Haemopoiesis
- 1. Haemopoiesis
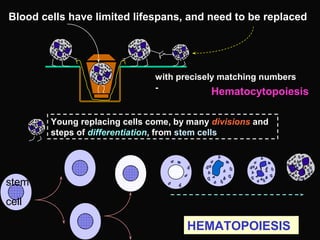
- 2. Blood cells have limited lifespans, and need to be replaced with precisely matching numbers - Young replacing cells come, by many divisions and steps of differentiation, from stem cells stem cell Hematocytopoiesis HEMATOPOIESIS
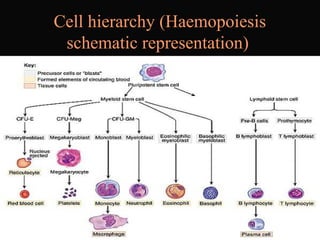
- 3. Cell hierarchy (Haemopoiesis schematic representation)
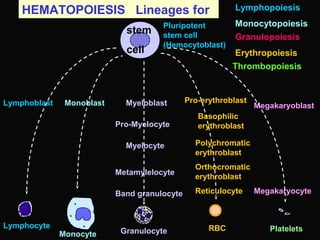
- 5. stem cell HEMATOPOIESIS Lineages for Granulocyte Lymphocyte Monocyte PlateletsRBC Lymphopoiesis Granulopoiesis Monocytopoiesis Erythropoiesis Thrombopoiesis Lymphoblast Monoblast Myeloblast Myelocyte Metamylelocyte Band granulocyte Pro-Myelocyte Reticulocyte Pro-erythroblast Basophilic erythroblast Orthocromatic erythroblast Polychromatic erythroblast Megakaryoblast Megakaryocyte Pluripotent stem cell (Hemocytoblast)
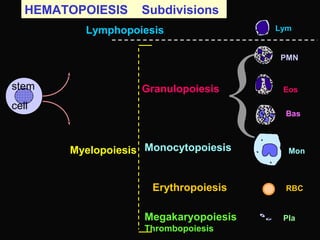
- 6. Megakaryopoiesis PMN Bas Lym Mon Eos Pla RBC Granulopoiesis Monocytopoiesis Erythropoiesis { Similar precursor produces Mast cells Monocyte or a related precursor gives rise to many specialized phagocytes & antigen-presenting cells Macrophages Kupffer cells Langerhans cells Dendritic cells Microglia Osteoclasts etc FURTHER DIFFERENTIATIONS Similar precursor produces Natural killer cells B lymphocytes become Plasma cells Thrombopoiesis
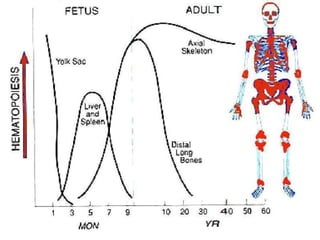
- 7. Sites of Haemopoiesis ŌĆó Yolk sac ŌĆó Liver and spleen ŌĆó Bone marrow ŌĆō Gradual replacement of active (red) marrow by tissue inactive (fatty) ŌĆō Expansion can occur during increased need for cell production
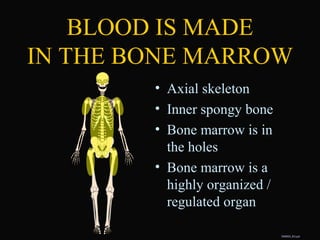
- 9. DMM00_B3.ppt ŌĆó Axial skeleton ŌĆó Inner spongy bone ŌĆó Bone marrow is in the holes ŌĆó Bone marrow is a highly organized / regulated organ BLOOD IS MADE IN THE BONE MARROW
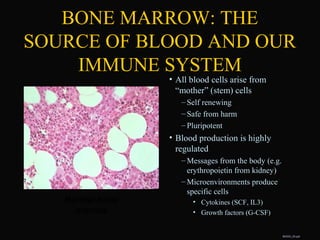
- 10. ŌĆó All blood cells arise from ŌĆ£motherŌĆØ (stem) cells ŌĆō Self renewing ŌĆō Safe from harm ŌĆō Pluripotent ŌĆó Blood production is highly regulated ŌĆō Messages from the body (e.g. erythropoietin from kidney) ŌĆō Microenvironments produce specific cells ŌĆó Cytokines (SCF, IL3) ŌĆó Growth factors (G-CSF) Normal bone marrow BAS03_20.ppt BONE MARROW: THE SOURCE OF BLOOD AND OUR IMMUNE SYSTEM
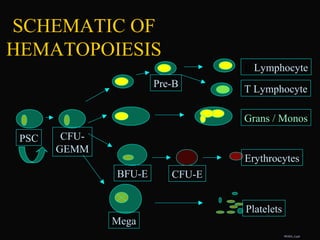
- 11. SCHEMATIC OF HEMATOPOIESIS PSC CFU- GEMM Platelets Mega Erythrocytes Pre-B B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte Grans / Monos BFU-E CFU-E RES03_3.ppt
- 12. Introduction ŌĆó Limited Life span of : ŌĆó Granulocytes ŌĆó Erythrocytes ŌĆó Platelets ŌĆó Lymphocytes
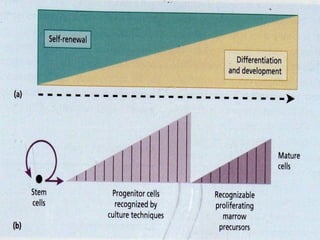
- 13. Introduction ŌĆó Stem cells ŌĆó Self renewal ŌĆó Plasticity ŌĆó Progenitor cells ŌĆó Developmentally-restricted cells ŌĆó Mature cells ŌĆó Mature cell production takes place from the more developmentally-restricted progenitors
- 14. Stem cells ŌĆó Self-renewal ŌĆó Normally in G0 phase of cell cycle ŌĆó The capacity for self-reproduction is vastly in excess of that required to maintain cell production for normal lifetime ŌĆó As cells increase in number they differentiate as well ŌĆó Multipotentiality ŌĆó Capacity to generate cells of all the lymphohaemopoietic lineages
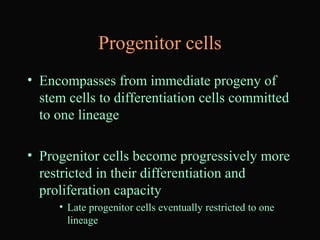
- 16. Progenitor cells ŌĆó Encompasses from immediate progeny of stem cells to differentiation cells committed to one lineage ŌĆó Progenitor cells become progressively more restricted in their differentiation and proliferation capacity ŌĆó Late progenitor cells eventually restricted to one lineage
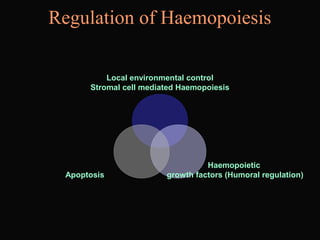
- 17. Regulation of Haemopoiesis ŌĆó There should be a balance between cell production and cell death except at the times of requirement Controlled cell death Controlled cell production
- 18. Regulation of Haemopoiesis Local environmental control Stromal cell mediated Haemopoiesis Haemopoietic growth factors (Humoral regulation)Apoptosis
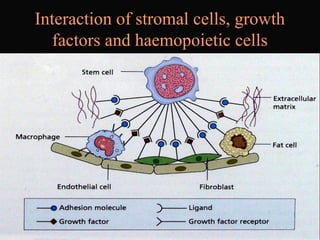
- 19. Interaction of stromal cells, growth factors and haemopoietic cells
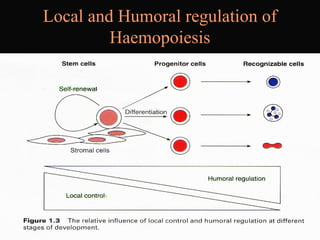
- 20. Local and Humoral regulation of Haemopoiesis
- 21. Haemopoietic growth factors ŌĆó GM-CSF ŌĆó Granulocyte-Macrophage colony stimulating factor ŌĆó M-CSF ŌĆó Macrophage colony stimulating factor ŌĆó Erythropoietin ŌĆó Erythropoiesis stimulating hormone (These factors have the capacity to stimulate the proliferation of their target progenitor cells when used as a sole source of stimulation) ŌĆó Thrombopoietin ŌĆó Stimulates megakaryopoiesis
- 22. Haemopoietic growth factors ŌĆó Cytokines ŌĆó IL 1 (Interleukin 1) ŌĆó IL 3 ŌĆó IL 4 ŌĆó IL 5 ŌĆó IL 6 ŌĆó IL 9 ŌĆó IL 11 ŌĆó TGF-╬▓ ŌĆó SCF (Stem cell factor, also known as kit-ligand) Cytokines have no (e.g IL-1) or little (SCF) capacity to stimulate cell proliferation on their own, but are able to synergise with other cytokines to recruit nine cells into proliferation
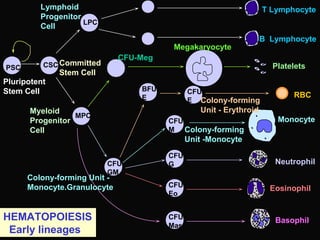
- 23. Basophil Eosinophil RBC Neutrophil T Lymphocyte Monocyte Platelets B Lymphocyte Pluripotent Stem Cell Committed Stem Cell CFU-Meg Megakaryocyte Lymphoid Progenitor Cell CSCPSC LPC MPC Myeloid Progenitor Cell BFU- E CFU- E Colony-forming Unit - Erythroid CFU- M Colony-forming Unit -Monocyte Colony-forming Unit - Monocyte.Granulocyte CFU- GM CFU- G CFU- Eo CFU- Mast HEMATOPOIESIS Early lineages
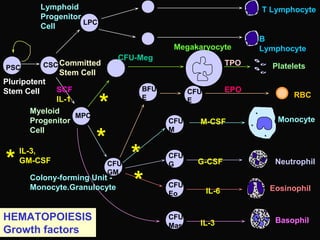
- 24. Basophil Eosinophil RBC Neutrophil T Lymphocyte Monocyte Platelets B Lymphocyte Pluripotent Stem Cell Committed Stem Cell CFU-Meg Megakaryocyte Lymphoid Progenitor Cell CSCPSC LPC MPC Myeloid Progenitor Cell BFU- E CFU- E CFU- M Colony-forming Unit - Monocyte.Granulocyte CFU- GM CFU- G CFU- Eo CFU- Mast HEMATOPOIESIS Growth factors M-CSF IL-3, GM-CSF* * * G-CSF IL-6 IL-3 SCF IL-1 * * EPO TPO
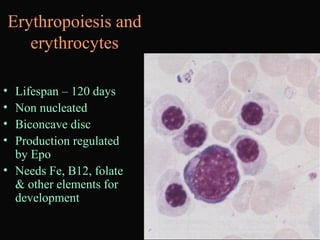
- 25. Erythropoiesis and erythrocytes ŌĆó Lifespan ŌĆō 120 days ŌĆó Non nucleated ŌĆó Biconcave disc ŌĆó Production regulated by Epo ŌĆó Needs Fe, B12, folate & other elements for development
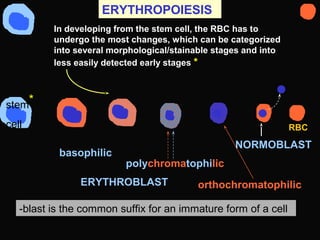
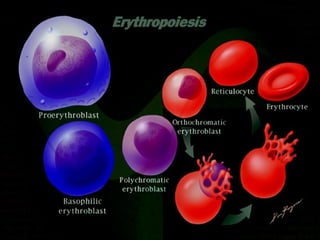
- 26. ERYTHROPOIESIS In developing from the stem cell, the RBC has to undergo the most changes, which can be categorized into several morphological/stainable stages and into less easily detected early stages * ERYTHROBLAST basophilic polychromatophilic stem cell orthochromatophilic NORMOBLAST RBC * -blast is the common suffix for an immature form of a cell
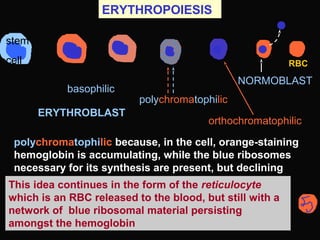
- 27. ERYTHROPOIESIS ERYTHROBLAST basophilic polychromatophilic stem cell orthochromatophilic NORMOBLAST RBC polychromatophilic because, in the cell, orange-staining hemoglobin is accumulating, while the blue ribosomes necessary for its synthesis are present, but declining This idea continues in the form of the reticulocyte which is an RBC released to the blood, but still with a network of blue ribosomal material persisting amongst the hemoglobin
- 28. ERYTHROPOIESIS 2 In developing from the stem cell, the RBC has to undergo the most changes, which can be categorized into several morphological/stainable stages and into less easily detected early stages stem cell ERYTHROBLAST PSC CSC MPC BFU-E Pluripotent Stem Cell Committed Stem Cell Myeloid Progenitor Cell Burst-forming Unit - Erythroid Used for some specialization, but more for massive cell division, as conveyed by ŌĆ£burstŌĆØ
Editor's Notes
- #4: Highly simplified diagram to demonstrate the stages of development of various cell types.
- #8: Embryonic haemopoietic stem cells-mesenchymal cells in yolk sac After 12 week fetal liver and spleen becomes the main site From week 20, bone marrow starts to become important and by the time of birth it is the main haemopoietic organ
- #13: Every day 1013 myeloid cells must be produced. In steady state the number of cells which are required is equal to the body weight. All these cells are derived from the stem cells. Stem cells are relatively few in number, comprising 0.01% to 0.05% of the marrow cells.
- #18: Cells in the different tissues of the body can signal the need of different levels of cell production e.g anoxic conditions lead to production of erythropoietin The control of cell death by apoptosis is being increasingly acknowledged to be of critical importance