04h Dew Point Corrosion.ppt
- 1. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 1 Dew Point Corrosion
- 2. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 2 Dew Point • Normally defined as the temperature and pressure at which a vapor condenses – e.g. water vapor => liquid water • Sometimes refers to sublimation point – e.g. ammonium chloride vapor => solid • We will also consider boil dry condition
- 3. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 3 Major Dew Point Issues • HCl dissolution into water at water dew points in unit overheads • Ammonium chloride sublimation from vapor and relation to water dew point • Ammonium bisulfide sublimation from vapor and relation to water dew point • Insufficient water wash volume
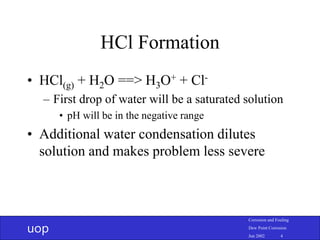
- 4. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 4 HCl Formation • HCl(g) + H2O ==> H3O+ + Cl- – First drop of water will be a saturated solution • pH will be in the negative range • Additional water condensation dilutes solution and makes problem less severe
- 5. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 5 Principal Problem Areas • Crude column overhead – Chlorides from crude – Water from crude and distillation column • FCC main column overhead – Chlorides from distillation column – Water from stripping steam in reactor, main column
- 6. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 6 Ammonium Chloride Formation • NH3(g) + HCl(g) <=> NH4Cl(g) • NH3 may be added as a neutralizer – Overheads of crude units and main columns of other units • NH3 may be formed from nitrogen and hydrogen in high temperature reactors – N2 + 3H2 <=> 2NH3 – Reformers, Hydrotreaters
- 7. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 7 Principal Problems • As temperature drops NH4Cl sublimates – Causes fouling • Water wash will correct fouling – Acidic, corrosive solution • Insufficient water wash – Damp solid – severe under deposit corrosion
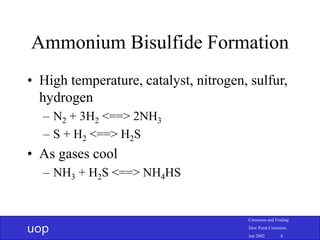
- 8. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 8 Ammonium Bisulfide Formation • High temperature, catalyst, nitrogen, sulfur, hydrogen – N2 + 3H2 <==> 2NH3 – S + H2 <==> H2S • As gases cool – NH3 + H2S <==> NH4HS
- 9. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 9 Principal Problems • As temperature drops NH4HS sublimates – Causes fouling • Water wash will correct fouling – Basic, corrosive solution/slurry • Insufficient water wash – Damp solid – severe under deposit corrosion
- 10. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 10 Ammonium Bisulfide Issues • Corrosivity of water solution function of – Kp in vapor – Liquid concentration – Temperature – Velocity
- 11. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 11 Ammonium Bisulfide Issues • Kp (mol% H2S x mol% NH3 in dry gas) – No corrosion to carbon steel if Kp < 0.02 • Kp can be higher for alloy material
- 12. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 12 Refinery Examples • Reactor effluent air coolers (REACs) for hydrotreaters and hydrocrackers • Sour water stripper overhead • FCC fractionation section
- 13. uop Corrosion and Fouling Dew Point Corrosion Jun 2002 13 Solutions • Water wash – Prevent fouling (NH4Cl, NH4HS) – Reduce corrosivity (NH4Cl, NH4HS, HCl)