04 Phenotype Change Mutation and Environment
- 1. Phenotype affected by mutations • Mutation – an unpredictable change in the genetic material of an organism • Gene mutation – change in the structure of a DNA molecule, producing a different allele of a gene • Chromosome mutation – changes in the structure or number of whole chromosomes in a cell ALBIO9700/2006JK
- 2. Mutation factors (mutagen): • Ionising radiation (alpha, beta and gamma radiation) • Ultraviolet radiation • Chemicals (mustard gas) ALBIO9700/2006JK
- 3. Types of mutations • Base substitution Silent mutation eg. CCT GAG GAG to CCT GTG GAG • Base addition eg. CCT GAG GAG to CCA TGA GGA G Frame shift • Base deletion eg. CCT GAG GAG to CCG AGG AG ALBIO9700/2006JK
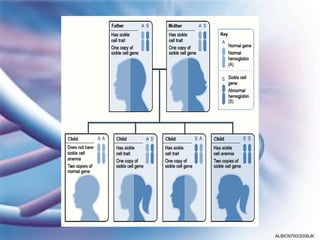
- 5. Examples of phenotype change caused by mutation • Sickle cell anaemia • Phenylketonuria ALBIO9700/2006JK
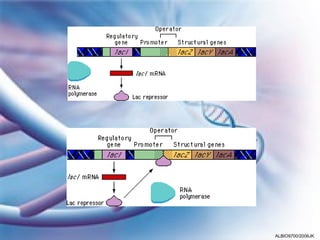
- 7. Phenotype affected by environment • Genotype of the organism does not always affect its phenotype in the same way • Eg. i) Human height ii) Dark tips to ears, nose, paws and tail in the Himalayan colouring in rabbits iii) lac operon in Escherichia coli ALBIO9700/2006JK
- 10. ALBIO9700/2006JK