Absolute & relative configuration
Download as PPTX, PDF25 likes10,263 views
1. Relative configuration compares the arrangement of atoms in space of one compound to another, while absolute configuration precisely describes the arrangement of atoms in space. 2. Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules were developed in the 1950s to determine absolute configuration, assigning R or S based on the atomic priorities and spatial arrangement of groups around chiral carbons. 3. To determine absolute configuration using Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules, groups attached to a chiral carbon are ranked by priority and the molecule is oriented such that the lowest priority group is in the back. Clockwise arrangement is labeled R and counterclockwise is S.
1 of 21
Downloaded 106 times



![No bonds are made or broken at the chiral carbon
in this experiment. Therefore, when (+) d-3-buten-2-ol
and (+) d -2-butanol have the same sign of rotation, the
arrangement of atoms in space at the chiral carbon atom
is analogous. The twohave the same relative configuration.
CH3CHCH2CH3
OH
Pd
[a] + 33.2┬░ [a] + 13.5┬░
Relative configuration
CH3CHCH
OH
CH2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/absoluterelativeconfiguration-161122075307/85/Absolute-amp-relative-configuration-5-320.jpg)
![Not all compounds that have the same relative
configuration have the same sign of rotation. No bonds
are made or broken at the chiral carbon in the
reaction shown, so the relative positions of the atoms
are the same. Yet the sign of rotation can change.
CH3CH2CHCH2Br
CH3
HBr
[a] -5.8┬░ [a] + 4.0┬░
Relative configuration
CH3CH2CHCH2OH
CH3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/absoluterelativeconfiguration-161122075307/85/Absolute-amp-relative-configuration-6-320.jpg)














Recommended
Stereochemistry-Organic Chemistry



Stereochemistry-Organic ChemistryMr.S.SEETARAM SWAMY
╠²
The document discusses different types of isomers including constitutional isomers, stereoisomers, geometric isomers (cis and trans), optical isomers (enantiomers), and diastereomers. It provides examples and definitions for each type of isomerism. Key points covered include how cis and trans isomers differ based on the orientation of groups around a double bond, how enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images that have different effects in living systems, and methods for assigning absolute configuration using Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules.Carbanions



CarbanionsvinayRVinay
╠²
Carbanions are carbon atoms with a negative charge that are formed through various mechanisms. They can be classified based on their formation method such as through heterocyclic cleavage, proton abstraction using a base, decarboxylation, addition of a nucleophile to an alkene, or formation of an organometallic compound. Carbanion stability depends on factors like the electronegativity of the carbon, inductive effects, resonance effects, and attachment to sulfur or phosphorus. Aromatic carbanions and those with electron-withdrawing groups are particularly stable due to resonance delocalization. Carbanions have applications in reactions like the Perkin reaction, Claisen condensation, benzoin condensation,Stereoisomers



StereoisomersAravinda Kumar
╠²
ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ£DRUGSŌĆØ do something in our body as a result of their molecular structure, which determines:
1. Physicochemical properties
2. Chemical / biochemical reactivity
3. Shape
4. STEREO-CHEMISTRY
Carbocations and carbanions



Carbocations and carbanionsAshitoshPanchal
╠²
This document discusses organic reaction intermediates, specifically carbocations and carbanions. It defines them as positively or negatively charged carbon-containing ions that are formed during chemical reactions and then react further to form final products. The key features, methods of formation, factors affecting stability, and synthetic applications of carbocations and carbanions are described. Inductive effects, resonance effects, and hyperconjugation influence the stability of these intermediates. Carbocations and carbanions are involved in many common organic reaction types such as eliminations, substitutions, additions, and rearrangements.FREE RADICALS , CARBENES AND NITRENES.pptx



FREE RADICALS , CARBENES AND NITRENES.pptxtenzinpalmo3
╠²
This document discusses free radicals, carbenes, and nitrenes. It defines each type of species, describes their characteristics such as electronic structure and stability. The document outlines different types for each species and methods for their formation and synthetic applications. Free radicals form through bond homolysis and vary in stability based on alkyl substituents. Carbenes are divalent carbon species that exist as singlet or triplet forms with different hybridizations. Nitrenes are analogous to carbenes but with nitrogen and vary in stability and spin state. Examples of formation and trapping methods are provided along with sample synthetic reactions for each reactive intermediate.Pericyclic reaction



Pericyclic reactionRANADEEPBORGOHAIN
╠²
This document discusses pericyclic reactions, which are concerted reactions where the transition state involves electrons moving in a cyclic pattern. It describes the key properties of pericyclic reactions, including that they are stereospecific and often light- or heat-activated. It then covers various classes of pericyclic reactions like electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions like the Diels-Alder reaction, sigmatropic rearrangements including the Cope rearrangement, and group transfer reactions. Examples are provided to illustrate each reaction type.Projection formulae



Projection formulaeKritikaChandel1
╠²
Detailed information about Flying wedge projection, Newman projection, Sawhorse projection, and Fischer projection.Stereochemistry



StereochemistryAZMIN MOGAL
╠²
stereochemistry and drug action ; basic introduction about stereochemistry and stereoisomers ; pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics concept of stereochemistry ; easson Stedman hypothesis ; stereo selectivity criteria .Stereochemistry (Configuration of Geometrical Isomers)



Stereochemistry (Configuration of Geometrical Isomers)Ashwani Dhingra
╠²
These slides explain the DL and RS system of nomenclature of optical isomers along with sequence rules.Topicity



TopicityDr. Krishna Swamy. G
╠²
Homomorphic ligands / groups/ atoms, Homotopic, heterotopic, enantiotopic, prochirality and diastereotopic ligands and faces with examplesCahn ingold-prelog nomenclature



Cahn ingold-prelog nomenclatureBiji Saro
╠²
The document summarizes the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) system of stereochemistry nomenclature. It outlines the main rules for assigning priority to groups around a stereocenter and determining whether a molecule is R or S. Examples are provided to illustrate the rules, such as assigning priorities based on atomic number and distinguishing between cis and trans isomers. The importance of distinguishing between enantiomers is also briefly discussed.Knorr Pyrazole Synthesis (M. Pharm) 



Knorr Pyrazole Synthesis (M. Pharm) MohdShafeeque4
╠²
The document discusses the Knorr pyrazole synthesis reaction which converts hydrazines or derivatives and 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds to pyrazoles using an acid catalyst. The mechanism involves acid-catalyzed imine formation on either carbonyl carbon, followed by attack of the other nitrogen on the other carbonyl group. This forms a diimine compound which deprotonates to generate the final pyrazole product. Several examples of pyrazoles synthesized using this reaction are mentioned, including antipyrine, celecoxib, and metamizole sodium which have various medical applications.Retrosynthes analysis and disconnection approach 



Retrosynthes analysis and disconnection approach ProttayDutta1
╠²
Retrosynthetic analysis is a technique used to plan organic syntheses by working backwards from the target molecule. It involves mentally deconstructing the target molecule through sequential disconnections and functional group transformations until commercially available starting materials are reached. Each disconnection produces synthons, which are idealized fragments that represent possible reaction precursors. Common types of disconnections include C-X, C-C, and carbonyl bonds. The goal of retrosynthesis is to simplify the target structure and design multiple possible synthesis routes leading from simple starting materials to the target. It helps chemists discover efficient syntheses by considering the reactivity, selectivity, and availability of materials at each step.Reduction reactions



Reduction reactionsPriyanka Jaiswal
╠²
This document provides an overview of reduction reactions in organic chemistry. It discusses various types of reduction reactions including catalytic hydrogenation, hydride transfer reactions using reagents like LiAlH4 and NaBH4, dissolving metal reductions, and others. Specific metal hydride reductions using boron and aluminum reagents like sodium borohydride, sodium cyanoborohydride, lithium aluminum hydride, and diisobutylaluminum hydride are explained in detail including their mechanisms and selectivity. Diimide reduction is also briefly covered. The document concludes with a bibliography of reference books on organic reaction mechanisms.Photoaddition and photo fragmentation reaction



Photoaddition and photo fragmentation reactionAshu Vijay
╠²
Photoaddition and photofragmentation reactions involve the use of light to induce chemical reactions. Photoaddition reactions form a single product when electronically excited molecules add across double bonds or carbonyl groups. Photofragmentation reactions introduce functional groups by cleaving bonds upon absorption of light, forming reactive diradicals or intermediates like carbenes and nitrenes which can undergo further reactions. Primary photofragmentation involves alpha cleavage of a sigma bond directly attached to the chromophore to form diradicals. Beta cleavage occurs when a leaving group is on the alpha carbon through a beta elimination reaction.Stereochemistry (Conformational Isomerism)



Stereochemistry (Conformational Isomerism)Ashwani Dhingra
╠²
This document discusses conformational isomerism, which results from different three-dimensional arrangements of atoms that can form due to the rotation of single bonds. It focuses on the conformations of ethane, butane, cycloalkanes like cyclopropane and cyclohexane, and amine compounds. The key conformations discussed are staggered, eclipsed, chair, boat, and twist-boat, with the document explaining their relative stabilities and energies. It also discusses angle strain, torsional strain, and steric strain that can result from different conformations.Unit 3 Pyrrole



Unit 3 PyrroleSowmiya Perinbaraj
╠²
This document discusses the heterocyclic compound pyrrole. It begins by defining pyrrole as an unsaturated five-membered ring containing nitrogen. Pyrrole is an important compound found naturally in substances like alkaloids, hemoglobin, and chlorophyll. The document then describes several methods for synthesizing pyrrole, including the Paal-Knorr, Hantzsch, and Knorr syntheses. It also discusses some reactions pyrrole undergoes, such as electrophilic substitution and reduction. Finally, it lists several medicinal uses of pyrrole derivatives, including the amino acid proline, the stimulant nicotine, and drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease and pepticBasic aspects of Stereochemistry



Basic aspects of StereochemistryDHARMENDRA BARIA
╠²
This document provides an overview of stereochemistry. It begins by defining constitutional and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers have the same connectivity but different arrangements in space, and include enantiomers and diastereomers. The document then discusses chiral centers and molecules, and how the presence of a chiral center leads to chirality. It also covers topics such as optical activity, properties of enantiomers and diastereomers, meso compounds, geometric isomers, and resolving racemic mixtures. Resolution methods discussed include conversion to diastereomers and differential absorption chromatography.Seminar on name reaction



Seminar on name reactionnitin lambe
╠²
in this ppt 4 reactions are explain with mechanism namely clemenson,oppenauer,wolf kischner, and mpv reduction....this is useufl for introductory partAnomeric effect



Anomeric effectDaniel Morton
╠²
The anomeric effect was discovered in 1955 with the work of J.T. Edward, N.-J. Chu, and R.U. Lemieux.
Contributed by: Cody F. Bender, Charles E. Price (Undergraduates), University of Utah, 2016
Stereochemistry



StereochemistrySirod Judin
╠²
This chapter discusses stereochemistry and chirality. It defines stereoisomers such as enantiomers, which are nonsuperimposable mirror images, and diastereomers, which are not mirror images. Chiral carbons have four different groups and exist as enantiomers. Enantiomers have identical properties except for how they interact with other chiral molecules and rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions. Methods to determine chirality such as assigning R/S configurations and using Fischer projections are covered. The chapter also discusses resolving enantiomers through formation of diastereomers.Reactions intermediate



Reactions intermediatesaiswathivarma
╠²
This document provides an overview of various carbon-based reaction intermediates including carbocations, carbanions, carbenes, free radicals, nitrenes, and nitrenium ions. It discusses their generation, structure, stability, reactions, and detection methods. Key points include that carbocations are positively charged carbon species that react as electrophiles, while carbanions are negatively charged carbon species that react as nucleophiles. Carbenes contain a carbon with six valence electrons in a triplet or singlet state. Free radicals contain one or more unpaired electrons. Nitrenes and nitrenium ions involve a reactive nitrogen species. Detection methods include NMR, EPR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and trapping reactions.Annulenes and Heteroannulenes - Premie Fernandes



Annulenes and Heteroannulenes - Premie FernandesBebeto G
╠²
This document discusses annulenes and heteroannulenes. Annulenes are monocyclic conjugated systems represented by the general formula (CH)2m and include benzene and cyclooctatetraene. Heteroannulenes contain one or more heteroatoms in the ring, such as pyridine and thiophene. Aromaticity in these systems is determined by Huckel's rule of (4n+2)ŽĆ electrons. The document examines various annulene and heteroannulene structures of different ring sizes and whether they obey Huckel's rule and exhibit aromatic, anti-aromatic, or non-aromatic behavior.Aromaticity in benzenoid and non-benzenoid compunds



Aromaticity in benzenoid and non-benzenoid compundsSPCGC AJMER
╠²
This document summarizes aromaticity in benzoid and non-benzoid compounds. It defines aromaticity as the property of conjugated cycloalkenes that enhances stability through delocalization of pi electrons. The rules of aromaticity are outlined, including that aromatic compounds must be cyclic, have planar p-orbitals, and follow H├╝ckel's rule of 4n+2 pi electrons. Benzoid aromatics include benzene and polycyclic structures like naphthalene. Non-benzoid aromatics do not contain benzene rings and examples provided are azulene, tropone, and heterocyclic compounds.Mannich reaction



Mannich reactionAanchal Gupta
╠²
The Mannich reaction involves the condensation of an enolizable carbonyl compound, an amine or ammonia, and formaldehyde to form an aminomethyl derivative known as a Mannich base. Ketones are most commonly used as the carbonyl compound. The reaction proceeds via the generation of an imine intermediate from the carbonyl compound and amine, which then reacts with formaldehyde to form the Mannich base. Mannich bases have applications in synthesizing natural products like alkaloids and building ring systems.Heterocyclic compounds - Thiophene - Synthesis of Thiophene - Characteristic ...



Heterocyclic compounds - Thiophene - Synthesis of Thiophene - Characteristic ...Dr Venkatesh P
╠²
Thiophene can be synthesized through various methods including passing a mixture of acetylene and hydrogen sulfide over aluminum oxide at high temperature or by distilling sodium succinate with phosphorus pentasulfide. Thiophene undergoes characteristic reactions such as electrophilic substitution, reaction with organolithium reagents, and reductions. Some medicinal uses of thiophene derivatives include their use as local anesthetics, diuretics, anthelmintics, and antifungals.Fused heterocyclic compound indole



Fused heterocyclic compound indoleDrx Mathivanan Selvam
╠²
This slide discusses about basic indole nucleus, its chemistry, synthesis, reactions and medicinal uses of Indolyl derivatives..Indole is basically fused heterocyclic compoundFused heterocyclic compound isoquinoline



Fused heterocyclic compound isoquinolineDrx Mathivanan Selvam
╠²
This slides discusses about Isoquinoline nucleus (fused heterocyclic compound). this ring contain benzene ring fused with pyridine nucleus with nitrogen atomIsomerism Part - 2



Isomerism Part - 2Akhil Nagar
╠²
1) The document discusses absolute and relative configuration of stereoisomers. Absolute configuration is assigned using CIP rules which assign R and S labels based on priority of groups around a chiral carbon.
2) Relative configuration refers to D and L labels assigned based on comparison to glyceraldehyde stereochemistry. Compounds related to D-glyceraldehyde have the D label and those related to L-glyceraldehyde have the L label.
3) Chirality can arise without a chiral carbon center. Allene and substituted biphenyls lack chiral carbons but have restricted rotation that leads to enantiomers with optical activity.Stereochemistry configuration of R and S



Stereochemistry configuration of R and SSourav Shipu
╠²
The R/S system labels each chiral center in a molecule as either R or S based on the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. These rules assign priorities to the four substituents of a chiral center based on atomic number. The molecule is oriented so the lowest priority substituent is pointed away from the viewer. If the priorities of the remaining three decrease clockwise, it is labeled R; if counterclockwise, it is labeled S. This system has greater generality than the D/L system and can distinguish between diastereomers. The R/S labels do not correspond directly to whether a molecule is dextrorotatory or levorotatory.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Stereochemistry (Configuration of Geometrical Isomers)



Stereochemistry (Configuration of Geometrical Isomers)Ashwani Dhingra
╠²
These slides explain the DL and RS system of nomenclature of optical isomers along with sequence rules.Topicity



TopicityDr. Krishna Swamy. G
╠²
Homomorphic ligands / groups/ atoms, Homotopic, heterotopic, enantiotopic, prochirality and diastereotopic ligands and faces with examplesCahn ingold-prelog nomenclature



Cahn ingold-prelog nomenclatureBiji Saro
╠²
The document summarizes the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) system of stereochemistry nomenclature. It outlines the main rules for assigning priority to groups around a stereocenter and determining whether a molecule is R or S. Examples are provided to illustrate the rules, such as assigning priorities based on atomic number and distinguishing between cis and trans isomers. The importance of distinguishing between enantiomers is also briefly discussed.Knorr Pyrazole Synthesis (M. Pharm) 



Knorr Pyrazole Synthesis (M. Pharm) MohdShafeeque4
╠²
The document discusses the Knorr pyrazole synthesis reaction which converts hydrazines or derivatives and 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds to pyrazoles using an acid catalyst. The mechanism involves acid-catalyzed imine formation on either carbonyl carbon, followed by attack of the other nitrogen on the other carbonyl group. This forms a diimine compound which deprotonates to generate the final pyrazole product. Several examples of pyrazoles synthesized using this reaction are mentioned, including antipyrine, celecoxib, and metamizole sodium which have various medical applications.Retrosynthes analysis and disconnection approach 



Retrosynthes analysis and disconnection approach ProttayDutta1
╠²
Retrosynthetic analysis is a technique used to plan organic syntheses by working backwards from the target molecule. It involves mentally deconstructing the target molecule through sequential disconnections and functional group transformations until commercially available starting materials are reached. Each disconnection produces synthons, which are idealized fragments that represent possible reaction precursors. Common types of disconnections include C-X, C-C, and carbonyl bonds. The goal of retrosynthesis is to simplify the target structure and design multiple possible synthesis routes leading from simple starting materials to the target. It helps chemists discover efficient syntheses by considering the reactivity, selectivity, and availability of materials at each step.Reduction reactions



Reduction reactionsPriyanka Jaiswal
╠²
This document provides an overview of reduction reactions in organic chemistry. It discusses various types of reduction reactions including catalytic hydrogenation, hydride transfer reactions using reagents like LiAlH4 and NaBH4, dissolving metal reductions, and others. Specific metal hydride reductions using boron and aluminum reagents like sodium borohydride, sodium cyanoborohydride, lithium aluminum hydride, and diisobutylaluminum hydride are explained in detail including their mechanisms and selectivity. Diimide reduction is also briefly covered. The document concludes with a bibliography of reference books on organic reaction mechanisms.Photoaddition and photo fragmentation reaction



Photoaddition and photo fragmentation reactionAshu Vijay
╠²
Photoaddition and photofragmentation reactions involve the use of light to induce chemical reactions. Photoaddition reactions form a single product when electronically excited molecules add across double bonds or carbonyl groups. Photofragmentation reactions introduce functional groups by cleaving bonds upon absorption of light, forming reactive diradicals or intermediates like carbenes and nitrenes which can undergo further reactions. Primary photofragmentation involves alpha cleavage of a sigma bond directly attached to the chromophore to form diradicals. Beta cleavage occurs when a leaving group is on the alpha carbon through a beta elimination reaction.Stereochemistry (Conformational Isomerism)



Stereochemistry (Conformational Isomerism)Ashwani Dhingra
╠²
This document discusses conformational isomerism, which results from different three-dimensional arrangements of atoms that can form due to the rotation of single bonds. It focuses on the conformations of ethane, butane, cycloalkanes like cyclopropane and cyclohexane, and amine compounds. The key conformations discussed are staggered, eclipsed, chair, boat, and twist-boat, with the document explaining their relative stabilities and energies. It also discusses angle strain, torsional strain, and steric strain that can result from different conformations.Unit 3 Pyrrole



Unit 3 PyrroleSowmiya Perinbaraj
╠²
This document discusses the heterocyclic compound pyrrole. It begins by defining pyrrole as an unsaturated five-membered ring containing nitrogen. Pyrrole is an important compound found naturally in substances like alkaloids, hemoglobin, and chlorophyll. The document then describes several methods for synthesizing pyrrole, including the Paal-Knorr, Hantzsch, and Knorr syntheses. It also discusses some reactions pyrrole undergoes, such as electrophilic substitution and reduction. Finally, it lists several medicinal uses of pyrrole derivatives, including the amino acid proline, the stimulant nicotine, and drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease and pepticBasic aspects of Stereochemistry



Basic aspects of StereochemistryDHARMENDRA BARIA
╠²
This document provides an overview of stereochemistry. It begins by defining constitutional and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers have the same connectivity but different arrangements in space, and include enantiomers and diastereomers. The document then discusses chiral centers and molecules, and how the presence of a chiral center leads to chirality. It also covers topics such as optical activity, properties of enantiomers and diastereomers, meso compounds, geometric isomers, and resolving racemic mixtures. Resolution methods discussed include conversion to diastereomers and differential absorption chromatography.Seminar on name reaction



Seminar on name reactionnitin lambe
╠²
in this ppt 4 reactions are explain with mechanism namely clemenson,oppenauer,wolf kischner, and mpv reduction....this is useufl for introductory partAnomeric effect



Anomeric effectDaniel Morton
╠²
The anomeric effect was discovered in 1955 with the work of J.T. Edward, N.-J. Chu, and R.U. Lemieux.
Contributed by: Cody F. Bender, Charles E. Price (Undergraduates), University of Utah, 2016
Stereochemistry



StereochemistrySirod Judin
╠²
This chapter discusses stereochemistry and chirality. It defines stereoisomers such as enantiomers, which are nonsuperimposable mirror images, and diastereomers, which are not mirror images. Chiral carbons have four different groups and exist as enantiomers. Enantiomers have identical properties except for how they interact with other chiral molecules and rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions. Methods to determine chirality such as assigning R/S configurations and using Fischer projections are covered. The chapter also discusses resolving enantiomers through formation of diastereomers.Reactions intermediate



Reactions intermediatesaiswathivarma
╠²
This document provides an overview of various carbon-based reaction intermediates including carbocations, carbanions, carbenes, free radicals, nitrenes, and nitrenium ions. It discusses their generation, structure, stability, reactions, and detection methods. Key points include that carbocations are positively charged carbon species that react as electrophiles, while carbanions are negatively charged carbon species that react as nucleophiles. Carbenes contain a carbon with six valence electrons in a triplet or singlet state. Free radicals contain one or more unpaired electrons. Nitrenes and nitrenium ions involve a reactive nitrogen species. Detection methods include NMR, EPR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and trapping reactions.Annulenes and Heteroannulenes - Premie Fernandes



Annulenes and Heteroannulenes - Premie FernandesBebeto G
╠²
This document discusses annulenes and heteroannulenes. Annulenes are monocyclic conjugated systems represented by the general formula (CH)2m and include benzene and cyclooctatetraene. Heteroannulenes contain one or more heteroatoms in the ring, such as pyridine and thiophene. Aromaticity in these systems is determined by Huckel's rule of (4n+2)ŽĆ electrons. The document examines various annulene and heteroannulene structures of different ring sizes and whether they obey Huckel's rule and exhibit aromatic, anti-aromatic, or non-aromatic behavior.Aromaticity in benzenoid and non-benzenoid compunds



Aromaticity in benzenoid and non-benzenoid compundsSPCGC AJMER
╠²
This document summarizes aromaticity in benzoid and non-benzoid compounds. It defines aromaticity as the property of conjugated cycloalkenes that enhances stability through delocalization of pi electrons. The rules of aromaticity are outlined, including that aromatic compounds must be cyclic, have planar p-orbitals, and follow H├╝ckel's rule of 4n+2 pi electrons. Benzoid aromatics include benzene and polycyclic structures like naphthalene. Non-benzoid aromatics do not contain benzene rings and examples provided are azulene, tropone, and heterocyclic compounds.Mannich reaction



Mannich reactionAanchal Gupta
╠²
The Mannich reaction involves the condensation of an enolizable carbonyl compound, an amine or ammonia, and formaldehyde to form an aminomethyl derivative known as a Mannich base. Ketones are most commonly used as the carbonyl compound. The reaction proceeds via the generation of an imine intermediate from the carbonyl compound and amine, which then reacts with formaldehyde to form the Mannich base. Mannich bases have applications in synthesizing natural products like alkaloids and building ring systems.Heterocyclic compounds - Thiophene - Synthesis of Thiophene - Characteristic ...



Heterocyclic compounds - Thiophene - Synthesis of Thiophene - Characteristic ...Dr Venkatesh P
╠²
Thiophene can be synthesized through various methods including passing a mixture of acetylene and hydrogen sulfide over aluminum oxide at high temperature or by distilling sodium succinate with phosphorus pentasulfide. Thiophene undergoes characteristic reactions such as electrophilic substitution, reaction with organolithium reagents, and reductions. Some medicinal uses of thiophene derivatives include their use as local anesthetics, diuretics, anthelmintics, and antifungals.Fused heterocyclic compound indole



Fused heterocyclic compound indoleDrx Mathivanan Selvam
╠²
This slide discusses about basic indole nucleus, its chemistry, synthesis, reactions and medicinal uses of Indolyl derivatives..Indole is basically fused heterocyclic compoundFused heterocyclic compound isoquinoline



Fused heterocyclic compound isoquinolineDrx Mathivanan Selvam
╠²
This slides discusses about Isoquinoline nucleus (fused heterocyclic compound). this ring contain benzene ring fused with pyridine nucleus with nitrogen atomSimilar to Absolute & relative configuration (20)
Isomerism Part - 2



Isomerism Part - 2Akhil Nagar
╠²
1) The document discusses absolute and relative configuration of stereoisomers. Absolute configuration is assigned using CIP rules which assign R and S labels based on priority of groups around a chiral carbon.
2) Relative configuration refers to D and L labels assigned based on comparison to glyceraldehyde stereochemistry. Compounds related to D-glyceraldehyde have the D label and those related to L-glyceraldehyde have the L label.
3) Chirality can arise without a chiral carbon center. Allene and substituted biphenyls lack chiral carbons but have restricted rotation that leads to enantiomers with optical activity.Stereochemistry configuration of R and S



Stereochemistry configuration of R and SSourav Shipu
╠²
The R/S system labels each chiral center in a molecule as either R or S based on the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. These rules assign priorities to the four substituents of a chiral center based on atomic number. The molecule is oriented so the lowest priority substituent is pointed away from the viewer. If the priorities of the remaining three decrease clockwise, it is labeled R; if counterclockwise, it is labeled S. This system has greater generality than the D/L system and can distinguish between diastereomers. The R/S labels do not correspond directly to whether a molecule is dextrorotatory or levorotatory.Stereochemistry configuration of r and s



Stereochemistry configuration of r and sSourav Shipu
╠²
The R/S system labels each chiral center in a molecule as either R or S based on the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. These rules assign priorities to the four substituents of a chiral center based on atomic number. The molecule is oriented so the lowest priority substituent is pointed away from the viewer. If the priorities of the remaining three decrease clockwise, it is labeled R; if counterclockwise, it is labeled S. This system has greater generality than the D/L system and can distinguish between diastereomers. The R/S labels do not correspond directly to whether a molecule is dextrorotatory or levorotatory.Stereochemistry part 2 Isomerism 2 



Stereochemistry part 2 Isomerism 2 AtulBendale2
╠²
ABSOLUTE AND RELATIVE CONFIGURATION, CIP SEQUENCE RULE, stereochemistry of allenes and biphenyls, Atropisomerism, Chirality in a molecule with no stereogenic (chiral) centre, Assigning R and S Configuration
Nomenclature of optical isomerism



Nomenclature of optical isomerismSowmiya Perinbaraj
╠²
The document discusses the representation and nomenclature of optical isomers. It defines:
- Wedge and dash projection and Fischer projection for representing 3D structures in 2D.
- The D/L and R/S systems for assigning configuration to chiral centers. The D/L system uses hydroxy acid/amino acid and sugar conventions while the R/S system uses Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules.
- Sequence rules for assigning priority to groups around a chiral center in the R/S system.
- Methods for determining R/S configuration including orientation of the lowest priority group and interchanging groups in Fischer projections.Optical activity in helicines



Optical activity in helicinesPRUTHVIRAJ K
╠²
The document discusses helicity and chirality in organic chemistry. It explains that helicity arises in molecules with a helical shape, which are inherently chiral. It also describes how overcrowding in molecules like helicenes can lead to helicity. The document then discusses asymmetric synthesis and how existing chiral centers induce asymmetric induction to form diastereomers in unequal amounts. It presents Cram's rule and Prelog's rule as methods to predict the configuration of the predominant diastereomer based on the existing chiral centers.Nomenclature of stereoisomers



Nomenclature of stereoisomersCollege of Pharmacy,Sri Ramakrishna Institute of Paramedical Sciences,Coimbatore
╠²
This document provides an overview of stereochemistry and the nomenclature of stereoisomers. It discusses different types of stereoisomers such as enantiomers and diastereomers. The document also covers the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules for assigning R/S configuration and provides examples of determining absolute and relative configuration using Fischer projections. Problems involving assigning configuration to chiral molecules are presented along with their solutions. Reference materials on stereochemistry are listed at the end.Stereochemistry notes



Stereochemistry notesDr. Krishna Swamy. G
╠²
Introduction to stereochemistry, Representation of 3D molecules, R/S nomenclature, D-L and M-P convention, Topicity, Prochirality, Allenes, Biphenyls, Spiranes, Hemispirane.Estereoq



EstereoqAlmadalista
╠²
The document discusses different types of isomers including constitutional isomers, stereoisomers, enantiomers, and diastereomers. It explains chirality and how molecules can be chiral if they are non-superimposable on their mirror images. The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system for assigning R/S configurations is described, which involves ranking substituents and determining clockwise or counterclockwise orientation. Enantiomers have opposite optical rotations while diastereomers can have any optical rotation. Molecules can have multiple chiral centers leading to multiple stereoisomers that may be enantiomers or diastereomers.L 8 geometric-isomerism_pch217_2013_2014



L 8 geometric-isomerism_pch217_2013_2014hmfb
╠²
1. The document discusses geometric isomerism in cyclic compounds and alkenes. Geometric isomers occur when restricted rotation around double bonds results in fixed positions of groups on the same or opposite sides.
2. It introduces the cis/trans system for naming geometric isomers as well as the E/Z system which is used when there are three or more different groups around a double bond.
3. The document also discusses conformations in open-chain compounds, which can rotate freely around sigma bonds and exist as staggered or eclipsed conformers.STEREOCHEMISTRY.pptx



STEREOCHEMISTRY.pptxsnehaj38
╠²
This document provides an overview of stereochemistry concepts including:
- Stereoisomers such as configurational, conformational, geometrical, optical isomers and relationships between them.
- Rules for assigning R/S and E/Z descriptors using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority system to name stereoisomers.
- Cis-trans nomenclature for geometrical isomers and its limitations.
- Fischer's D-L notation for distinguishing carbohydrates and amino acid enantiomers and determining configurations.
- Meso compounds which are achiral despite having multiple stereocenters due to an internal plane of symmetry.stereochemistry-1.pdf



stereochemistry-1.pdfamanueltafese2
╠²
The document discusses different types of isomers including constitutional isomers, stereoisomers, geometric isomers (cis and trans), enantiomers, and diastereomers. It provides examples of each type of isomer and methods for distinguishing between them, such as assigning R/S configurations using Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules and distinguishing cis and trans isomers based on whether substituents are on the same or opposite sides. Key topics covered include chiral centers, optical activity, specific rotation, meso compounds, racemic mixtures, and resolution of enantiomers.Configuration and conformers of biomolecules



Configuration and conformers of biomoleculesAnshika Bansal
╠²
This document discusses the concepts of configuration and conformers in biomolecules. It defines configuration as the permanent geometry of a molecule that can only change by breaking bonds, while conformation refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule that can change without breaking bonds. The document outlines different concepts used to describe configuration, including cis-trans for double bonds, D-L and R-S systems for chiral carbons, and (+)-(-) enantiomers related to rotation of plane-polarized light. It also discusses the need to study biomolecular structure and provides examples of conformers in proteins and nucleic acids, ranging from primary to quaternary structure.Lec11.pdf



Lec11.pdfAakashSoni65
╠²
1. Optical activity arises in organic compounds that lack a plane of symmetry and exist as enantiomers, which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
2. Compounds with stereocenters, such as a carbon atom bonded to four different groups, can exist as distinct stereoisomers including enantiomers and diastereomers.
3. The maximum number of stereoisomers for a molecule with n stereocenters is 2n; however, some stereoisomers may be identical or achiral "meso" compounds lacking asymmetry.Bp401tt fmf rnjrkNEW STEREOCHEMISTRY .pdf



Bp401tt fmf rnjrkNEW STEREOCHEMISTRY .pdfparmarkeval1610
╠²
This document discusses stereochemistry and optical isomerism. It defines stereochemistry as the detailed study of the three dimensional structure of organic compounds. Isomers can be constitutional/structural isomers or stereoisomers. Stereoisomers differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms but have the same connectivity. Optical isomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images called enantiomers. For a molecule to exhibit optical activity, it must lack symmetry elements like a plane of symmetry and have a chiral center. The R-S system and CIP rules are used to assign configuration of chiral centers.Chirality and its biological role (English language) - www.wespeakscience.com



Chirality and its biological role (English language) - www.wespeakscience.comZeqir Kryeziu
╠²
This presentation focuses on organic chemistry, especially stereochemistry for 3D shape of molecules. When the same chemical substance differs in its spatial construct it changes in a drastic way its own features, in a biological environment. SGGU_UNIT-1(A)_RS NOMENCLATURE FOR BSc SEM-VI



SGGU_UNIT-1(A)_RS NOMENCLATURE FOR BSc SEM-VINandan Pomal
╠²
SGGU_UNIT-1(A)_RS NOMENCLATURE FOR BSc SEM-VISteriochemistry_Deo_Madam_plllllllpt.pdf



Steriochemistry_Deo_Madam_plllllllpt.pdfGarvitAhuja5
╠²
It is a PowerPoint presentation of stereochemistryOptical isomerism



Optical isomerismjeff_xuruihua
╠²
1. The document discusses the history and concepts of optical isomerism, including the discovery of enantiomers by Pasteur and the proposal of the tetrahedral carbon model by van't Hoff.
2. It defines key terms like enantiomers, diastereomers, and meso compounds. Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images while diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images. Meso compounds have an internal plane of symmetry and are optically inactive.
3. Methods for separating enantiomers like crystallization and forming diastereomeric salts are described. The importance of enantiomers in biology is highlighted, as most biomolecules andSteriochemistry syb sc



Steriochemistry syb scdnyaneshwar1970
╠²
This document provides information about stereochemistry and isomers. It discusses the following key points:
1. Stereochemistry refers to the 3D properties of molecules and has its own terminology. Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures.
2. There are different types of isomers including constitutional, stereoisomers, and optical isomers. Chiral carbon atoms can give rise to optical isomers that are non-superimposable mirror images called enantiomers.
3. Absolute configuration at chiral centers can be assigned using Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules which involve assigning priority to substituents and determining clockwise or counterclockwise orientation. The number of optical isNomenclature of stereoisomers



Nomenclature of stereoisomersCollege of Pharmacy,Sri Ramakrishna Institute of Paramedical Sciences,Coimbatore
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
How to create security group category in Odoo 17



How to create security group category in Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
This slide will represent the creation of security group category in odoo 17. Security groups are essential for managing user access and permissions across different modules. Creating a security group category helps to organize related user groups and streamline permission settings within a specific module or functionality.Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde
╠²
¤ōó Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
¤ö¼ Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
¤ōī What YouŌĆÖll Learn in This Presentation
Ō£ģ History & Evolution of Antibiotics
Ō£ģ Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
Ō£ģ Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
Ō£ģ Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
Ō£ģ Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
Ō£ģ Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
Ō£ģ Clinical Applications & Challenges.
¤ÜĆ Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
¤æē Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
¤öö Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatIntellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
╠²
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀Żs



Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀ŻsPooky Knightsmith
╠²
For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM
╠²
Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit? Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatAdministrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
╠²
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
╠²
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxHow to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
╠²
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
╠²
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
Ō£ģ Soft Tissue Therapy ŌĆō The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
Ō£ģ Sports Taping Techniques ŌĆō Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
Ō£ģ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia ŌĆō A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatAbsolute & relative configuration
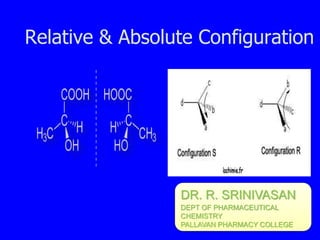
- 1. Relative & Absolute Configuration DR. R. SRINIVASAN DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY PALLAVAN PHARMACY COLLEGE
- 2. Configuration Arrangement of atoms or gps of atoms around the asymmetric centre 3 difference conventions are: D&L, d&l and +&- 2 are same used to indicate the sign of rotation of 2 enantiomers Relative configuration(D & L) compares the arrangement of atoms in space of one compound with those of another. Absolute configuration is the precise arrangement of atoms in space. There is no significance difference between sign of rotation & configuration of an enantiomers because of a compound and derivative have differences in sign of rotations eg. Lactic acid
- 3. Relative configuration compares the arrangement of atoms in space of one compound with those of another until the 1950s, all configurations were relative Absolute configuration(actual arrangement of atom in space) is the precise arrangement of atoms in space. we can now determine the absolute configuration of almost any compound Configuration
- 4. Relative configuration Any compd prep from or converted into D glyceraldehyde and prep or converted into Lglyceraldehyde are called relative configuration eg. D-glyceraldehyde to D Glyceric acid
- 5. No bonds are made or broken at the chiral carbon in this experiment. Therefore, when (+) d-3-buten-2-ol and (+) d -2-butanol have the same sign of rotation, the arrangement of atoms in space at the chiral carbon atom is analogous. The twohave the same relative configuration. CH3CHCH2CH3 OH Pd [a] + 33.2┬░ [a] + 13.5┬░ Relative configuration CH3CHCH OH CH2
- 6. Not all compounds that have the same relative configuration have the same sign of rotation. No bonds are made or broken at the chiral carbon in the reaction shown, so the relative positions of the atoms are the same. Yet the sign of rotation can change. CH3CH2CHCH2Br CH3 HBr [a] -5.8┬░ [a] + 4.0┬░ Relative configuration CH3CH2CHCH2OH CH3
- 7. Absolute configuration Clears the basic defects of D&L(relative configuration)were over come when we study in structure of more than one asymmetric C atom. However it is overcome by Cahn Ingold & Prelog (1956, 1964) which is based on three dimensional formula
- 8. Three imp features of absolute configuration (R&S system Nomenclature) are: 1. Four different group attached to the asymmetric carbon atom or atoms are arranged in a priority sequence in accordance to the sequences rules After assigning the priorities of the 4 group or atoms attached to chiral carbon the molecules is imagined to be a position where the atom or group of lowest i.e., arrangement towards clockwise direction is specified as R & anticlockwise direction is R 2. R ŌĆōrectus(latin) for right S-sinister ŌĆō left used as D & L series
- 9. 3. When the molecule is more than one asymmetric centre the procedure is applied to each for explain the of compound towards clockwise R configuration and anticlockwise S configuration
- 10. Naming from the Perspective Formula 1 2 3 4 1. Rank the groups bonded to the asymmetric carbon 2. If the group (or atom) with the lowest priority is bonded by hatched wedge,
- 11. 3. If necessary, rotate the molecule so that the lowest priority group (or atom) is bonded by a hatched wedge 4.
- 12. HH3C H H chiral carbon in a ring R ŌĆöCH2C=C > ŌĆöCH2CH2 > ŌĆöCH3 > ŌĆöH
- 13. Rules for Fischer projections Arrange the molecule so that horizontal bonds at chiral carbon point toward you and vertical bonds point away from you. Br Cl F H
- 14. Rules for Fischer projections Projection of molecule on page is a cross. When represented this way it is understood that horizontal bonds project outward, vertical bonds are back. Br Cl F H
- 15. Rules for Fischer projections Projection of molecule on page is a cross. When represented this way it is understood that horizontal bonds project outward, vertical bonds are back. Br Cl F H
- 16. SEQUENCE RULE: 4 RULES ARE GOVERN THE ARRANGMENT OF 4 DIFFERENT GROUP AROUND AN ASYMMETRIC C ATOM RULE 1: In case all the four atoms directly attached to the asymmetric carbon atom are different from one another, sequence of priorities is determined by atomic numbers The atoms of higher molecular weight higher priority and lower molecular weight the last priority
- 17. Rule 2: If the two atoms directly attached to asymmetric centre having same atomic number the priority may be determined by comparing the next atom and so on
- 18. Rule 3: A double or triple bonded atom X is equivalent to two or less such atom thus the priority of order is aldehyde or CooH gp or OH gp
- 20. Rule 4: In case of geometrical stereo isomeric group the cis gp precedes trans gp similarly isomer R precedes S gp In case of pseudosymmetric centre the symbol R & S replaced r & s



