Types of computer viruses
- 1. TYPES OF COMPUTER VIRUSES PRESENTED BY SHIELA MAE BARASON GRADE 10 SPECIAL SCIENCE CLASS
- 2. OBJECTIVES: ’ü▒Knowing the 9 kinds of viruses in your software. ’ü▒Knowing its structure/image.
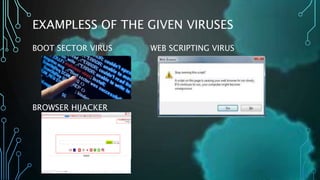
- 3. NINE (9) TYPES OF COMPUTER VIRUSES ’āś BOOT SECTOR VIRUS This virus got attention when floppy disks were used to boot a computer. In modern computers, this virus could appear on the ŌĆ£Master Boot RecordŌĆØ. In the partitioned storage device of your computer, it is the first sector to take place.
- 4. ’āśWEB SCRIPTING VIRUS ŌĆóSimilar to the hyperlinks that we used in Microsoft Word, many websites rest on codes to provide engaging content to their users. For example, since the trends of watching videos online have now become very popular ŌĆō more than 2 Billion Videos are streamed on Facebook every day, these videos also execute a specific code.
- 5. ŌĆóThese codes can be exploited and it is very troublesome to note that this exploitation has taken place on some very notable sites. All the hackers have to do it to leave a comment in the Comments Section of the website which contains that code. Thus, even without the Webmaster knowing it, the code gets exerted into the site.
- 6. ’āśBROWSER HIJACKER is a form of unwanted software that modifies a web browser's settings without a user's permission, to inject unwanted advertising into the user's browser. A browser hijacker may replace the existing home page, error page, or search engine with its own. It functions by installing malicious code into the memory of your computer, infecting current programs and any others you may install in the future.
- 7. ’āśRESIDENT VIRUS ŌĆó It functions by installing malicious code into the memory of your computer, infecting current programs and any others you may install in the future. ŌĆóAfter inserting itself directing into the memory of your system, this virus has the capability to take a number of actions. One of its more troublesome features is its ability to run away. Leaving behind the file which was originally
- 8. ’āśDIRECT ACTION VIRUS ŌĆóSimilar to the Vienna virus which shocked computers in 1998, this virus comes into action after you have executed the file. The load is delivered to your computer and the virus becomes active. ŌĆóHowever, this virus has a limitation. It takes no action unless the file which is infected gets implemented again.
- 9. ’āśPOLYMORPHIC VIRUS Polymorphic virus has exploited this limitation beautifully as it changes its code every time the infected file is executed. Thus, it becomes nearly impossible for any ordinary antivirus to track it down.
- 10. ’āśFILE INFECTOR VIRUS Although the word ŌĆ£fileŌĆØ in its name might suggest otherwise, this virus does not take the help of files every time. In fact, the file is only the starting point as the file infector dwarfs the first file after which it re-writes the file.
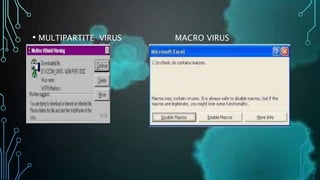
- 11. ’āśMULTIPARTITE VIRUS A multipartite virus is a fast-moving virus that uses file infectors or boot infectors to attack the boot sector and executable files simultaneously. Mostviruses either affect the boot sector, the system or the program files.
- 12. ’āśMACRO VIRUS Appearing in the form of a word document which seemingly links the user to pornographic websites, Melissa is one of the most known Micro Virus. Going one step further, this virus not only exploits the user but also his/her friends by mailing the copies of the infected virus document to the contact list.
- 13. EXAMPLESS OF THE GIVEN VIRUSES BOOT SECTOR VIRUS WEB SCRIPTING VIRUS BROWSER HIJACKER
- 14. RESIDENT VIRUS DIRECT ACTION VIRUS POLYMORPHIC VIRUS FILE INFECTOR VIRUS
- 15. ŌĆó MULTIPARTITE VIRUS MACRO VIRUS
- 17. BE AWARE ! AND SHARE !