01_C_3_Introduction Machine Protection.ppt
- 1. Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD SIPROTEC 4 - Application and exercises of generator/motor protection SIPROTEC 4 - Application and exercises of generator/motor protection
- 2. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 2 Presenter: Bernd Sommer PTD EA12 Phone 0911-433-8222 Fax 0911-433-7396 email Bernd.Sommer@siemens.com Training: Generator Protection Introduction into Machine Protection
- 3. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 3 Rotating Machines: ’ü« Generators (asynchronous and synchronous) ’ü« Motors (asynchronous and synchronous) Stand still Machines: ’ü« Transformers (variable design and vector groups) The machine protection includes all numerical devices which are able to de detect faults and abnormal operating conditions on machines and react according the situation. It protects the objects against inadmissible stress and itŌĆÖs indirect also a human protection. The protection devices must fulfil the following 3S criteria: ’ü« Selectivity (switch off of the faulty system) ’ü« Speed (fast as necessary) ’ü« Security (high security and reliability) What are Machines and what is Machine Protection?
- 4. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 4 Internal Faults: Stator: ’ü« Earth Faults ’ü« Short Circuits (two and three phase) ’ü« Inter-turn Faults (at separate stator windings) ’ü« Overload Rotor, Excitation Circuit: ’ü« Earth Faults (single, double) ’ü« Failure in the Excitation (partly or loss of excitation) ’ü« Voltage Rise ’ü« Over-excitation (U/f) Faults in Synchronous Generators (1)
- 5. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 5 Grid/Transformer: ’ü« Earth Faults ’ü« Short Circuits ’ü« Overload ’ü« Unbalanced Load ’ü« Asynchronous Condition (cap.load, long short circuit duration) ’ü« Torsion Stress ’ü« Under-frequency (PG < PL) In Turbine, Regulation: ’ü« Loss of Prime Mover (Reverse power) ’ü« Over- and Under-voltage ’ü« Over- and Under-frequency ’ü« Over-excitation (U/f) (Wrong regulation) Faults in Synchronous Generators (2) External Faults:
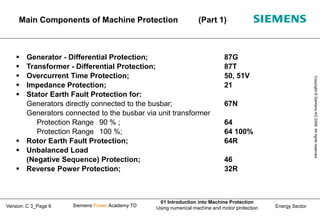
- 6. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 6 ’é¦ Generator - Differential Protection; 87G ’é¦ Transformer - Differential Protection; 87T ’é¦ Overcurrent Time Protection; 50, 51V ’é¦ Impedance Protection; 21 ’é¦ Stator Earth Fault Protection for: Generators directly connected to the busbar; 67N Generators connected to the busbar via unit transformer Protection Range 90 % ; 64 Protection Range 100 %; 64 100% ’é¦ Rotor Earth Fault Protection; 64R ’é¦ Unbalanced Load (Negative Sequence) Protection; 46 ’é¦ Reverse Power Protection; 32R Main Components of Machine Protection (Part 1)
- 7. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 7 ’é¦ Overvoltage Protection (Undervoltage); 59, (27) ’é¦ Over and Under-frequency Protection; 81 ’é¦ Underexcitation (Loss of field) Protection; 40 ’é¦ Stator Overload Protection; 49 ’é¦ Over-excitation (U/f) Protection; 24 ’é¦ Out of Step Protection; 78 ’é¦ Breaker Failure Protection; 50BF ’é¦ Rotor Overload Protection; 49R (Overcurrent at excitation transformer) ’é¦ Interturn Fault Protection (separate Stator windings - hydro generators) ’é¦ Tripping matrix (Software matrix) Main Components of Machine Protection (Part 2)
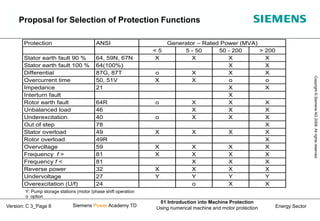
- 8. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 8 Protection ANSI Generator ŌĆō Rated Power (MVA) < 5 5 - 50 50 - 200 > 200 Stator earth fault 90 % 64, 59N, 67N X X X X Stator earth fault 100 % 64(100%) X X Differential 87G, 87T o X X X Overcurrent time 50, 51V X X o o Impedance 21 X X Interturn fault X Rotor earth fault 64R o X X X Unbalanced load 46 X X X Underexcitation 40 o X X X Out of step 78 X Stator overload 49 X X X X Rotor overload 49R X Overvoltage 59 X X X X Frequency f > 81 X X X X Frequency f < 81 X X X Reverse power 32 X X X X Undervoltage 27 Y Y Y Y Overexcitation (U/f) 24 o X X Y: Pump storage stations (motor /phase shift operation o option Proposal for Selection of Protection Functions
- 9. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 9 At the unit protection more than one trips and breakers are to handle. It depends on the fault type, the plant design and plant operation, generator operation and general operation philosophy. ’ü« Generator Breaker ’ü« Excitation Breaker ’ü« Turbine Rapid Shut Down ’ü« HV Network Breaker ’ü« Auxiliary Supply Breaker 1 ’ü« Auxiliary Supply Breaker 2 ’ü« Aux. Supply Changeover ’ü« SEE/SFC, Unit-trafo ’ü« SEE/SFC, Aux.-trafo ’ü« Reserve ’ü« Special Trips at Hydro Stations (e.g. braking) Breakers Protection Functions Tripping Concept
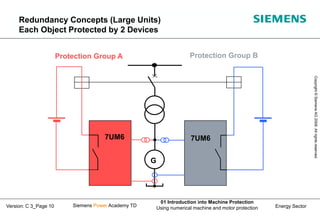
- 10. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 10 7UM6 Protection Group B G 7UM6 Protection Group A Redundancy Concepts (Large Units) Each Object Protected by 2 Devices
- 11. Energy Sector Copyright ┬® Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Siemens Power Academy TD 01 Introduction into Machine Protection Using numerical machine and motor protection Version: C 3_Page 11 G 7UM62 Without Redundancy Invest cost optimisation G 7UM62 Partly Redundancy (also limitations at the CTs and VTs and trip circuits) System/-cost optimisation 7UM61 Alternatives to the Full Redundancy