Soil Texture and Structure by Salman Saeed
- 1. Course Title: Plant Physiology and Ecology Course Instructor: SALMAN SAEED Botany department UNIVERSITY college of management & Sciences, Khanewal, PAKSITAN
- 2. 2
- 3. SOIL TEXTURE ?The look and the feel of a soil is referred as soil texture which is determined by the relative proportion of mineral particles of different sizes present in the soil. ? Soil are composed of sand ,slit and clay particles. ? Stones and gravels are excluded from the textural classes. 3 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 4. SIZE OF THE PARTICLES ?Particle size is determined by the diameter of individual soil fragments. ? According to the International system of soil classification ,size of different particle are as follows: ? Clay ¨C less than 0.002 mm ? Slits ¨C 0.002mm to 0.02mm ? Sand ¨C 0.02mm to 2.0mm ? very fine sand ¨C 0.02mm to 0.10mm ? Fine sand ¨C 0.10mm to 0.25mm ? Medium sand ¨C 0.25mm to o.50mm ? Coarse sand ¨C 0.50mm to 1.0mm ? Very coarse sand ¨C 1.0mm to 2.0mm ? Gravel - larger than 2.0 mm 4 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 5. FIGURE SHOWING DIFFERENT SOIL PARTICLES 5 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 6. HOW THESE PARTICLES CAN BE SEPARATED ? To separate the particle of different sizes ,the organic matter of soil is oxidized and inorganic cementation is removed to breakdown structural aggregation. ? Fine fractions are removed from coarser material by sedimentation technique. ? Coarse fraction is dried and graded by sieving. 6 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 7. ? Stones and gravels are retained by 2.0 mm perforated plate sieve , the coarse sand retain on a 70 mesh wire sieve ( 0.23 mm per opening) while the fine sand passes through the 70 mesh. ? Slit and clay fractions are graded according to sedimentation velocity in a liquid column. 7 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 8. TEXTURAL GROUPS ? On the basis of proportion of different size particle ,soils are classified into different textural groups; TEXTURAL GROUPS RELATIVE PROPORTION OF DIFFERENT SIZED MINERAL PARTICLE Sandy soil 85% sand + 15%clay or slit or both Loamy sand 70% sand + 30% clay or slit or both Loam soil 50% sand +50% clay or slit or both slit 90% slit + 10% sand 8 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 9. TEXTURAL CLASSES OF SOILS SERIAL NUMBER SOIL CLASSES OR TEXTURAL NAMES RANGE IN RELATIVE PERCENTAGE OF SOIL SEPARATES SAND SLIT CLAY 1 Sandy soil 85-100 0-15 0-10 2 Loamy sand 70-90 0-30 0-15 3 Sandy loam 43-80 0-50 0-20 4 Loam 23-52 28-50 7-27 5 Slit loam 0-50 50-88 0-27 6 Slit 0-20 8-10 0-12 7 Sandy clay loam 45-80 0-28 20-35 8 Clay loam 20-45 15-53 27-40 9 Slity clay loam 0-20 40-73 27-40 10 Sandy clay 45-65 0-20 35-45 11 Slit clay 0-20 40-60 40-60 12 clay 0-45 0-40 40-100 9 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
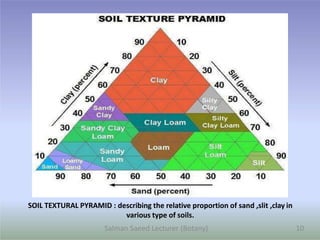
- 10. SOIL TEXTURAL PYRAMID : describing the relative proportion of sand ,slit ,clay in various type of soils. 10 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 11. PROPERTIES ? Loamy soil are a balance between sand , slit and clay particles and considered as the most desirable soils for agricultural. ? Sandy soil have coarse texture .They hold water and mineral poorly . Water and air penetrate easily thats why ,they warm readily in spring and cool quickly in autumn. ? Clayey soil hold large volume of water and retain minerals . They are very slow to warm in spring and cool more slowly in autumn. ? Slity soil are intermediate in characteristics and properties between sandy and clayey soil. 11 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 12. WHY DIFFERENT SOIL TEXTURES HAVE THE PROPERTIES THEY DO ? ? Sand and slit are generally irregular in shape ,ranging from rectangular or blocky to chunky ,spherical shapes. ? Clay particles are made up of two to three flat crystalline plates , layered or laminated together. These particle can be hexagonal in shape with distinct edges , or they may form irregularly shaped flakes or even rods. ? Allophane (an amorphous material ) have same tiny size as clay particle and is prevalent in soils developed from volcanic ash. 12 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 13. ROLE OF SOIL TEXTURE ? Soil texture is a qualitative classification tool used in both the field and laboratory to determine classes for agricultural soils based on their physical texture. ? It directly influences soil-water relationship ,aeration and root penetration through its relationship with interpartical pore space. 13 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 14. ? Soil texture is of ecological interest ,for the dominant particle size present in any area have a effect on the flora and fauna of an area. ? It affects the nutritional status of soil ? The presence of fine textured soil in lower part of soil body may partially compensate for coarser soil in upper layers , through a mixture of fine coarse soil particles can combine many of the advantages provided by either type texture. 14 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 15. What is soil structure, how does it form, and why is it important? ? Soil structure is the arrangement of the soil particles into clusters or aggregates of various sizes and shapes. ? Aggregates that occur naturally in the soil are referred to as peds, while clumps of soil caused by tillage are called clods. Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 16. What is soil structure, how does it ¨C Fungal activity form, and why is it important ? Structure is formed in two steps. ? 1. A clump of soil particles sticks loosely together. These are created through: ¨C Plant roots surrounding the soil and separating clumps ¨C Freezing and thawing of soil ¨C Soil becomes wet and then dries ¨C The soil is tilled Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 17. What is soil structure, how does it form, and why is it important 17 ? 2. Weak aggregates are cemented to make them distinct and strong. ? Clay, iron oxides, and organic matter may act as cements. ¨CWhen soil microorganisms break down plant residues, they produce gums that also glue peds together. Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 18. What is soil structure, how does it crusts that reduce crop stands. form, and why is it important ? Soil structure is important for several reasons: ¨CIt improves soil tilth. ¨CIt improves permeability. ¨CIt resists the beating action of raindrops, minimizing the formation of Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 19. What are the various soil structures 2. Massive and what do they look like? ? There are eight primary types of structure. They are: ¨C Granular ¨C Crumb ¨C Platy ¨C Prismatic or Columnar ¨C Blocky ¨C Structureless ? 1. Single grain Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 20. Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany)
- 21. THANK YOU 21 Salman Saeed Lecturer (Botany) Email: Salmanbotanistgmail.com