assignment strategies for wireless networks, including fixed channel assignment where each cell is predetermined channels and dynamic channel assignment where channels are allocated on request based on factors like channel occupancy. It also describes a partially overlapping channel (FPOC) assignment strategy that aims to increase capacity while minimizing interference through intelligent channel allocation between neighboring nodes.Mobile Network Layer



Mobile Network LayerRahul Hada
Ěý
Mobile Network Layer protocols and mechanisms allow nodes to change their point of attachment to different networks while maintaining ongoing communication. Key concepts include:
- Mobile IP adds mobility support to IP, allowing nodes to use the same IP address even when changing networks. It relies on home agents and care-of addresses.
- Registration allows mobile nodes to inform their home agent of their current location when visiting foreign networks. Tunneling and encapsulation techniques are used to forward packets to mobile nodes' current locations.
- Various routing protocols like DSDV have been developed for mobile ad hoc networks which have no fixed infrastructure and dynamic topologies.Wireless body area network



Wireless body area networkPratik Gondaliya
Ěý
This document discusses wireless body area networks (WBANs), which allow for inexpensive and continuous health monitoring through connecting various medical sensors and appliances located inside and outside the human body via wireless communication. WBANs have a three-tier architecture, consisting of intelligent sensor nodes on the body (Tier 1), a personal server like a cell phone (Tier 2) that interfaces with the sensors, and a medical server (Tier 3) that authenticates users, stores patient data, analyzes sensor data, and can alert emergency services if needed. WBANs allow remote monitoring of patients with chronic conditions and can alert hospitals to health issues even before symptoms occur.Adhoc wireless



Adhoc wirelessIpsita Sharma
Ěý
Ad hoc wireless networks allow devices to connect and communicate with each other without a centralized access point. Nodes in an ad hoc network relay messages through intermediate hops to reach destinations. Examples include Bluetooth networks and wireless mesh networks. Issues in ad hoc networks include medium access control, routing with mobility and bandwidth constraints, and providing quality of service guarantees.WIRELESS ATM BY SAIKIRAN PANJALA



WIRELESS ATM BY SAIKIRAN PANJALASaikiran Panjala
Ěý
The document discusses the emerging field of wireless ATM networks. It notes that both wireless technologies and ATM are still in their infancy, with no standards yet established. The document outlines some key aspects of wireless ATM networks, including using small picocell coverage areas served by base stations connected via a wired ATM backbone. It also discusses challenges like locating mobile units and establishing connections in the network. Overall, the document examines issues in developing protocols for wireless ATM networks to support broadband communications in the future.Manet



ManetPushkar Dutt
Ěý
Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANET) has become an exciting and important technology in recent years because of the rapid proliferation of wireless devices. A mobile adhoc network consists of mobile nodes that can move freely in an open environment. Communicating nodes in a Mobile Adhoc Network usually seek the help of other intermediate nodes to establish communication channels. In such an environment, malicious intermediate nodes can be a threat to the security of conversation between mobile nodes. The security experience from the Wired Network world is of little use in Wireless Mobile Ad hoc networks, due to some basic di_erences between the two Networks. Therefore, some novel solutions are required to make Mobile Adhoc Network secure.Improving coverage and capacity in cellular systems



Improving coverage and capacity in cellular systemsTarek Nader
Ěý
Cellular networks use various techniques to expand coverage and increase capacity as needs change over time, including cell splitting, beam tilting, cell sectoring, microcells, and frequency borrowing. Cell splitting involves dividing larger cells into smaller cells served by lower-power base stations to enable more spatial frequency reuse and greater system capacity, though it increases handoffs and costs. Beam tilting reduces interference between cells by tilting antenna beams downward. Cell sectoring divides cells into wedge-shaped sectors each with their own channels to decrease interference while reducing trunking efficiency. Microcells add capacity in hotspot areas without changing reuse factors. Frequency borrowing assigns congested cells frequencies from adjacent cells dynamically.Similar to Wireless sensor network (20)
A Review Paper On Communication Protocols For Wireless Sensor Networks



A Review Paper On Communication Protocols For Wireless Sensor NetworksBria Davis
Ěý
This document reviews communication protocols for wireless sensor networks. It begins by describing the basic components and applications of wireless sensor networks. It then discusses three main classifications of routing protocols for wireless sensor networks: hierarchical, flat, and location-based. Under each classification, several example protocols are described. Factors affecting the design of routing protocols, such as node deployment, energy efficiency, and quality of service, are also discussed. Finally, the document reviews several past studies that have analyzed and compared different routing protocols for wireless sensor networks.Optimized Projected Strategy for Enhancement of WSN Using Genetic Algorithms



Optimized Projected Strategy for Enhancement of WSN Using Genetic AlgorithmsIJMER
Ěý
This document summarizes an optimized projected strategy for enhancing wireless sensor networks using genetic algorithms. It describes a heterogeneous wireless sensor network model with normal, intermediate, and advanced sensor nodes having different initial energy levels. The proposed approach selects cluster heads based on the nodes' battery power and residual energy, giving intermediate and advanced nodes a higher probability of becoming cluster heads to balance energy consumption across the network. The strategy aims to increase the stability period when the first node dies and the overall network lifetime.An Adaptive Energy Efficient Reliable Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Ne...



An Adaptive Energy Efficient Reliable Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Ne...IDES Editor
Ěý
A reliable routing protocol for wireless sensor
networks (WSN) should be capable of adjusting to
constantly varying network conditions while conserving
maximum power. Existing Routing protocols provide
reliability at the cost of high energy consumption. In this
paper, we propose to develop an Adaptive Energy Efficient
Reliable Routing Protocol (AEERRP) with the aim of
keeping the energy consumption low while achieving high
reliability. In our proposed protocol, the data forwarding
probability is adaptively adjusted based on the measured
loss conditions at the sink. So only for high loss rates, a node
makes use of high transmission power to arrive at the sink.
Whenever the loss rate is low, it adaptively lessens the
transmission power. Since the source rebroadcasts the data,
until the packet loss is minimized, high data reliability is
achieved. By simulation results we show that the proposed
protocol achieves high reliability while ensuring low energy
consumption and overhead.QoS in WSN thesis



QoS in WSN thesisSujaritha Sundaresan
Ěý
This document is a project report submitted by four students for their Bachelor of Engineering degree. It examines quality of service improvement in wireless sensor networks. Specifically, it studies cluster-based routing protocols like LEACH and proposes modifications to LEACH called MODLEACH that introduces efficient cluster head replacement and dual transmitting power levels. Thresholding techniques are also incorporated into MODLEACH to further boost performance based on metrics like throughput, network lifetime and cluster head formations. The report analyzes and compares the performance of LEACH, MODLEACH, MODLEACH with hard thresholds and MODLEACH with soft thresholds through simulation and implementation in Qualnet and Matlab.De3211001104



De3211001104IJMER
Ěý
This document summarizes and compares several routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. It begins with an introduction to wireless sensor networks and discusses some of the key challenges in routing for these networks, such as large numbers of sensor nodes, energy constraints, and random node deployment. The document then categorizes routing protocols as flat-based, hierarchical-based, or location-based and focuses on reviewing various dynamic and static hierarchical/clustering-based routing protocols. Several popular protocols are described in detail, including LEACH, EECS, PEGASIS, and EEPSC. The pros and cons of each approach are discussed.Computational Analysis of Routing Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Network



Computational Analysis of Routing Algorithm for Wireless Sensor NetworkIRJET Journal
Ěý
This document discusses an energy-efficient routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks (WSNs) proposed by the authors. It begins with background on WSNs and challenges related to limited energy. Then, it discusses prior work on routing protocols like LEACH and proposes a new algorithm. The key contributions are formulating control node selection as an optimization problem considering energy and distance, and using particle swarm optimization to solve this problem. This aims to improve energy efficiency for multi-tasking in software-defined WSNs compared to traditional protocols.Spread Spectrum Based Energy Efficient Wireless Sensor Networks



Spread Spectrum Based Energy Efficient Wireless Sensor NetworksIDES Editor
Ěý
The Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) is
considered to be one of the most promising emerging
technologies. However one of the main constraints which
is holding back its wide range of applications is the
battery life of the sensor node and thus effecting the
network life. A new approach to this problem has been
presented in this paper. The proposed method is suitable
for event driven applications where the event occurrence
is very rare. The system uses spread spectrum as a means
of communication.IRJET- A Comprehensive Study in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) using Artif...



IRJET- A Comprehensive Study in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) using Artif...IRJET Journal
Ěý
This document discusses using an artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm to optimize wireless sensor networks (WSN). It begins with an introduction to WSNs, including their topologies, types, limitations, and applications. It then provides details on ABC algorithms and how they can be applied to improve the performance of WSNs by addressing issues like energy efficiency, reliable data transmission, and network lifetime. The document concludes that ABC algorithms have been shown to be effective optimization techniques for complex problems in WSNs.Routing protocolsin Wireless sensor network 



Routing protocolsin Wireless sensor network dilip pareek
Ěý
This document provides an overview and critical review of routing protocols in wireless sensor networks. It begins with an introduction to wireless sensor networks and their applications. It then discusses several related works on routing protocols. The main body discusses different types of routing protocols, including location-based protocols like MECN and GEAR, hierarchical protocols like LEACH and PEGASIS, and data-centric protocols like SPIN and Directed Diffusion. It provides examples of each type and evaluates them based on factors like energy efficiency, scalability, reliability and more. Finally, it lists references for further reading on routing protocols in wireless sensor networks.Wireless Sensor Networks



Wireless Sensor NetworksSRAVANIP22
Ěý
This document outlines the course objectives, outcomes, and content for a Wireless Sensor Networks course. The course objectives are to determine network architecture, node discovery, deployment strategies, fault tolerance, network security, and challenges of wireless networking at various protocol layers. The course content includes an overview of wireless sensor networks, network architectures, single node architecture and components, energy consumption, operating systems, and gateway concepts. It provides modules on topics such as applications, enabling technologies, and optimization goals.A Review On Reactive And Proactive Wireless Sensor Networks Protocols



A Review On Reactive And Proactive Wireless Sensor Networks ProtocolsMary Montoya
Ěý
This document reviews and summarizes reactive and proactive wireless sensor network protocols. It begins with an abstract discussing the importance of energy utilization in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) due to resource-constrained battery-powered sensor nodes. The document then provides background on WSNs, describing their origin, characteristics, and applications. It discusses routing protocols for WSNs, categorizing them as proactive (table-driven) or reactive (on-demand). Specific protocols discussed include Low Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy (LEACH) and Stable Cluster Head Election (SCHE) Protocol, which are cluster-based routing protocols aimed at improving energy efficiency and extending network lifetime.G0933443



G0933443IOSR Journals
Ěý
VEBEK is an energy-efficient framework for secure communication in wireless sensor networks. It uses dynamic encryption keys based on the residual virtual energy of sensor nodes, eliminating the need for rekeying messages. Each packet is encrypted with a different one-time key, improving security. VEBEK provides authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation without enlarging packets through modular design. It can efficiently detect and filter malicious data through two operational modes: VEBEK-1 watches all neighbors, VEBEK-2 watches some nodes statistically. Evaluation shows VEBEK eliminates malicious data without transmission overhead.Ijetr021229



Ijetr021229ER Publication.org
Ěý
ER Publication,
IJETR, IJMCTR,
Journals,
International Journals,
High Impact Journals,
Monthly Journal,
Good quality Journals,
Research,
Research Papers,
Research Article,
Free Journals, Open access Journals,
erpublication.org,
Engineering Journal,
Science Journals,
Ijetr021229



Ijetr021229Engineering Research Publication
Ěý
Engineering Research Publication
Best International Journals, High Impact Journals,
International Journal of Engineering & Technical Research
ISSN : 2321-0869 (O) 2454-4698 (P)
www.erpublication.orgA Review Study on Shortest Path in WSN to detect the Abnormal Packet for savi...



A Review Study on Shortest Path in WSN to detect the Abnormal Packet for savi...Editor IJMTER
Ěý
The main motive of this research is to study energy-efficient data-gathering mechanisms to
abnormal packet data for saving the energy. To detect the abnormal packet irregularities is useful for
saving energy, as well as for management of network, because the patterns found can be used for
both decision making in applications and system performance tuning. Node distribution in WSNs is
either deterministic or self-organizing and application dependant. The sensor nodes in WSNs have
minimum energy and they use their energy for communication and sensing.3. journal paper nov 10, 2017 ( dhyan)



3. journal paper nov 10, 2017 ( dhyan)IAESIJEECS
Ěý
This document summarizes research on energy efficient multipath routing techniques in wireless sensor networks. It reviews 24 related works that propose and evaluate various multipath routing protocols to increase network lifetime and balance energy consumption. The routing protocols are categorized based on path establishment, network structure, and protocol operation. Key goals of multipath routing include minimizing total energy consumption, extending network lifetime, improving load balancing, and providing reliable and efficient data transmission.Some Aspects of Wireless Sensor Networks



Some Aspects of Wireless Sensor Networkspijans
Ěý
The development of the wireless sensor networks (WSNs) in various applications like Defense, Health,
Environment monitoring, Industry etc. always attract many researchers in this field. WSN is the network
which consists of collection of tiny devices called sensor nodes. Sensor node typically combines wireless
radio transmitter-receiver and limited energy, restricted computational processing capacity and
communication band width. These sensor node sense some physical phenomenon using different
transduces. The current improvement in sensor technology has made possible WSNs that have wide and
varied applications. While selecting the right sensor for application a number of characteristics are
important. This paper provides the basics of WSNs including the node characteristics. It also throws light
on the different routing protocols.Some aspects of wireless sensor networks



Some aspects of wireless sensor networkspijans
Ěý
The development of the wireless sensor networks (WSNs) in various applications like Defense, Health,
Environment monitoring, Industry etc. always attract many researchers in this field. WSN is the network
which consists of collection of tiny devices called sensor nodes. Sensor node typically combines wireless
radio transmitter-receiver and limited energy, restricted computational processing capacity and
communication band width. These sensor node sense some physical phenomenon using different
transduces. The current improvement in sensor technology has made possible WSNs that have wide and
varied applications. While selecting the right sensor for application a number of characteristics are
important. This paper provides the basics of WSNs including the node characteristics. It also throws light
on the different routing protocols.G017344246



G017344246IOSR Journals
Ěý
This document provides an overview of hierarchical energy protocols in wireless sensor networks. It discusses several key protocols including LEACH, PEGASIS, TEEN, and APTEEN. LEACH is described as a clustered-based protocol that randomly selects cluster heads to help distribute the energy load. PEGASIS is presented as an improvement on LEACH that forms chains between sensor nodes to help reduce energy usage. TEEN is a reactive protocol designed for time-critical applications, using hard and soft thresholds to reduce transmissions. Finally, APTEEN is summarized as an extension of TEEN that aims to support both periodic data collection and responding to important events.A review of Hierarchical energy Protocols in Wireless Sensor Network



A review of Hierarchical energy Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networkiosrjce
Ěý
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) is a double blind peer reviewed International Journal that provides rapid publication (within a month) of articles in all areas of computer engineering and its applications. The journal welcomes publications of high quality papers on theoretical developments and practical applications in computer technology. Original research papers, state-of-the-art reviews, and high quality technical notes are invited for publications. Recently uploaded (20)
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ěý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxIntellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
Ěý
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
Ěý
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
Ěý
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spots—systemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AI—that could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
Ěý
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHEntity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ěý
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatOral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM
Ěý
Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit? Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ěý
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatInterim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
Ěý
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRM



How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRMCeline George
Ěý
This slide will represent how to configure Recurring revenue. Recurring revenue are the income generated at a particular interval. Typically, the interval can be monthly, yearly, or we can customize the intervals for a product or service based on its subscription or contract. Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdf



Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdfSamarHosni3
Ěý
Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdfInventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory App



Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory AppCeline George
Ěý
This slide will helps us to efficiently create detailed reports of different records defined in its modules, both analytical and quantitative, with Odoo 17 ERP.Wireless sensor network
- 1. CALCUTTA INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT, KOLKATA, BATCH 2009-2013, C.S.E DEPARTMENT, DURING 4rth YEAR 2012 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK - A Survey by RAMESH VERMA ANIL KUMAR PRAVIND KUMAR
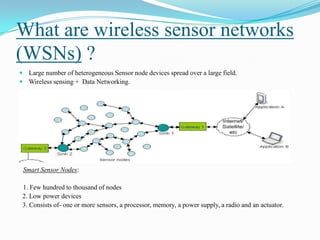
- 2. What are wireless sensor networks (WSNs) ? ď‚— Large number of heterogeneous Sensor node devices spread over a large field. ď‚— Wireless sensing + Data Networking. Smart Sensor Nodes: 1. Few hundred to thousand of nodes 2. Low power devices 3. Consists of- one or more sensors, a processor, memory, a power supply, a radio and an actuator.
- 3. ENERGY REQUIREMENTS FOR NODES ď‚— Can harvest energy during the idle time . ď‚— Sensor nodes can efficiently convert environmental energy to its electrical energy. ď‚— Self powered circuitry of nodes.
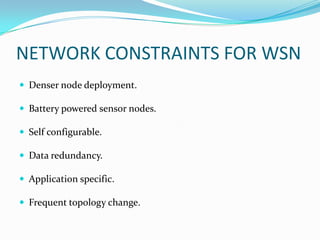
- 4. NETWORK CONSTRAINTS FOR WSN ď‚— Denser node deployment. ď‚— Battery powered sensor nodes. ď‚— Self configurable. ď‚— Data redundancy. ď‚— Application specific. ď‚— Frequent topology change.
- 5. NETWORK DESIGN OBJECTIVES  Low power consuming nodes are required.  Scalability – network protocol design should be scalable to different network sizes.  Can deliver data over noisy ,error prone, time varying wireless channel.  Efficient use of bandwidth.  Fault tolerancnce
- 6. ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN WSN Responsible for maintaining routes in the network Types: 1. Location based protocols 2. Data-centric protocols 3. Hierarchical based protocols 4. Mobility based protocols 5. Multi-path based protocols 6. QOS based protocols
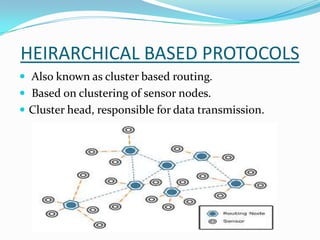
- 7. HEIRARCHICAL BASED PROTOCOLS ď‚— Also known as cluster based routing. ď‚— Based on clustering of sensor nodes. ď‚— Cluster head, responsible for data transmission.
- 8. LEACH PROTOCOL ď‚— Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy. ď‚— Clustering task is rotated among nodes. ď‚— Its operation is divided into two rounds 1. Setup phase: organize network into clusters 2. Steady state phase: data aggregation, compression and transmission to the sink.
- 9. APPLICATIONS  Monitoring and control of industrial appliances.  In military for surveillance .  Forest fire detection.  Agriculture and Ocean-for monitoring fish  Medical- Monitoring people’s locations and health condition.
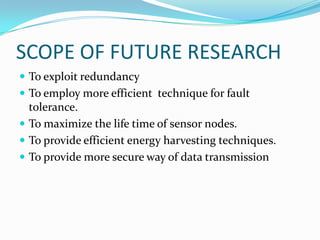
- 10. SCOPE OF FUTURE RESEARCH ď‚— To exploit redundancy ď‚— To employ more efficient technique for fault tolerance. ď‚— To maximize the life time of sensor nodes. ď‚— To provide efficient energy harvesting techniques. ď‚— To provide more secure way of data transmission
- 11. FUTURE SCOPE
- 12. CONCLUSION The ultimate objective behind the routing protocol is to keep the sensor operating for as far as possible, thus extending the network lifetime.
- 13. REFERENCES  S.K. Singh, M.P. Singh, and D.K. Singh, “A survey of Energy-Efficient Hierarchical Cluster-base Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks”  M. J. Handy, M. Haase, D. Timmermann” A survey on low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy with deterministic cluster-head section”  Jamal N. Al-Karaki and Ahmed E. Kamal,” Routing techniques in wireless sensor networks: A survey”
- 14. THANK YOU!






