Solid state and types of solids
- 1. SOLID STATE SARANYA H C KEYI SAHIB TRAINING COLLEGE
- 3. CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS A crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions.
- 4. AMORPHOUS SOLIDS An amorphous solid is any noncrystalline An amorphoussolid is a material in which the atoms and molecules are not organized in a definite lattice pattern. Such solids include glass, plastic, and gel.
- 5. CLOSE PACKING IN CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS The packing of constituent particles during the formation of a crystal takesplace in such a way that the available space is used most economically and a state of maximum possible density is reached. This type of packing is called close packing
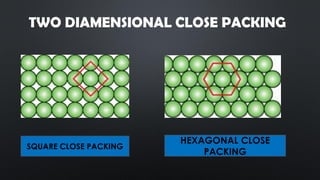
- 6. TWO DIAMENSIONAL CLOSE PACKING SQUARE CLOSE PACKING HEXAGONAL CLOSE PACKING
- 7. SQUARE CLOSE PACKING ? In this arrangement the particles in the adjacent rows show horizontal as well as vertical arrangement in the plane ? Each central sphere is in contact with 4 other spheres
- 8. HEXAGONAL CLOSE PACKING ? In this arrangement particles of the second row are placed in the depressions between particles of first row. ? Each particle is in contact with six other particles which are arranged hexagonally around it.
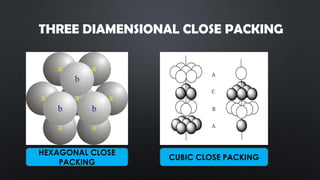
- 9. THREE DIAMENSIONAL CLOSE PACKING HEXAGONAL CLOSE PACKING CUBIC CLOSE PACKING
- 10. CO-ORDINATION NUMBER In any crystal lattice, the number of nearest neighbours with which a given particle is in contact is called the co-ordination number CN=6
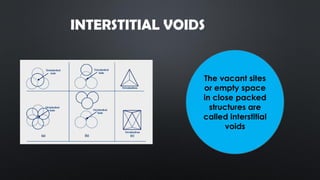
- 11. INTERSTITIAL VOIDS The vacant sites or empty space in close packed structures are called interstitial voids
- 12. MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Classified into mainly into two ? ?
- 13. DIAMAGNETIC SUBSTANCES ? Weakly repelled by the magnetic field ? Electrones paired
- 14. PARAMAGNETIC SUBSTANCES ? Weakly attracted by the magnetic field ? Contain unpaired electrones
- 15. THANK YOU