Rdx 230907
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes462 views
The document provides an overview of various consumer behavior models used in strategic marketing. It discusses foundations of consumer behavior models including behavioral learning, personality research, and information processing approaches. It then summarizes different types of models like variety seeking, satisfaction, network, and discrete choice models. Specific stochastic models for brand choice are explained in detail including zero order, Markov, and post-purchase feedback models. Non-compensatory models like conjunctive, disjunctive, and lexicographic models are also briefly covered.
1 of 30
Downloaded 26 times






















Ad
Recommended
Brand loyalty and other models
Brand loyalty and other modelsRajesh Deshpande
?
The document discusses quantitative models related to consumer behavior, specifically focusing on brand purchase and switching models. It elaborates on various decision-making frameworks such as compensatory and non-compensatory models, as well as describing the Markov model for predicting market share changes over time. Additionally, the document covers the Bush-Mosteller model for buyer behavior and the Colombo-Morrison model addressing brand loyalty and consumer switching probabilities.Multidimensional scaling & Conjoint Analysis
Multidimensional scaling & Conjoint AnalysisOmer Maroof
?
The document discusses multidimensional scaling (MDS) and conjoint analysis, which are techniques used in marketing research. MDS is used to identify dimensions that objects are perceived by and position objects with respect to those dimensions. Conjoint analysis determines the relative importance of product attributes based on how consumers make trade-off judgments between different attribute combinations. Both techniques provide insights to help with product positioning and development.Bugarin exclusividade_exclusao_2010
Bugarin exclusividade_exclusao_2010Blanca Lazarte
?
This document summarizes and extends previous work on exclusion in multidimensional screening models. It relaxes assumptions on preferences and consumer types, and extends previous results to allow for oligopoly market structures and free entry. It applies the results to credit markets, automobiles, research grants, regulation of monopolies, and involuntary unemployment. The key conclusion is that exclusion of some consumers is generically optimal for sellers in markets with multidimensional private information, and this result holds under more general conditions than previously shown.Herman et al
Herman et alSEKOLAH BISNIS INDONESIA
?
The document examines how four factors - whether a bundle is pure or mixed, the price discount of a pure bundle compared to individual components, the functional complementarity of bundle components, and the number of components - affect consumers' intentions to purchase product and service bundles. Two studies were conducted on automobile and automotive service bundles that varied the four factors. The findings showed that pure bundles generated greater purchase intentions than mixed bundles. Larger price discounts and components that were very functionally related also led to higher purchase intentions. Intention was highest for bundles with five components due to cognitive limitations. Several interactions between the factors were also found to influence purchase intentions.Lieh ming luo
Lieh ming luoSEKOLAH BISNIS INDONESIA
?
This document presents a valuation model for money-back guarantees (MBG) using a real-options approach. It defines the perceived post-purchase product value as a stochastic process and values the MBG as a put option. A 2x2x2 factorial experiment is conducted to examine the effects of price, perceived risk, and consumer risk aversion on MBG value. The empirical results support the theoretical model. The study provides retailers a way to understand consumer value of MBGs in different situations and improve MBG pricing strategies.26555128 c-b-models
26555128 c-b-modelsDr. Ravneet Kaur
?
The document summarizes several early models of consumer behavior:
1) The EKB model focuses on the decision making process and how it is impacted by inputs, information processing, decision variables, and external factors.
2) The Howard-Sheth model deals with different buying categories and factors like inputs, perceptions, learning, and outputs.
3) Bettman's model emphasizes information processing and includes constructs like motivation, attention, information acquisition and evaluation, and decision processes.
4) The HCB model incorporates external and internal influences, self-concept, desires, needs, and the consumer decision making process from problem recognition to post-purchase.4 Ps Of Marketing Research (1)
4 Ps Of Marketing Research (1)Nishant Kanani
?
The document discusses various statistical techniques used in marketing research, including univariate, bivariate, and multivariate analysis. It provides examples of using t-tests, chi-square tests, and ANOVA to analyze differences in groups for attributes like brand usage, purchase behavior based on demographics, and customer ratings. Hypothesis tests are conducted on single samples, independent samples, and paired samples to examine differences between groups.Wine 2010
Wine 2010Jai S
?
This document summarizes a research paper about pricing a product with positive externalities over multiple time periods. It studies a game-theoretic model where a monopolist seller sets a price trajectory and consumers choose when to purchase. The summary is:
1) It studies existence and uniqueness of equilibria in this game and designs an algorithm to compute a near-optimal revenue-maximizing price trajectory for the seller.
2) In special cases of a single consumer type or linear valuation functions, it shows well-behaved equilibria are unique and the optimal trajectory is increasing prices over time.
3) It provides an approximation algorithm via a novel rectangular covering problem to find the near-optimal increasingMonopoly Market Structure Assignment Help
Monopoly Market Structure Assignment HelpSample Assignment
?
This document compares the incentives for a firm to innovate a new product under different market structures: secure monopoly, ex post duopoly, and perfect competition. It presents a model of horizontal product differentiation on a Hotelling line with two goods, an initial good A and a potential new good B. It finds that under these conditions, the incentive for a firm to innovate product B can be higher when it holds a secure monopoly over good A than when it would face competition, unlike the ranking for process innovations found by Arrow. The coordination of prices across the two goods under monopoly allows the incentive to exceed what a rivalrous firm would gain.Competitor analysis
Competitor analysisdrgurudutta
?
This document provides guidance on analyzing competitors. It discusses the objectives of competitor analysis as understanding competitors' strengths/weaknesses and likely strategies/responses. Key aspects covered include:
1. Identifying direct competitors in the same product/customer markets using substitution-in-use analysis and purchase data.
2. Also identifying indirect competitors serving similar customer needs through different resources, and potential competitors with the capabilities to enter the market.
3. Gathering information on competitors' strategies, costs, resources to assess vulnerabilities and predict actions/responses to strategic moves.
The document provides a framework for systematically analyzing competitors at different levels to inform strategic decision making.Repositioning of Wendy's
Repositioning of Wendy'sTeri Grossheim
?
This document analyzes the positioning of five fast food brands (McDonald's, Taco Bell, Wendy's, Subway, and Burger King) using perceptual mapping techniques. Wendy's requested this analysis due to poor Q2 sales. The analysis found that Wendy's ranked lowest in preference but highest in attributes like taste and value. It suggests Wendy's reposition itself to emphasize these strengths and move into open spaces on the perceptual map, such as towards attributes like speed and modern d¨¦cor, to potentially improve sales performance. However, the analysis notes perceptual mapping provides only a snapshot and Wendy's should carefully evaluate any changes based on costs, resources required, and whether ongoing studies are preferred.Mass customization design_choice_menu
Mass customization design_choice_menuJuli Bennette
?
This document summarizes a method for designing choice menus for mass customization. The method involves 3 phases: 1) Identifying relevant product attributes through focus groups and customer analysis. Attributes are organized in a table by customer segments if identified. 2) Obtaining attribute importance weights and formally clustering customers through a questionnaire. 3) Modeling customer preferences using stated preference techniques to design optimized choice menus tailored for different customer segments. The goal is to balance flexibility and complexity in the menus. A real-world case application in a utility company supported the method's ability to elicit customer preferences for choice menu design.A Study On Mobile Phone Users
A Study On Mobile Phone UsersAvni Jain
?
This document describes a study conducted on mobile phone users' satisfaction in Delhi, India. The study used a stratified random sample of 562 mobile phone users through surveys, interviews, and focus groups. The study aimed to understand usage patterns, satisfaction levels, reasons for dissatisfaction, preferences for phone attributes and services. The sample was diverse in age, occupation, service provider, and phone usage duration. Key findings will analyze consumer behavior and provide insights to help service providers improve customer satisfaction.CURRENT RESEARCH ON REVERSE AUCTIONS: PART II -IMPLEMENTATION ISSUES ASSOCIAT...
CURRENT RESEARCH ON REVERSE AUCTIONS: PART II -IMPLEMENTATION ISSUES ASSOCIAT...ijmvsc
?
The article discusses implementation issues associated with reverse auctions in procurement, emphasizing when these auctions should be used and the decision-making processes involved. It explores factors like supplier competition, the nature of goods or services, and the importance of clear specifications in successful execution. The document advocates for a strategic approach to using reverse auctions as a valuable e-procurement tool for both public and private sectors.The relationship between customer value and pricing strategies
The relationship between customer value and pricing strategiesshampy kamboj
?
This study empirically analyzes the relationship between customer value and market prices in the washing machines market. The researchers:
1. Used conjoint analysis to assess the customer value of attributes for a sample of 129 washing machine models. This provided a measure of customer value for each model.
2. Compared the customer values from the conjoint analysis to the actual market prices of the 129 models using regression analysis.
3. Found limited alignment between price and customer value, with overpricing and underpricing of products being common. This suggests that value-based pricing is not fully established in practice in this market.Perceptor model
Perceptor modelSunny Bose
?
The document outlines a model developed by Glen L. Urban for designing and positioning frequently purchased consumer products, focusing on brand trial and repeat purchase processes. It introduces a long-run market share model based on trial and repeat probabilities, utilizing Markov processes and perceptual mapping to estimate market share and understand consumer behavior. Key components include the ultimate trial model, perception and preference mapping, and probability calculations for both trial and repeat purchases to analyze new brand positioning in relation to existing competitors.Consumer behavior
Consumer behavioramitgurus
?
The document discusses the consumer behavior model and buyer's decision process. It outlines the factors that influence consumer behavior, including environmental stimuli and buyer characteristics. It then describes the stages of the buyer's decision process: need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. It also discusses concepts like involvement, consideration sets, and how preferences are formed based on attributes, importance weights, and beliefs.Consumer decision making process slide
Consumer decision making process slide elulu123
?
The document discusses the consumer decision-making process of evaluating alternatives. It is the third step where consumers compare different solutions to a problem by looking at attributes such as performance, design, price and value for computers. Consumers will evaluate each brand based on these attributes and form beliefs about how each brand rates. They may consult others or salespeople for information. Consumers will compare brands in their consideration set based on relevant criteria to make their choice. Common criteria include country of origin, price, and brand reputation. Consumers may use decision heuristics or rules of thumb to make choices quickly.Consumer decision making process slide me
Consumer decision making process slide meelulu123
?
The document discusses the consumer decision-making process of evaluating alternatives. It is the third step where consumers compare different solutions to a problem by looking at attributes such as performance, design, price and value for computers. Consumers will evaluate each brand based on attributes and form beliefs, consulting others or salespeople for information. They will consider brands in their evoked set and evaluate them based on determinate attributes that products differ on. Common evaluative criteria include country of origin, price, and brand reputation. Consumers may use heuristics, decision rules or cognitive models like compensatory or non-compensatory models to evaluate alternatives quickly and make a decision.Models of cb
Models of cbAshish Hande
?
The document outlines various models of consumer buying behavior, including traditional and contemporary frameworks such as the economic model, learning model, psychological model, and sociological model. Each model addresses different aspects of consumer decision-making, including the influences of price, learning, social factors, and information processing. It also highlights the complexity and interdependence of these models in understanding how consumers evaluate and choose products.Models of consumer behaviour
Models of consumer behaviourVikram g b
?
This document discusses several models of consumer buying behavior:
- Traditional models include the economic, learning, psychological, and sociological models.
- Contemporary models include the Howard-Sheth model, Nicosia model, Engle-Kollat-Blackwell model, EBM model, and organizational buying models.
- The Nicosia model explains consumer behavior as a system with stimuli as input and behavior as output across four fields: consumer/firm attributes, search/evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase.Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02
Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02Mohit Kumar
?
This document discusses several models of consumer buying behavior, including traditional models like the economic, learning, and psychological models as well as contemporary models like the Howard Sheth model. It then provides more detailed explanations of several key models, including the economic model and its assumptions and criticisms, the learning model and how it helps marketers understand consumer learning, and the Engle-Blackwell-Miniard model which views consumer behavior as a five-step decision making process along with related variables. The document analyzes several models' strengths and limitations in summarizing consumer behavior.Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02
Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02Mohit Kumar
?
This document discusses several models of consumer buying behavior, including traditional models like the economic, learning, and psychological models as well as contemporary models like the Howard Sheth model. It then provides more detailed explanations of several key models, including the economic model and its assumptions and criticisms, the learning model and how it helps marketers understand consumer learning, and the Engle-Blackwell-Miniard model which views consumer behavior as a five-step decision making process along with related variables. The document analyzes several models' strengths and limitations in summarizing consumer behavior.Models of consumer behaviour.ppt presentation
Models of consumer behaviour.ppt presentationFalakNaaz79
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of consumer behavior, defined as the decision-making process and actions individuals take regarding goods and services. It highlights the significance of studying consumer behavior for effective marketing strategies, identifying opportunities, and understanding consumer needs, as well as detailing various models explaining consumer behavior, including economic, learning, psychoanalytic, sociological, and contemporary models like Howard-Sheth and Engel-Kollat Blackwell. Additionally, it discusses factors influencing consumer decisions such as social influences, psychological factors, and individual characteristics.Consumer Behavior Model used for business .pptx
Consumer Behavior Model used for business .pptxShashi Kant
?
This document provides an overview of several models of consumer behavior and decision-making. It discusses:
- Schiffman and Kanuk's model of consumer decision-making which views the process as having three stages: input, process, and output.
- Assael's model which categorizes consumer purchasing behavior based on participation level and brand differentiation.
- The black box or stimulus-response model which views environmental stimuli as inputs and consumer responses as outputs, with the decision-making process occurring within the "black box".
- Sheth's model of buying behavior which describes the rational brand choice process and includes variables like attention, comprehension, attitude, and purchase intention/behavior.
- The limitations andMRS Advanced Analytics
Innovation Symposium
Presentation
MRS Advanced Analytics
Innovation Symposium
PresentationMRS
?
Using a combination of choice modeling and econometric techniques, the authors develop an integrated approach to more accurately forecast how changes in price could impact both market share and market volume. Choice modeling captures consumer preferences and brand switching, while econometric modeling accounts for macroeconomic factors. By combining the output of share simulations from choice models with volume projections from econometric models, the authors are able to estimate how changes in price could impact both a brand's share and the overall market size. The methodology was validated across different product categories and markets, demonstrating predictive accuracy rates of around 88% on average. consumer behavior model
consumer behavior model Kritika Handoo
?
This document discusses various models of consumer behavior including traditional models like the economic, learning, and psychoanalytic models as well as contemporary models like the Howard Sheth, Nicosia, Webster and Wind, and Engel, Blackwell and Minard models. It provides details on key aspects of each model such as their assumptions, variables, decision processes, and limitations. The economic model views consumers as rational decision makers seeking to maximize utility within constraints. The learning model examines how experiences shape consumer behavior. Contemporary models offer more holistic perspectives that integrate additional influences.20 improved questions for midterms medina
20 improved questions for midterms medinaAnna Medina
?
The document discusses marketing concepts like value, brand equity, market orientation, and marketing communications models. It provides questions and answers related to chapters in Kotler's marketing management textbook. Specifically, it defines value as a customer's expectation and perceived benefit. It also discusses the hierarchy of effects model for marketing communications and factors to consider when setting an advertising budget.20 improved questions for midterms medina
20 improved questions for midterms medinaAnna Medina
?
The document discusses key concepts from marketing textbooks, including definitions of value, brand personality, market orientation, marketing information systems, types of market samples, customer databases, market segmentation, brand identity, points of parity/difference, and barriers to entry. It provides questions and answers about these topics from chapter reviews for a marketing management textbook.Chapter 8Judgment and Decision MakingBased on High Consumer
Chapter 8Judgment and Decision MakingBased on High Consumer JinElias52
?
Chapter 8 discusses high-effort judgment and decision-making processes that consumers use when faced with choices, such as estimating likelihoods, biases, and the evaluation of brands. It contrasts compensatory models, where high ratings can offset low ones, with noncompensatory models that do not allow for trade-offs among attributes. Additionally, it highlights the influence of emotional and contextual factors on consumer decisions, as well as various choice tactics employed in low-effort decision-making contexts.More Related Content
What's hot (7)
Monopoly Market Structure Assignment Help
Monopoly Market Structure Assignment HelpSample Assignment
?
This document compares the incentives for a firm to innovate a new product under different market structures: secure monopoly, ex post duopoly, and perfect competition. It presents a model of horizontal product differentiation on a Hotelling line with two goods, an initial good A and a potential new good B. It finds that under these conditions, the incentive for a firm to innovate product B can be higher when it holds a secure monopoly over good A than when it would face competition, unlike the ranking for process innovations found by Arrow. The coordination of prices across the two goods under monopoly allows the incentive to exceed what a rivalrous firm would gain.Competitor analysis
Competitor analysisdrgurudutta
?
This document provides guidance on analyzing competitors. It discusses the objectives of competitor analysis as understanding competitors' strengths/weaknesses and likely strategies/responses. Key aspects covered include:
1. Identifying direct competitors in the same product/customer markets using substitution-in-use analysis and purchase data.
2. Also identifying indirect competitors serving similar customer needs through different resources, and potential competitors with the capabilities to enter the market.
3. Gathering information on competitors' strategies, costs, resources to assess vulnerabilities and predict actions/responses to strategic moves.
The document provides a framework for systematically analyzing competitors at different levels to inform strategic decision making.Repositioning of Wendy's
Repositioning of Wendy'sTeri Grossheim
?
This document analyzes the positioning of five fast food brands (McDonald's, Taco Bell, Wendy's, Subway, and Burger King) using perceptual mapping techniques. Wendy's requested this analysis due to poor Q2 sales. The analysis found that Wendy's ranked lowest in preference but highest in attributes like taste and value. It suggests Wendy's reposition itself to emphasize these strengths and move into open spaces on the perceptual map, such as towards attributes like speed and modern d¨¦cor, to potentially improve sales performance. However, the analysis notes perceptual mapping provides only a snapshot and Wendy's should carefully evaluate any changes based on costs, resources required, and whether ongoing studies are preferred.Mass customization design_choice_menu
Mass customization design_choice_menuJuli Bennette
?
This document summarizes a method for designing choice menus for mass customization. The method involves 3 phases: 1) Identifying relevant product attributes through focus groups and customer analysis. Attributes are organized in a table by customer segments if identified. 2) Obtaining attribute importance weights and formally clustering customers through a questionnaire. 3) Modeling customer preferences using stated preference techniques to design optimized choice menus tailored for different customer segments. The goal is to balance flexibility and complexity in the menus. A real-world case application in a utility company supported the method's ability to elicit customer preferences for choice menu design.A Study On Mobile Phone Users
A Study On Mobile Phone UsersAvni Jain
?
This document describes a study conducted on mobile phone users' satisfaction in Delhi, India. The study used a stratified random sample of 562 mobile phone users through surveys, interviews, and focus groups. The study aimed to understand usage patterns, satisfaction levels, reasons for dissatisfaction, preferences for phone attributes and services. The sample was diverse in age, occupation, service provider, and phone usage duration. Key findings will analyze consumer behavior and provide insights to help service providers improve customer satisfaction.CURRENT RESEARCH ON REVERSE AUCTIONS: PART II -IMPLEMENTATION ISSUES ASSOCIAT...
CURRENT RESEARCH ON REVERSE AUCTIONS: PART II -IMPLEMENTATION ISSUES ASSOCIAT...ijmvsc
?
The article discusses implementation issues associated with reverse auctions in procurement, emphasizing when these auctions should be used and the decision-making processes involved. It explores factors like supplier competition, the nature of goods or services, and the importance of clear specifications in successful execution. The document advocates for a strategic approach to using reverse auctions as a valuable e-procurement tool for both public and private sectors.The relationship between customer value and pricing strategies
The relationship between customer value and pricing strategiesshampy kamboj
?
This study empirically analyzes the relationship between customer value and market prices in the washing machines market. The researchers:
1. Used conjoint analysis to assess the customer value of attributes for a sample of 129 washing machine models. This provided a measure of customer value for each model.
2. Compared the customer values from the conjoint analysis to the actual market prices of the 129 models using regression analysis.
3. Found limited alignment between price and customer value, with overpricing and underpricing of products being common. This suggests that value-based pricing is not fully established in practice in this market.Similar to Rdx 230907 (20)
Perceptor model
Perceptor modelSunny Bose
?
The document outlines a model developed by Glen L. Urban for designing and positioning frequently purchased consumer products, focusing on brand trial and repeat purchase processes. It introduces a long-run market share model based on trial and repeat probabilities, utilizing Markov processes and perceptual mapping to estimate market share and understand consumer behavior. Key components include the ultimate trial model, perception and preference mapping, and probability calculations for both trial and repeat purchases to analyze new brand positioning in relation to existing competitors.Consumer behavior
Consumer behavioramitgurus
?
The document discusses the consumer behavior model and buyer's decision process. It outlines the factors that influence consumer behavior, including environmental stimuli and buyer characteristics. It then describes the stages of the buyer's decision process: need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. It also discusses concepts like involvement, consideration sets, and how preferences are formed based on attributes, importance weights, and beliefs.Consumer decision making process slide
Consumer decision making process slide elulu123
?
The document discusses the consumer decision-making process of evaluating alternatives. It is the third step where consumers compare different solutions to a problem by looking at attributes such as performance, design, price and value for computers. Consumers will evaluate each brand based on these attributes and form beliefs about how each brand rates. They may consult others or salespeople for information. Consumers will compare brands in their consideration set based on relevant criteria to make their choice. Common criteria include country of origin, price, and brand reputation. Consumers may use decision heuristics or rules of thumb to make choices quickly.Consumer decision making process slide me
Consumer decision making process slide meelulu123
?
The document discusses the consumer decision-making process of evaluating alternatives. It is the third step where consumers compare different solutions to a problem by looking at attributes such as performance, design, price and value for computers. Consumers will evaluate each brand based on attributes and form beliefs, consulting others or salespeople for information. They will consider brands in their evoked set and evaluate them based on determinate attributes that products differ on. Common evaluative criteria include country of origin, price, and brand reputation. Consumers may use heuristics, decision rules or cognitive models like compensatory or non-compensatory models to evaluate alternatives quickly and make a decision.Models of cb
Models of cbAshish Hande
?
The document outlines various models of consumer buying behavior, including traditional and contemporary frameworks such as the economic model, learning model, psychological model, and sociological model. Each model addresses different aspects of consumer decision-making, including the influences of price, learning, social factors, and information processing. It also highlights the complexity and interdependence of these models in understanding how consumers evaluate and choose products.Models of consumer behaviour
Models of consumer behaviourVikram g b
?
This document discusses several models of consumer buying behavior:
- Traditional models include the economic, learning, psychological, and sociological models.
- Contemporary models include the Howard-Sheth model, Nicosia model, Engle-Kollat-Blackwell model, EBM model, and organizational buying models.
- The Nicosia model explains consumer behavior as a system with stimuli as input and behavior as output across four fields: consumer/firm attributes, search/evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase.Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02
Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02Mohit Kumar
?
This document discusses several models of consumer buying behavior, including traditional models like the economic, learning, and psychological models as well as contemporary models like the Howard Sheth model. It then provides more detailed explanations of several key models, including the economic model and its assumptions and criticisms, the learning model and how it helps marketers understand consumer learning, and the Engle-Blackwell-Miniard model which views consumer behavior as a five-step decision making process along with related variables. The document analyzes several models' strengths and limitations in summarizing consumer behavior.Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02
Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649-phpapp02Mohit Kumar
?
This document discusses several models of consumer buying behavior, including traditional models like the economic, learning, and psychological models as well as contemporary models like the Howard Sheth model. It then provides more detailed explanations of several key models, including the economic model and its assumptions and criticisms, the learning model and how it helps marketers understand consumer learning, and the Engle-Blackwell-Miniard model which views consumer behavior as a five-step decision making process along with related variables. The document analyzes several models' strengths and limitations in summarizing consumer behavior.Models of consumer behaviour.ppt presentation
Models of consumer behaviour.ppt presentationFalakNaaz79
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of consumer behavior, defined as the decision-making process and actions individuals take regarding goods and services. It highlights the significance of studying consumer behavior for effective marketing strategies, identifying opportunities, and understanding consumer needs, as well as detailing various models explaining consumer behavior, including economic, learning, psychoanalytic, sociological, and contemporary models like Howard-Sheth and Engel-Kollat Blackwell. Additionally, it discusses factors influencing consumer decisions such as social influences, psychological factors, and individual characteristics.Consumer Behavior Model used for business .pptx
Consumer Behavior Model used for business .pptxShashi Kant
?
This document provides an overview of several models of consumer behavior and decision-making. It discusses:
- Schiffman and Kanuk's model of consumer decision-making which views the process as having three stages: input, process, and output.
- Assael's model which categorizes consumer purchasing behavior based on participation level and brand differentiation.
- The black box or stimulus-response model which views environmental stimuli as inputs and consumer responses as outputs, with the decision-making process occurring within the "black box".
- Sheth's model of buying behavior which describes the rational brand choice process and includes variables like attention, comprehension, attitude, and purchase intention/behavior.
- The limitations andMRS Advanced Analytics
Innovation Symposium
Presentation
MRS Advanced Analytics
Innovation Symposium
PresentationMRS
?
Using a combination of choice modeling and econometric techniques, the authors develop an integrated approach to more accurately forecast how changes in price could impact both market share and market volume. Choice modeling captures consumer preferences and brand switching, while econometric modeling accounts for macroeconomic factors. By combining the output of share simulations from choice models with volume projections from econometric models, the authors are able to estimate how changes in price could impact both a brand's share and the overall market size. The methodology was validated across different product categories and markets, demonstrating predictive accuracy rates of around 88% on average. consumer behavior model
consumer behavior model Kritika Handoo
?
This document discusses various models of consumer behavior including traditional models like the economic, learning, and psychoanalytic models as well as contemporary models like the Howard Sheth, Nicosia, Webster and Wind, and Engel, Blackwell and Minard models. It provides details on key aspects of each model such as their assumptions, variables, decision processes, and limitations. The economic model views consumers as rational decision makers seeking to maximize utility within constraints. The learning model examines how experiences shape consumer behavior. Contemporary models offer more holistic perspectives that integrate additional influences.20 improved questions for midterms medina
20 improved questions for midterms medinaAnna Medina
?
The document discusses marketing concepts like value, brand equity, market orientation, and marketing communications models. It provides questions and answers related to chapters in Kotler's marketing management textbook. Specifically, it defines value as a customer's expectation and perceived benefit. It also discusses the hierarchy of effects model for marketing communications and factors to consider when setting an advertising budget.20 improved questions for midterms medina
20 improved questions for midterms medinaAnna Medina
?
The document discusses key concepts from marketing textbooks, including definitions of value, brand personality, market orientation, marketing information systems, types of market samples, customer databases, market segmentation, brand identity, points of parity/difference, and barriers to entry. It provides questions and answers about these topics from chapter reviews for a marketing management textbook.Chapter 8Judgment and Decision MakingBased on High Consumer
Chapter 8Judgment and Decision MakingBased on High Consumer JinElias52
?
Chapter 8 discusses high-effort judgment and decision-making processes that consumers use when faced with choices, such as estimating likelihoods, biases, and the evaluation of brands. It contrasts compensatory models, where high ratings can offset low ones, with noncompensatory models that do not allow for trade-offs among attributes. Additionally, it highlights the influence of emotional and contextual factors on consumer decisions, as well as various choice tactics employed in low-effort decision-making contexts.Marketing analytics
Marketing analyticsData Science Thailand
?
The document discusses marketing analytics as a vital aspect of creating customer value, covering topics such as marketing information systems, marketing research methodologies, econometrics and its applications in forecasting sales based on advertising expenditure, and the choice modeling using random utility models. It emphasizes the importance of data-driven decision-making and the use of statistical models to better understand consumer behavior and optimize marketing strategies. Additionally, it addresses key marketing concepts including price elasticity and the significance of reference pricing.Consumer decision making process final
Consumer decision making process finalVaishali Sehrawat
?
Consumer decision making involves a process where consumers identify their needs, gather information about alternatives, evaluate options, and make a purchase decision. This process is influenced by psychological, economic, and environmental factors. There are three main types of consumer buying decisions - routine response behavior for everyday low-involvement purchases, limited decision making for moderate-involvement purchases, and extensive decision making for high-involvement purchases. A consumer's decision making process typically involves need recognition, information search, and leads to a purchase and post-purchase evaluation.5. Consumer Decision Making Process.pptx
5. Consumer Decision Making Process.pptxkaveeshasathsarani3
?
Consumer decision making involves multiple steps: problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase, and post-purchase behavior. There are different types of buying decisions based on involvement - extensive problem solving for high involvement purchases, limited problem solving for some involvement, and routinized response for low involvement purchases. The decision making process considers influencers, decision makers, buyers, and users and uses heuristics to evaluate alternatives based on attributes.New Product Forecasting Models Review
New Product Forecasting Models ReviewArt Christiani
?
The document discusses several models for forecasting new product sales, including:
- Parfitt & Collins model which predicts share based on trial, repeat rates, and buying rate.
- Fourt-Woodlock model which estimates volume as a function of cumulative trial, repeat percentage rates by depth of repeat, and buying rate.
- Assessor model which evaluates new product appeal among different consumer segments through in-person interviews.
It also describes the Hendry market structure model which integrates factors like category share/loyalty, available switchers, and new product effectiveness to forecast share. Bases model measures purchase interest, transaction size, and frequency to estimate unit sales.Consumer Buying Process and Modelss.ppt
Consumer Buying Process and Modelss.pptssuser4cc185
?
Kotler's consumer buying behavior model examines the influences on purchasing decisions, incorporating elements from various disciplines including psychology and sociology. It describes several models of consumer behavior, including monactic models that focus on single disciplines and eclectic models that consider multiple factors simultaneously. Key models discussed include the Howard-Sheth model, Engel-Blackwell-Minard model, and Nicosia model, each illustrating different aspects of consumer decision-making processes.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Financial_Statements_Presentation.pptxindia students
Financial_Statements_Presentation.pptxindia studentssandhyadeepakca
?
Financial_Statements_Presentation.pptxKeyman Training_ Edited Module_ver1.ppsx
Keyman Training_ Edited Module_ver1.ppsxfarooquidrfaisal
?
KeyMan Insurance Policy It's Benefits and Features 1.1 national service scheme studetns college government college.pptx
1.1 national service scheme studetns college government college.pptxsharath75
?
1.1 national service scheme studetns college government collegOAT_RI_Ep31 WeighingTheRisks_Apr25_Financials.pptx
OAT_RI_Ep31 WeighingTheRisks_Apr25_Financials.pptxhiddenlevers
?
How will the tariffs and other economic noise affect capex and the markets during the trade wars?chapter 5.pptx: Urban Poverty and Public Policy
chapter 5.pptx: Urban Poverty and Public PolicyAtoshe Elmi
?
This chapter analysis Urban Poverty and Public Policy conditionals1 cccccccccccccccccccccc.ppt
conditionals1 cccccccccccccccccccccc.pptAhaf5
?
eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeMacroeconomic Study of the country - Vietnam.pptx
Macroeconomic Study of the country - Vietnam.pptxAnkush Upadhyay
?
PPT summarises our study of the economy as a whole of VietnamBringing data to life | Bricks, mortar and data: understanding house and rent...
Bringing data to life | Bricks, mortar and data: understanding house and rent...Office for National Statistics
?
For our ninth webinar, we explained how we create housing price statistics and the methodologies behind them. We explored how we identify an 'average' property, the changes observed in the market over time, and the tools you can use to answer these questions yourself. INVESTMENT ANALYSIS AND PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT-1.pptx
INVESTMENT ANALYSIS AND PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT-1.pptxAnkush Upadhyay
?
This presentation analyzes investment strategies for a 30-year-old risk-averse investor with ?50 lakhs. Based on a 35:65 equity-debt allocation, it recommends equity investments in HAL, BEL, and Bajaj Auto due to their strong financials and low debt, and debt investments in government and tax-free bonds with stable yields. The analysis balances risk and return for long-term portfolio growth in the defense sector and public sector bonds.Financial_Statements_Presentation (1).pptx
Financial_Statements_Presentation (1).pptxsandhyadeepakca
?
Financial_Statements_Presentation (1).pptxThe Economics of Dravidian Model- Equity and Social Justice
The Economics of Dravidian Model- Equity and Social JusticeCentre for Social Initiative and Management
?
This is a presentation on The Economics of Dravidian Model. It provides information on how this model has helped people of Tamil Nadu to achieve greater GDP Growth, better social justice and equity. Lakshmi Coin ($LUCK) | $LUCK | divine coin.pptx
Lakshmi Coin ($LUCK) | $LUCK | divine coin.pptxlakshmicoinsmedia
?
Lakshmi Coin ($LUCK) is a BEP-20 token on the Binance Smart Chain , inspired by Goddess Lakshmi to promote abundance and healing. Its mission is to blend spiritual and financial empowerment, supporting humanitarian causes and bridging ancient values with modern DeFi for real-world impact through giving. $LUCK is designed to feed the poor, help the sick, support communities, fund animal shelters and rescues, and provide for underprivileged children. It's part of "The Divine Tokens Ecosystem," which combines spirituality, DeFi, and Play-to-Earn (P2E) elements, with future plans for advanced game mechanics, multi-chain expansion, and an NFT marketplace.Reviving Heritage through the Abhay Bhutada FoundationˇŻs Support.pdf
Reviving Heritage through the Abhay Bhutada FoundationˇŻs Support.pdfRaj Kumble
?
This presentation unfolds over seven slides, beginning with an introduction to ShivsrushtiˇŻs immersive design and historical focus. It then highlights the strategic nature of the Abhay Bhutada FoundationˇŻs support, emphasizing long-term maintenance and educational outreach. The deck explores how the park integrates modern technology to engage visitors, followed by its inclusive access programs for underprivileged students and rural communities. Hands-on learning experiences and community empowerment initiatives illustrate the parkˇŻs commitment to active participation and local development. Finally, the presentation concludes by reflecting on the leadership lessons imparted through Shivsrushti and the enduring cultural impact of the FoundationˇŻs patronage.Chapter 4.pptx: Urban Land use patterns and land values
Chapter 4.pptx: Urban Land use patterns and land valuesAtoshe Elmi
?
This chapter is all about analysis of the urban land uses patterns, land values and the role of local states Analytical procedures for audit and assurance
Analytical procedures for audit and assuranceNguytHi7
?
Didu nay iluoc sua.d6i theo-quy dinh tai Dieu 1 cua euytit dinh s6 t146l2004/eDN[{NN vd vi6c sua a6i oiau z quyciainl s6 +lstzooatqo NHt[\r 2gt4t2oo4 cira thdng ioc
Ngan hang Nhd nu6c ban hdnh HO th5ng tiri khoan k6 toan c6c T6 chric tin dung, c6 hi0u luc
kd tu ngdy 04 thaag 10 nlm 2004Bringing data to life | Bricks, mortar and data: understanding house and rent...
Bringing data to life | Bricks, mortar and data: understanding house and rent...Office for National Statistics
?
The Economics of Dravidian Model- Equity and Social Justice
The Economics of Dravidian Model- Equity and Social JusticeCentre for Social Initiative and Management
?
Ad
Rdx 230907
- 1. Consumer Behaviour A presentation on strategic marketing models By Group 1
- 2. Group Members Sameer Sanghani Neha Chaudhary Atit Shah Deesa Kamdar Joanna Barsey Sagar Thukral Samina Papeya Nirav Shah
- 3. Foundations of Consumer Behaviour Models Consumer behaviour models are based on certain traditions: Behavioural Learning Under this theory consumersˇŻ prior experience is the primary determinant of future behaviour Personality Research Consumer attempts to reconcile his behaviour, othersˇŻ behaviour, the state of his environment etc with prior beliefs. Information Processing The characteristic nature of the individuals customersˇŻ decision making process and changing belief Attitude Models Product attributes are drivers of the consumer decision process
- 4. Nature of Consumer Behavior models Consumers are Different Choice Decisions differ Context of Purchases Differ
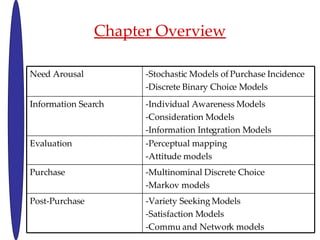
- 5. Chapter Overview -Variety Seeking Models -Satisfaction Models -Commu and Network models Post-Purchase -Multinominal Discrete Choice -Markov models Purchase -Perceptual mapping -Attitude models Evaluation -Individual Awareness Models -Consideration Models -Information Integration Models Information Search -Stochastic Models of Purchase Incidence -Discrete Binary Choice Models Need Arousal
- 6. Stochastic Models Brand Choice Model
- 7. Consumer Behavior Multiple approaches for modeling consumer behavior For low involvement products- little conscious random decision making takes place; STOCHASTIC models are appropriate Concentrate on Random nature of the choice process than on a deterministic explanation
- 8. Stochastic Model-Brand Choice B.C.model can be differentiated by how they deal with Population heterogeneity Purchase event feedback Exogenous market factors
- 9. Purchase Feedback Models Zero order model- assume no feedback Markov model- assume only previous brand choice affect present event feedback Learning model- assume entire purchase history affects current choice (recent having more effect)
- 10. ?
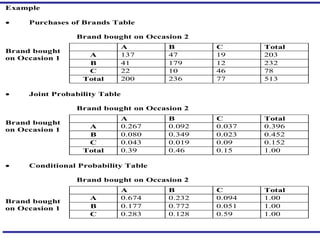
- 11. p( i , j ) = joint probability that a consumer will purchase brand i on the second purchase occasion and brand j on the first purchase occasion P( i / j ) = conditional probability that a customer will purchase brand i on the second purchase occasion given that brand j was purchased on the first occasion
- 12. Purchase Probability are related as follows: p( i / j ) = p( i , j ) ----- (1) p( j ) where p(j) = probability of purchasing brand j on the first purchase occasion so p( j ) = m j , the market share of brand j ˇĆ p( i , j ) = m i ----- (2) j ˇĆ p( i / j ) = 1 i
- 13. Zero Order Model The assumptions they make about consumer preferences and choice 2. The number of brand they consider
- 14. Moderately Heterogeneous Population (2) Heterogeneous Population (1) Extremely Heterogeneous Population ( Mostly Brand Loyal (3) f (p), Distribution Actors Population P, Probability of Purchase Bernoulli Model
- 15. Simple Multiple Brand model Joint probability of a consumer purchasing brand i and j on successive purchase occasions p( i , j ) = km i m j ----- (3) where m i and m j are the market share of respective brand p( i , i ) = m i ¨C km i (1 - m i ) ----- (4)
- 16. From (4), k = 1 - ˇĆp( i , i ) ----- (5) 1 - ˇĆm i 2 p( i ) = m i ----- (6) p( i / j ) = km i ( j = i ) ----- from (1) = 1 ¨C k(1 - m i ) ( j = i ) ----- from (1,4,6)
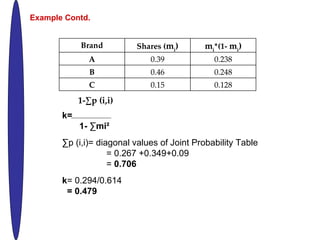
- 17. 1-ˇĆp (i,i) k= 1- ˇĆmi? ˇĆ p (i,i)= diagonal values of Joint Probability Table = 0.267 +0.349+0.09 = 0.706 k = 0.294/0.614 = 0.479 Example Contd. Brand Shares ( m i ) m i *(1- m i ) A 0.39 0.238 B 0.46 0.248 C 0.15 0.128
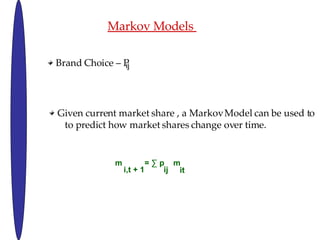
- 18. Markov Model Assumptions ¨C Stationary (probabilities do not change) Homogeneity One purchase per time period Zero Order Model ¨C Brand choice is independent Other models assume ¨C Post purchase event feedback . Markov Model assumes that only the previous brand purchase affects the present purchasing choice
- 19. Markov Models Brand Choice ¨C P ij Given current market share , a Markov Model can be used to to predict how market shares change over time. m = ˇĆ p m i,t + 1 ij it
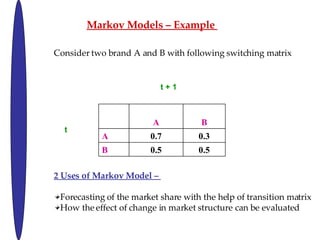
- 20. Markov Models ¨C Example Consider two brand A and B with following switching matrix t + 1 t 2 Uses of Markov Model ¨C Forecasting of the market share with the help of transition matrix How the effect of change in market structure can be evaluated A B A 0.7 0.3 B 0.5 0.5
- 21. Markov Models Price shift Limitations Stationarity - unrealistic a firm loosing market position will take corrective action.
- 22. Post Purchase and purchase feedback After purchasing and experiencing a product, a consumerˇŻs reaction is important for future purchases. Biehal (1983) showed that, for auto repair services, the outcome of prior experience is more important than external search in choosing the next service provider.
- 23. Post purchase behavior affects attitude which in turn affects the consumerˇŻs behavior. Post purchase affects how the consumer communicates about the product through WOM. A purchase can affect future purchases through variety seeking.
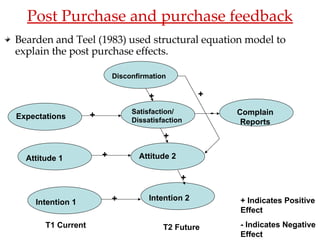
- 24. Bearden and Teel (1983) used structural equation model to explain the post purchase effects. Post Purchase and purchase feedback + Indicates Positive Effect - Indicates Negative Effect Disconfirmation Expectations Attitude 1 Intention 1 Satisfaction/ Dissatisfaction Attitude 2 Intention 2 Complain Reports + + + + + + + - T1 Current T2 Future
- 25. Lattin and McAlister modeled a consumerˇŻs utility for brand on a given consumption occasion as a diminishing proportion of the value of the features it shares with the brand the consumer chose on previous occasion. V i\j = V i ¨C ¦Ë S ij Where, Vi\j = Utility of i given that j was chosen previously Vi = unconditional utility of i ¦Ë = discount factor indicating consumerˇŻs variety- seeking intensity. Sij = value to the customer of all want-satisfying features shared by i and j
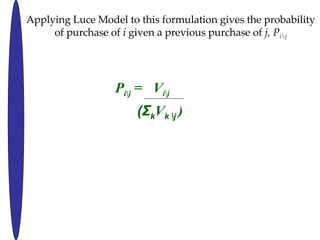
- 26. P i\j = V i\j (¦˛ k V k \j ) Applying Luce Model to this formulation gives the probability of purchase of i given a previous purchase of j, P i\j
- 27. ~ Previous consumption alters the unconditional brand choice probability, V i, that is, ~ P i\j ¨C V i < 0, then j is a substitute for product i (the consumption of brand j lowers the probability of choosing brand i ) ~ While P i\j ¨C V i > 0, then j is a compliment for product i (the consumption of brand j increases the probability of choosing brand i )
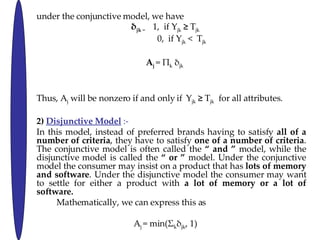
- 28. (B) Noncompensatory Models Conjunctive Model :- In a conjunctive model a consumer prefers a brand only if it meets certain minimum, acceptable standards on all of a number of key dimensions. If any one attribute is deficient, the product is eliminated from contention. Let Y JK = perceived level of attribute k in brand j T jk = minimum threshold level that is acceptable (negatively valued attributes such as price that have a maximum level can be multiplied by -1) ¦Ä jk = 1, if brand j is acceptable on attribute k 0, otherwise A j = 1, if it is a preferred brand overall 0, otherwise
- 29. under the conjunctive model, we have ¦Ä jk = 1, if Y jk ˇÝ T jk 0, if Y jk < T jk A j = ¦° k ¦Ä jk Thus, A j will be nonzero if and only if Y jk ˇÝ T jk for all attributes. 2) Disjunctive Model :- In this model, instead of preferred brands having to satisfy all of a number of criteria , they have to satisfy one of a number of criteria . The conjunctive model is often called the ˇ° and ˇ± model, while the disjunctive model is called the ˇ° or ˇ± model. Under the conjunctive model the consumer may insist on a product that has lots of memory and software . Under the disjunctive model the consumer may want to settle for either a product with a lot of memory or a lot of software. Mathematically, we can express this as A j = min(¦˛ k ¦Ä jk , 1) Where A j and ¦Ä jk are defined as before.
- 30. 3) Lexicographic Model :- This model assumes that all attributes are used, but in a stepwise manner. Brands are evaluated on the most important attributes first; then a second attribute is used only if there are ties, and so forth. Mathematically, if we assume that the attributes are arranged in order from most important to least important, then brand j is the preferred brand if: y ji > y jk for all brands k,k = 2,ˇ,k