Wave (ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч)
- 1. SK SABBIR ALI NORTH WESTERN UNIVERSITY BANGLADESH WELCOME
- 2. а¶ђа¶ња¶ЈаІЯ а¶Єа¶ЃаІВа¶є аІІ) ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч аІ®) ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶ђаІИපගඣаІНа¶ЯаІНа¶ѓ аІ©) ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඙аІНа¶∞а¶Ха¶Ња¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗබ аІ™) ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶Йබඌයа¶∞а¶£ аІЂ) а¶Ча¶Ња¶ґа¶£а¶ґа¶§а¶Х аІИа¶£а¶£а¶®а¶Њ аІђ) ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч
- 3. ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч' аІИа¶Њ ඥаІЗа¶Й а¶єа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Њ а¶Па¶Х а¶ІаІНа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ ඙а¶∞аІНа¶£а¶ЊаІИаІГටаІНට а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Чබඌ ථ а¶∞аІНа¶Њ ඥа¶Хඌථ а¶Ьа¶°а¶Љ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Па¶Х а¶ЄаІНඕඌථ ඥаІЗа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х а¶Еථඃ а¶ЄаІНඕඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Чථ ගපග а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌපа¶∞ට а¶Ха¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ පа¶ХථаІНටаІБ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х පථа¶Ь පථа¶Ь а¶ЄаІНඕඌථ ඥаІЗа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х а¶ЄаІНඕඌථඌථаІНටපа¶∞ට а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ ථඌ а•§ පа¶Ха¶ЫаІБ පа¶Ха¶ЫаІБ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶њаІВа¶£а¶ѓ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Ља¶У (а¶ЕаІЗа¶£а¶ЊаІО ඥа¶Хඌථ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ а¶Ыа¶Ња¶°а¶Ља¶Ња¶З) а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌපа¶∞ට а¶єа¶ЩаІНа¶Чට ඙ඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞а•§ а¶Па¶ІаІНа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶єа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Њ ටඌපධඊටа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЪаІМа¶ЃаІНа¶ђа¶Х ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶ПаІИа¶В а¶єа¶ѓа¶Ља¶ЩаІНа¶Чටඌ а¶Ѓа¶єа¶Ња¶Ха¶∞аІНа¶ЈаІАа¶ѓа¶Љ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч[ а¶Ьа¶°а¶Љ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶∞ а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Чබඌ а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ а¶Ђа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ඥа¶∞аІН ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶ЄаІГපඣаІНа¶ЯаІН а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ ටඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х а¶∞аІНඌපගа¶Х ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч аІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а•§ а¶Па¶З ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶∞ ඥа¶Хඌථ а¶ЄаІНඕඌඃඊඊаІА පаІИа¶ЪаІНаІБඃපට а¶Ша¶Яа¶Ња¶ѓа¶Љ ථඌ, аІИа¶∞а¶В а¶Па¶З ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞а¶ЄаІН඙බථ аІИа¶Њ а¶Ха¶ЃаІН඙ථ බаІНа¶ђа¶Ња¶∞а¶Њ а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌප ට а¶єа¶ѓа¶Ља•§а¶ЄаІБටа¶∞а¶Ња¶В а¶∞аІНඌපගа¶Х ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඪථаІНа¶ЪаІНа¶Њ а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ а¶Ьථඃ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓа¶Яа¶њ පඪаІНඕපටඪаІНඕඌ඙а¶Х а¶ПаІИа¶В а¶ЕපаІИපගථаІНථ а¶єа¶Уа¶ѓа¶Ља¶Њ ඙аІНа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Ља¶Ња¶Ьථ ඙ඌපථа¶∞ а¶Й඙පа¶∞ටа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч
- 4. ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶ђаІИපගඣаІНа¶ЯаІНа¶ѓ аІІ)ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶ЄаІГපඣаІНа¶ЯаІН а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶∞ а¶ЄаІН඙බථ аІИа¶Њ а¶Ха¶ЃаІН඙а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ а¶Ђа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а•§ පа¶ХථаІНටаІБ а¶Па¶∞ ඙аІНа¶∞аІЗа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІИ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Њ а¶ЄаІНඕඌථඌථаІНටපа¶∞ට а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ ථඌ පаІБа¶ІаІНаІБඁඌටаІНа¶∞ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ පаІЗටа¶∞ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Љ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ња¶Ха¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Чබඌ ථ а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌපа¶∞ට а¶єа¶ѓа¶Ља•§ аІ®)ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඥаІИа¶Ч а¶У а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞ а¶ЄаІН඙බа¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ ඥаІИа¶Ч а¶Ж а¶Ња¶¶а¶Ња•§ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶ЄаІИ а¶Ьа¶Ња¶ѓа¶Ља¶Ча¶Ња¶ѓа¶Љ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඥаІИа¶Ч а¶Па¶Ха¶З аІЗа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х පа¶ХථаІНටаІБ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Њ පаІИපаІЗථаІНථ ඥаІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ч а¶ЄаІН඙පබට а¶єа¶ѓа¶Ља•§ а¶Єа¶Ња¶Ѓа¶ѓа¶ЊаІИа¶ЄаІНඕඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Чථ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞ ඥаІИа¶Ч а¶ЄаІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЪаІНа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Љ ඥаІИа¶ґа¶ња•§ аІ©)а¶ЄаІИ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶З ගපග а¶У ටаІЗа¶ѓ а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъа¶Ња¶∞а¶£ а¶Ха¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞а•§ аІ™)ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ පаІИа¶ЄаІНටඌа¶∞,а¶Ха¶ЃаІН඙ථ, ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Чබබа¶Ша¶£а¶ѓ а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ыа•§ аІЂ)ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Еа¶ЧаІНа¶∞а¶Ча¶Ња¶Ѓа¶ЉаІА аІИа¶Њ පඪаІНඕа¶∞ а¶єа¶ЩаІНа¶Чට ඙ඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞а•§ аІђ)а¶Жа¶°а¶Љ аІИа¶Њ පඁаІНа¶ђа¶Х а¶ЕаІЗа¶£а¶ЊаІО а¶ЕථаІБ඙аІНа¶∞а¶ЄаІНඕ аІИа¶Њ а¶ЕථаІБබබа¶Ша¶£а¶ѓ аІИа¶∞а¶ЊаІИа¶∞ а¶єа¶ЩаІНа¶Чට ඙ඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞а•§ аІ≠)а¶Па¶∞ ඙аІНа¶∞පට඀ ථ, ඙аІНа¶∞පටඪа¶∞а¶£,аІИඃපටа¶ЪаІНа¶Ња¶∞,а¶Е඙аІИа¶§а¶£ ථ а¶Ша¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Яа•§ аІЃ)ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඙аІНа¶∞аІИа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶єа¶∞ а¶ЕපаІЗа¶ЃаІБа¶Ц аІИа¶Њ පබа¶Х а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ыа•§
- 5. ඙ඌපථа¶ЩаІНа¶Чට а¶Эа¶Ња¶Ња¶Б඙ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ඙ඌපථа¶∞ а¶Й඙පа¶∞ටа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶ЄаІГපඣаІНа¶ЯаІН а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ
- 6. ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඙аІНа¶∞а¶Ха¶Ња¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗබ а¶ЕථаІБ඙аІНа¶∞а¶ЄаІНඕ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч вАҐ ඥа¶∞аІН ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъа¶Њ а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ පබа¶Х а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞ а¶ЄаІН඙බа¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ха¶∞ а¶Єа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗ а¶Єа¶Ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ха¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£ аІЗа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х ටඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х а¶ЕථаІБ඙аІНа¶∞а¶ЄаІНඕ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч аІИ а¶Њ а¶єа¶ѓа¶Ља•§ ඥа¶∞аІНඁථ ටඌපධඊටа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЪаІНаІМа¶ЃаІНа¶ђа¶Ха¶ЉаІАа¶ѓа¶Љ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч аІИа¶Њ а¶ЄаІБටඌа¶∞ а¶Ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ІаІНа¶ѓ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Љ а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌපа¶∞ට ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶ЕථаІБබаІИа¶∞аІНа¶ШаІНа¶ѓ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч вАҐ а¶ЕථаІБබබа¶Ша¶£а¶ѓ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъа¶Њ а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ පබа¶Х а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞ а¶ЄаІН඙බа¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ха¶∞ а¶Єа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗ ඪඁඌථаІНටа¶∞а¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ч аІЗа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ха•§ а¶Па¶∞ а¶Йබඌයа¶∞а¶£ а¶єа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Њ а¶ња¶ђаІНබ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча•§
- 7. A = ඙ඌපථа¶∞ а¶ЧаІЗа¶ЉаІАа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞. B = а¶Еа¶ЧаІЗа¶ЉаІАа¶∞ ඙ඌපථа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶§а•§ а¶Й඙පа¶∞ටа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶∞ а¶Па¶Ха¶Яа¶њ аІИа¶ЄаІНටаІБа¶∞ а¶Й඙аІИаІГටаІНටඌа¶Ха¶Ња¶∞ а¶Чපට а¶ЧаІЗа¶ЉаІАа¶∞ටඌ а¶Ха¶Ѓа¶Ња¶∞ а¶Єа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗ а¶Єа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗ ඪඁඌථ а¶єа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Љ а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Є 1 = ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъа¶Ња¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£а¶∞ පබа¶Х 2 = ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ња¶ЉаІАа¶∞аІНа¶Ја¶£ 3 = ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч඙ඌබ 1 а¶Єа¶∞ а¶Ыපබට ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч පаІАа¶ЈаІН аІИа¶Њ а¶ЪаІНаІВ а¶°а¶Ља¶Њ а¶ПаІИа¶В ට а¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч඙ඌаІИ аІИа¶Њ ට බаІНа¶ђа¶Ња¶∞а¶Њ а¶ђаІИපගඣаІНа¶ЯаІНඌපඃඊට
- 8. ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඙аІНа¶∞а¶Ха¶Ња¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗබ а¶ЕථаІБ඙аІНа¶∞а¶ЄаІНඕ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶ЕථаІБබаІИа¶∞аІНа¶ШаІНа¶ѓ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч
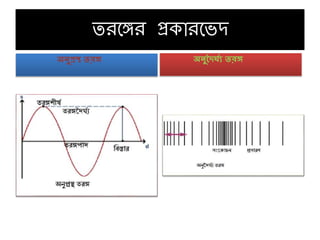
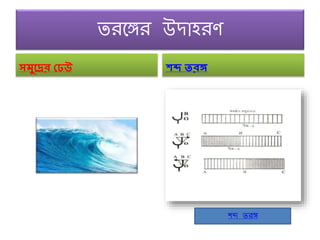
- 9. 1)а¶Єа¶ЃаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗа¶∞ ඥаІЗа¶Й - ඙ඌපථа¶∞ а¶Й඙පа¶∞ටа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌපа¶∞ට ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча•§ 2)ඥаІИටඌа¶∞ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч, а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶За¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞а¶Ња¶Уа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶ЉаІЗ, а¶ЕаІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ඌපයට а¶∞පග, බаІГගඃඁඌථ а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Њ, а¶Еපටа¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІИа¶ЧаІБථඊаІА а¶∞පග, а¶Па¶ХаІНа¶Є ඥа¶∞, а¶ПаІИа¶В а¶Ча¶Ња¶Ѓа¶Њ а¶∞පග බаІНа¶ђа¶Ња¶∞а¶Њ ටඌපධඊටа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЪаІНаІМа¶ЃаІНа¶ђа¶Х ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч ඐටа¶∞а¶ЉаІА. а¶Па¶З а¶ІаІНа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£а¶∞ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඥаІЗа¶ЩаІНа¶ЧටаІНа¶∞ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъа¶Њ а¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ а¶Ьථඃ ඥа¶Хඌථ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ ඙аІНа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Ља¶Ња¶Ьථ а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ а¶®а¶Ња•§ а¶њаІВа¶£а¶ѓ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓ а¶Па¶З ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶Чපටа¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІИа¶Ч а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞ ඥаІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ча¶∞ ඪඁඌථ 3)а¶ња¶ђаІНබ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч вАФ а¶§а¶∞ , а¶Хආගථ аІИа¶Њ аІИа¶Ња¶ѓа¶ЉаІИа¶ЉаІАа¶ѓа¶Љ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Љ а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌපа¶∞ට а¶∞аІНඌපගа¶Х ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶∞аІНа¶Њ а¶Жа¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Чබа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х පаІНа¶∞аІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£а¶∞ а¶ЕථаІБаІЗаІВ පට а¶Ґа¶¶а¶ѓа¶Ља•§ 4)а¶ЯаІНа¶∞аІНඃඌප඀а¶Х ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч 5)аІЗаІВ а¶Ха¶ЃаІН඙ඊаІАа¶ѓа¶Љ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч - аІЗаІВ පඁа¶Ха¶ЃаІН඙ аІИа¶Њ පаІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ђа¶Ња¶∞а¶£а¶Ьපථට а¶Ха¶Ња¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£ ඙аІГපаІЗаІИа¶ЉаІАа¶∞ ඥаІЗටа¶∞ පබа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Љ ඙аІНа¶∞аІИඌපයට ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча•§ පටථ а¶ІаІНа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£а¶∞ аІЗаІВ а¶Ха¶ЃаІН඙ඊаІАа¶ѓа¶Љ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ы - S, P, а¶ПаІИа¶В L. 6)а¶Ѓа¶єа¶Ња¶Ха¶∞аІНа¶ЈаІАа¶ѓа¶Љ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч - а¶Ѓа¶єа¶Ња¶Ха¶∞аІНа¶ЈаІАа¶ѓа¶Љ ඥаІЗа¶ЩаІНа¶ЧටаІНа¶∞ а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Чබඌ ථа¶Ьපථට а¶Ха¶Ња¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£ а¶ЙබаІНа¶≠аІВට а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞ ඪඁඌථ ඥаІИа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ч а¶ІаІНа¶ЊаІИඁඌථ, а¶Еපට аІЗа¶ЉаІАа¶£ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча•§ а¶П ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ ඙аІНа¶∞а¶ХаІГ පට а¶Ьඌථඌ а¶∞аІНа¶Ња¶ѓа¶Ља¶Жа¶ЗථඪаІНа¶Яа¶Ња¶За¶ЩаІНа¶Чථа¶∞ а¶Єа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶Ња¶∞а¶£ а¶Жа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч඙පаІЗа¶ХටටаІНටаІНа¶ђ ඥаІЗа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ха•§ 7)а¶Ьධඊටඌ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч,а¶ШаІВа¶£а¶£а¶Ња¶ѓа¶Ља¶Ѓа¶Ња¶® ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶ЙаІО඙ථаІНථ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а•§ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶Йබඌයа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶£а¶∞ а¶Ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ІаІНа¶ѓ а¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ѓа¶Ља¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ы
- 10. ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ а¶Йබඌයа¶∞а¶£ а¶Єа¶ЃаІБබаІНа¶∞аІЗа¶∞ ඥаІЗа¶Й පඐаІНබ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶ња¶ђаІНබ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч
- 14. ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ вАҐ ඥа¶∞аІН а¶Ьа¶°а¶Љ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ බаІНа¶ђа¶Ња¶∞а¶Њ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Єа¶ЮаІНа¶Ъඌපа¶∞ට а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ ටඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ аІИ а¶Њ а¶∞аІНа¶Ња¶ѓа¶Ља•§ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Х පථඁаІНථප පа¶Цට аІЗа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІИ ඙аІНа¶∞а¶Ха¶Ња¶∞ඌථаІНටа¶∞ а¶Ха¶∞а¶Њ а¶∞аІНа¶Ња¶ѓа¶Ља¶Ља¶Г вАҐ а¶Єа¶ЉаІАපඁට а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ а¶ПаІИа¶В а¶Еа¶Єа¶ЉаІАа¶Ѓ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ вАҐ а¶Єа¶∞ බа¶∞පа¶Ца¶Х а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ а¶∞аІНපබ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ ඥа¶∞аІН ඥа¶Хඌථ පаІИබаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Чට а¶ЕаІИපඪаІНඕට පаІЗථаІНථ පаІЗථаІНථ ටа¶∞а¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶∞ පаІИа¶ЄаІНටඌа¶∞ ඥа¶∞аІНа¶Ња¶Ч а¶Ха¶∞а¶Њ а¶∞аІНа¶Ња¶ѓа¶Ља•§ вАҐ ඥයඌа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ьපථඃඊඌඪ аІИа¶Њ а¶Єа¶Ѓ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Ѓа¶∞ а¶Ха¶£а¶Ња¶ЧаІБа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч а¶Ња¶∞ а¶ђаІИපගඣаІНа¶ЯаІНа¶ѓ а¶ЄаІНඕඌථа¶ЩаІНа¶ЧаІЗа¶ЩаІНа¶Чබ ඙පа¶∞аІИа¶ґа¶§а¶£ ට а¶єа¶ѓа¶Љ а¶®а¶Ња•§ вАҐ а¶Жа¶За¶ЩаІНа¶Ча¶Єа¶Ња¶ЯаІНа¶∞аІНප඙а¶Х а¶Ѓа¶Ња¶ІаІНа¶ѓа¶Ѓ