Mapping skills
- 2. LATITUDES • Horizontal lines (east to west) • Divide the earth into northern and southern hemispheres • Measured in degrees North & South • Maximum possible latitude: 90 degrees (North & south poles)
- 3. LONGITUDES • Vertical lines (north to south) • Divide the earth into Eastern and western hemispheres • Measured in degrees East & West • Maximum possible longitude: 180 degrees
- 4. INTERNATIONAL DATE LINE • Opposite the prime meridian • Lies in the pacific ocean • Not a straight line • Separates two calendar days • Eastern hemisphere is one day ahead of the western hemisphere
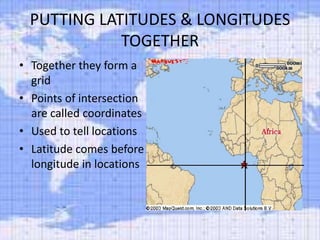
- 5. PUTTING LATITUDES & LONGITUDES TOGETHER • Together they form a grid • Points of intersection are called coordinates • Used to tell locations • Latitude comes before longitude in locations
- 7. PHOTOGRAPHS • 3 types: Landscape photographs Aerial Photographs Satellite Images
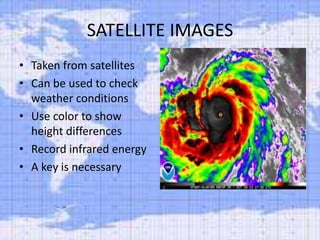
- 8. SATELLITE IMAGES • Taken from satellites • Can be used to check weather conditions • Use color to show height differences • Record infrared energy • A key is necessary
- 9. KEY FOR A SATELLITE IMAGE COLOR FEATURES White-cream Beaches, sand dunes, sandy areas Yellow Areas with little vegetation cover Pink-red Trees, parks and lawns in urban areas Red-Magenta Forest (deep red) Dark blue to black Deep waters- oceans, rivers, dams or lakes