07 communication
- 1. Communication Model The Communication Plan Specifying agent-agent transactions Transaction patterns
- 2. Role of Communication Model specifies knowledge/information transfer procedures top-level control over task execution multiple knowledge-intensive tasks additional communication tasks explanation facilities example: basic system-user interaction Communication Model 2
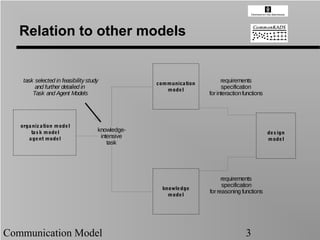
- 3. Relation to other models task selected in feasibility study communica tion requirements and further detailed in mode l specification Task and Agent Models for interaction functions orga niz a tion mode l ta s k mode l knowledge- de s ign a ge nt mode l intensive mode l task requirements specification knowle dge for reasoning functions mode l Communication Model 3
- 4. Input for communication modeling Task Model list of leaf tasks carried out by the considered agents Knowledge Model transfer functions Agent Model description of relevant agents: capabilities, responsibilities constraints. Communication Model 4
- 5. Information systems: communication More and more, IS are becoming information + communication systems: distributed applications (telematics) virtual organizations CSCW intelligent multi-agent systems workflow management concurrent engineering business chain management and integration Communication Model 5
- 6. Communication between actors Information modeling must cover: ŌĆō Organizational/Business analysis ŌĆō Task/Workplace analysis ŌĆō Actor/Agent analysis (both human and system) Usually, several actors cooperate in a business process or task, so ŌĆō Communication model intends to capture agent interactions within a joint task Communication Model = conceptual specification of: what kind of information objects are exchanged between agents in cooperating in and carrying out a task, and how? Communication Model 6
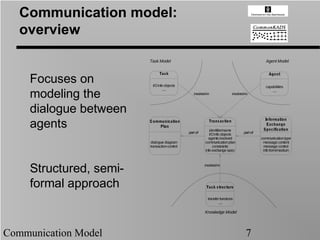
- 7. Communication model: overview Task Model Agent Model Tas k Agent Focuses on I/O info objects capabilities ..... ..... modeling the involved-in involved-in dialogue between Information agents Communication Plan part-of Trans action identifier/name part-of Exchange Specification I/O info objects agents involved communication type dialogue diagram communication plan message content transaction control constraints message control info exchange spec info form/medium involved-in Structured, semi- formal approach Tas k s tructure transfer functions ..... Knowledge Model Communication Model 7
- 8. Communication Model: overview Layered approach to Communication Modeling Three levels: 1. The overall communication plan, which governs the full dialogue between two agents 2. The individual transactions that link two (leaf) tasks carried out by two different agents 3. The information exchange specification that details the internal message structure of a transaction Start to construct the global overview, and fill in the details later Communication Model 8
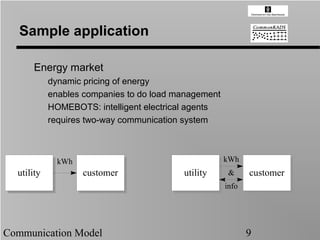
- 9. Sample application Energy market dynamic pricing of energy enables companies to do load management HOMEBOTS: intelligent electrical agents requires two-way communication system kWh kWh utility utility customer customer utility utility & customer customer info Communication Model 9
- 10. Transaction key component of Communication Model describes what information objects are exchanged indicates agents and tasks involved go-between of two tasks carried out by different agents building blocks for the full dialogue between two agents transactions have an internal structure example: obtain Communication Model 10
- 11. Other CM concepts Communication plan governs the full dialogue between the agents organization of transactions Information exchange specification details transaction structure consists of messages only necessary for complex communications Communication Model 11
- 12. Communication Plan easiest to begin with the overall communication plan describes full top-level dialogue typical transactions data input asking or answering questions presentation of reasoning results explanation of results Communication Model 12
- 13. Communication plan activities for each agent: list all tasks for each task: identify set of associated agent-agent transactions results combined in ŌĆ£dialogue diagram" DD depicts transactions between two agents draw a DD for each combination of two agents that exchange a reasonable amount of information specify control over the transactions Communication Model 13
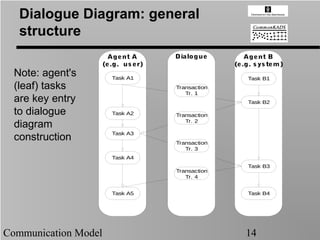
- 14. Dialogue Diagram: general structure Agent A Dialogue Agent B (e.g. us er) (e.g. s ys tem) Note: agent's Task A1 Task B1 (leaf) tasks Transaction Tr. 1 are key entry Task B2 to dialogue Task A2 Transaction Tr. 2 diagram Task A3 construction Transaction Tr. 3 Task A4 Task B3 Transaction Tr. 4 Task A5 Task B4 Communication Model 14
- 15. New Customer Services: ICT Technology Through networked microprocessors, devices can 'talk to', 'negotiate', 'make decisions', and 'cooperate' with one another. ŌĆō Smart equipment agents we call homebots (inspired by Star Trek and Asimow's Robot Stories) We use this,e.g., for distributed power load management (Further info: see separate case) Benefits: ŌĆō handles much larger scale ŌĆō higher degree of automation & decentralized flexible approach ŌĆō proactive for the customer Communication Model 15
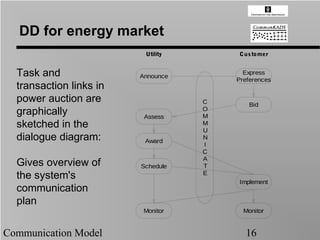
- 16. DD for energy market Utility Cus tomer Task and Announce Express Preferences transaction links in power auction are C Bid O graphically Assess M sketched in the M U dialogue diagram: Award N I C A Gives overview of Schedule T E the system's Implement communication plan Monitor Monitor Communication Model 16
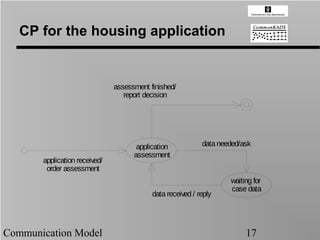
- 17. CP for the housing application assessment finished/ report decision application data needed/ask assessment application received/ order assessment waiting for case data data received / reply Communication Model 17
- 18. Transactions in the Homebots System Transaction list: ŌĆō 1. Kick-off the auction: sends a trigger signal to the customer agents to commence a load management action ŌĆō 2. Submit the bids: transmits the bids from the customer agents to the auctioneer for further processing ŌĆō 3. Present the awarded power allocation: informs the customer agents about the results of the auction ŌĆō 4. Present the associated real-time schedule: provides the customer agents with the calculated schedule that implements the awarded allocation ŌĆō 5. Receive the resulting real-time implementation data: transmits the actual metering data (Needed for billing and for assessing the need for further load management actions) Communication Model 18
- 19. Transaction control notations state diagrams pseudo-code with special control primitives SEND, RECEIVE CARRY-OUT (SEND/RECEIVE combination) WAIT-until/while PROCESS (task) ; (sequence) REPEAT-until/while, IF THEN ELSE & (AND), | (choice), V (OR) Communication Model 19
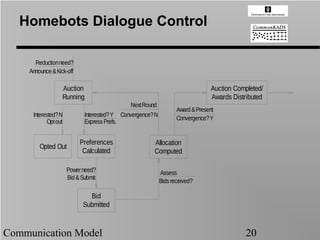
- 20. Homebots Dialogue Control Reduction need? Announce & Kick-off Auction Auction Completed/ Running Awards Distributed Next Round Award & Present Interested? N Interested? Y Convergence? N Convergence? Y Opt out Express Prefs. Preferences Allocation Opted Out Calculated Computed Power need? Assess Bid & Submit Bids received? Bid Submitted Communication Model 20
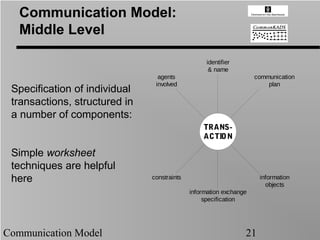
- 21. Communication Model: Middle Level identifier & name agents communication involved plan Specification of individual transactions, structured in a number of components: TRANS- ACTION Simple worksheet techniques are helpful here constraints information objects information exchange specification Communication Model 21
- 22. Illustration Middle Level: Homebots System (II) Submit-the-bid transaction description (Worksheet CM-1) ŌĆō Identifier/Name: Transaction 2: Submit-the-bid ŌĆō Information objects: linking Bid and Assess tasks: (1) bid; (2) going price or going allocation (depending on domain theory) ŌĆō Agents involved: (1) customer agents; (2) auctioneer/utility agent ŌĆō Communication plan: Homebots (base version) ŌĆō Constraints: (1) decision procedure for bidding completeness; (2) market convergence postcondition ŌĆō Information Exchange Spec: See Worksheet CM-2 Note: this transaction contains more than one message, and so is composite Communication Model 22
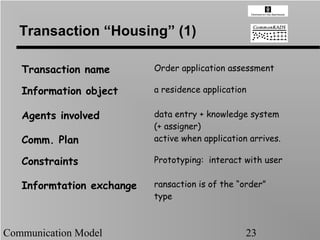
- 23. Transaction ŌĆ£HousingŌĆØ (1) Transaction name Order application assessment Information object a residence application Agents involved data entry + knowledge system (+ assigner) Comm. Plan active when application arrives. Constraints Prototyping: interact with user Informtation exchange ransaction is of the ŌĆ£orderŌĆØ type Communication Model 23
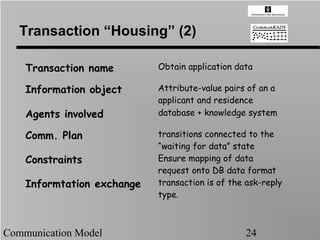
- 24. Transaction ŌĆ£HousingŌĆØ (2) Transaction name Obtain application data Information object Attribute-value pairs of an a applicant and residence Agents involved database + knowledge system Comm. Plan transitions connected to the ŌĆ£waiting for dataŌĆØ state Constraints Ensure mapping of data request onto DB data format Informtation exchange transaction is of the ask-reply type. Communication Model 24
- 25. Composite Transactions "I'm getting cold, so could you please shut the door?'' ŌĆō First part is just information: notification message ŌĆō Second part is request for action by the other agent: task delegation message So, within one transaction: two messages differring in both content and intent Transactions not only transmit content, but also an intended relationship between two agents. Both these aspects must be explicitly specified. ŌĆō Compare: "Hey, idiot, shut the door, I'm getting cold!" Communication Model 25
- 26. Speech Acts Agent communication languages often inspired by so-called speech act theory Makes distinctions between: Content ('locutionary nature') of a speech act or message -- what is actually being said -- Intended effect ('illocutionary force') on the other agent Actual effect ('perlocutionary force') on the other agent ŌĆō N.B. nice communication modeling exercises: "It's the economy, stupid!'' Edward Albee's Who's Afraid of Virginia Woolf? Communication Model 26
- 27. Communication Model: Detail Level Detailed message specification: 1. Content (locution): by means of a propositional statement 2. Intention (illocution): by means of typing a message Predefined types: ŌĆō Task Delegation: Request; Require; Order; Reject-td ŌĆō Task Adoption: Propose; Offer; Agree; Reject-ta ŌĆō Pure Information Exchange: Ask; Reply; Report; Inform Note: Intention = purpose x commitment ŌĆō Cf. performatives in KQML (DARPA Knowledge Sharing Effort) and esp. COSY (Daimler-Benz) Communication Model 27
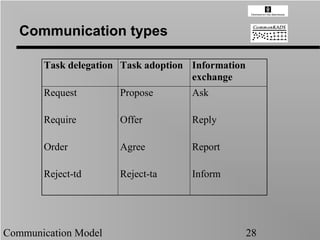
- 28. Communication types Task delegation Task adoption Information exchange Request Propose Ask Require Offer Reply Order Agree Report Reject-td Reject-ta Inform Communication Model 28
- 29. Semantics of Communication Types Request/Propose: potential for cooperation, but agent wishes to negotiate on the terms. Loosely: `I have an interest, but not yet a commitment'. Require/Offer: agent already has made a pre-commitment, and intends to prompt the receiving agent for its commitment. This type thus denotes a conditional commitment. Order/Agree: agent has made a commitment, and thus will act accordingly. Reject-td/ta: denote that the agent does not want to commit or cooperate. Ask/Reply: have as intent a query for information from another agent, and delivery of information in return. Report: types a message sent after an agent has acted towards a (previously) agreed task goal, with the intention to let the other agent know the status of achievement (e.g. success, failure, outcome of the action). Inform: refers to a message type that just delivers information objects to another agent. Indicates an independent informative action: no previous request or agreement involved. Communication Model 29
- 30. Typed Message Patterns Not only typing of single messages possible. Also, natural chains of message types can be formed (cf. COSY): Communication type patterns Communication Patterns INFORM ORDER REQUIRE REQUEST 1) REPORT AGREE REJECT-ta PROPOSE OFFER REJECT-ta 3) 5) 7) ASK AGREE OFFER PROPOSE REPLY REPORT ORDER REJECT-td REQUEST REQUIRE REJECT-td 2) 4) 6) 8) Communication Model 30
- 31. Worksheet CM-2: Information Exchange Specification Only needed for complex communication patterns energy market Worksheet structure Transaction Identifier/Name Agents involved: sender, receiver Information items Message specification Message control Communication Model 31
- 32. Transaction ŌĆ£submit-the-bidŌĆØ: message specifications Bid-message Auction-data-message type:PROPOSE type: INFORM content: bid content: market data from: customer agent from: auctioneer to: auctioneer to: customer agent Opt-out-message Next-round-message type: REJECT-TA type: REQUEST content: no part content: trigger next round from: customer agent from: auctioneer to: auctioneer to: customer agent Communication Model 32
- 33. Information items role: core object support item ŌĆō explanation texts of domain material rock photographs, mineral photographs ŌĆō reasoning traces ŌĆō WHY/HOW explanations syntactic form: data string, diagram, ... medium: pop-up window, command-line interface, human intervention, ŌĆ” cf. Design issues Communication Model 33
- 34. Control over messages Refinement of control in communication plan Notations: the same State diagram Pseudo code Communication Model 34
- 35. Transaction: submit-the-bid REPEAT WHILE <market convergence condition not satisfied> IF <interest in load management> THEN PROCESS(bid-task); SEND(BID-MESSAGE) ELSE SEND(OPT-OUT-MESSAGE) END-IF IF <bids received> THEN PROCESS(assess-task) ELSE PROCESS(decision subprocedure [e.g. WAIT...]) END-IF SEND(AUCTION-DATA-MESSAGE) & SEND(NEXT-ROUND-MESSAGE) END-REPEAT Communication Model 35
- 36. Validation techniques Communication-plan walk-through adequacy transaction structure completeness list of information items need for help or explanation Wizard-of-Oz technique experimental technique to validate interaction mock-up software Communication Model 36
- 37. Nielsen's guidelines for usability engineering Present a simple and natural dialogue Speak the user's language Minimize the user's memory load Maintain consistency in terminology Give feedback about what is going on Show clearly marked exits from unwanted states Offer shortcuts for the experienced user ŌĆ”.. Communication Model 37
- 38. Guidelines for balancing the communication model Key inputs: leaf tasks TM transfer function KM Take agent capabilities into account (see AM) syntactic form of media is area of both CM and DM guideline: in CM if conceptual reason Decide here about support information not in design model Communication Model 38
- 39. Communication model activities Identify core information objects to be exchanged between agents Identify associated transactions Draw important dialogue diagrams Combine this to a full communication plan Specify the individual transactions worksheets CM-1 and CM-2 Validate and balance the model Communication Model 39
























![Transaction: submit-the-bid
REPEAT WHILE <market convergence condition not satisfied>
IF <interest in load management>
THEN PROCESS(bid-task); SEND(BID-MESSAGE)
ELSE SEND(OPT-OUT-MESSAGE)
END-IF
IF <bids received>
THEN PROCESS(assess-task)
ELSE PROCESS(decision subprocedure [e.g. WAIT...])
END-IF
SEND(AUCTION-DATA-MESSAGE) &
SEND(NEXT-ROUND-MESSAGE)
END-REPEAT
Communication Model 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-communication-121214134029-phpapp01/85/07-communication-35-320.jpg)



