Antianginal drug
- 1. Presented by: Mr. Shaikh Akhil M.Pharm Asst. Prof. Dept. of Pharmacology, BCCO Pharmacy, Naigaon, S.R.T.M. University, Nanded
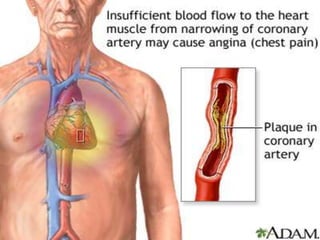
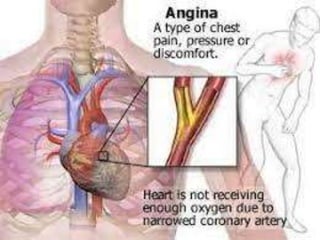
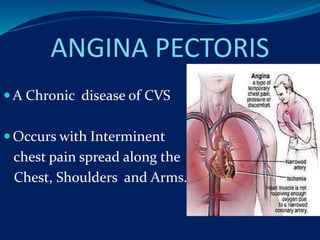
- 4. ANGINA PECTORIS ´éù A Chronic disease of CVS ´éù Occurs with Interminent chest pain spread along the Chest, Shoulders and Arms.
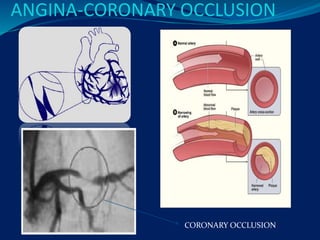
- 5. Angina- Characterstics sudden severe pressing chest pain Radiating- neack jaw back arm ( left) Different from CAD- Angina pectoris, acute syndrome, arrythmia,short breath Caused by- decreased O2 in coronary blood flow spasm of ventricle & muscle Obstruction of blood vessels by- atheroma Increase Demand of O2 decrease the supply of O2 ----angina Angina pectoris: a heart condition marked by paroxysms of chest pain due to reduced oxygen to the heart ÔÇó Angina pectoris, or angina, as it is commonly referred to, and coronary artery disease or arteriosclerosis are closely related. ÔÇó Angina occurs in people who have some form of blockage in the coronary arteries. In other words, it occurs in people with coronary heart disease.
- 7. Types Of Angina Pectoris 1. Stable Angina 2. Unstable Angina 3. Variant Angina (PrinzmetalÔÇÖs Angina)
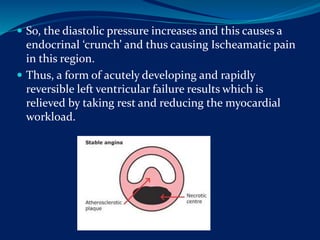
- 8. STABLE ANGINA ´éù Predictable ´éù Occurs on exercise, emotion or eating. ´éù Caused by increase demand of the heart and by a fixed narrowing of coronary vessels, almost always by atheroma. ´éù Coronary obstruction is ÔÇÿfixedÔÇÖ ´éù Blood flow fails to increase during increased demand despite the local factors mediated ÔÇÿvasodilationÔÇÖ and so ischeamic pain is felt.
- 9. ´éù So, the diastolic pressure increases and this causes a endocrinal ÔÇÿcrunchÔÇÖ and thus causing Ischeamatic pain in this region. ´éù Thus, a form of acutely developing and rapidly reversible left ventricular failure results which is relieved by taking rest and reducing the myocardial workload.
- 10. UNSTABLE ANGINA ´éù This is characterized by Pain that occurs with less excertion , cumulating pain at rest. ´éù The pathology is similar to that involved in Myocardial Infraction, namely platelet-fibrin thrombus associated with a ruptured atheromatous plaque, but without complete occulation of the vessels. ´éù The risk of infraction is subtanial, and the main aim of therapy is to reduce this.
- 11. VARIANT ANGINA (PRINZMETALÔÇÖS ANGINA) ´éù Uncommon ´éù Occurs at rest generally during sleep ´éù Caused by Large Coronary Artery Spasm ´éù Usually associated with atheromatous disease ´éù Abnormally reactive and hypertrophied segments in the Coronary Artery ´éù Drugs aimed at preventing & relieving Coronary Spasm.
- 12. DIAGNOSIS 1. STRESS (EXERCISE) TEST. 2. ECG (ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY) 3. CHEST X-RAY 4. CARDIAC ANGIOGRAPHY 5. BLOOD TEST (BIO-MARKERS)
- 13. 1. EXERCISE TEST/STRESS TEST ´éù Used to measure heartÔÇÖs response to exercise ´éù Patient asked to walk on a treadmill while the physician takes the ECG ´éù So any changes in heart function can be determined ´éù Alternatively the patient recieves an injection of a radioisotope (generally Thallium) which makes the heart visible to a special-linked camera ´éù 90% accurate ´éù But doesnÔÇÖt identify the exactly where and how the coronary arteries are blocked.
- 14. 2. ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG) ´éù Measures electrical activity of the heart ´éù Provides info about the changes or damages to the heart muscle ´éù DoesnÔÇÖt detect the narrowing of the coronary arteries ´éù During an Anginal attack the ECG may show 1. S-T phase depression. 2. T- phase inversion and/or 3. Ventricular arrythmia ´éù ECG- more abnormal with Unstable Angina where the elevation in S-T segment is found.
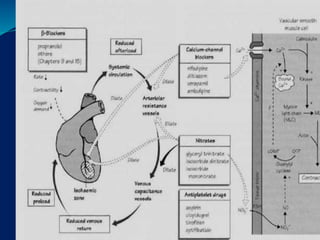
- 15. Anti Anginal Drugs 1. Nitrate- ÔÇó short acting- Glyceryl trinitrate, isosorbide dinitrate ÔÇó Long acting- Isosorbide dinitrate, isosorbide mononitrate 1. Beta blocker- propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol 2. Calcium channel locker- verapamil, diltiazem, amlodipine 3. Potassium channel opener- nicorandil 4. NA+ channel blocker- Ranolazine
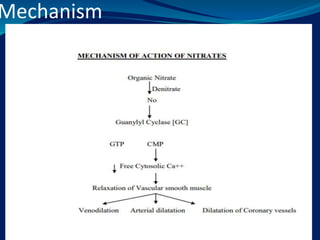
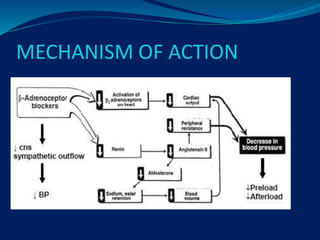
- 17. NITRATES Nitrate- ÔÇó short acting- Glyceryl trinitrate, isosorbide dinitrate ÔÇó Long acting- Isosorbide dinitrate, isosorbide mononitrate Nitrates- Nitrate are the vasodilator 1. Nitrates are converted to nitric oxide in the presence of by-gulutathion-s-transferase & aldehyde reductase 2. Nitric oxide activate the vascular guanylyl cyclase 3. Guanylyl cyclase is increase the synthesis of cAMP( cyclic guanosine monophosphate) 4. cGMP cause the dephosphorylation of protein kinase 5. This prevent interaction of action with myosin 6. They also decrease free cytosolic calcium 7. The smooth muscle relexation
- 18. Mechanism
- 19. ´éù Side effects Headache, Increased mortality, Recurrence of Myocardial Infraction, Dizziness, Flushing, Rapid heart beat, Restlessness, Dry mouth, Skin rash, Nausea PK- nitrates are lipid soluble well absorbed frum buccal mucous, intestine, skin Ingested orally First pass metabolism in liver, half life is longere ÔÇó Interaction- Sildenafil is interact with nitrates cause dangerous- severe hypotension ( reduce the body oxygen leavel which can hearts & brain damage
- 20. MARKETED FORMULATIONS ´éù GTN Sorbitrate (PIRAMAL) ´éù Vasovin (TORRENT) ´éù ISMO retard (PIRAMAL) ´éù Angicor (NOVARTIS) Nitroglyceride Isosorbide-5- monophosphate
- 21. K + channel opener ´éù Nicorandil ´éù open ATP sensitive K+ channel ´éù hyperpolaraziation ´éù Relaxation vascular smooth muscle ´éù se Preload se Afterload se Workload ´éù Increase coronary dilation ´éù Decrease angina ´éù Side effects- flushing, dizziness, palpitation, weakness, headache, nausea, vomiting
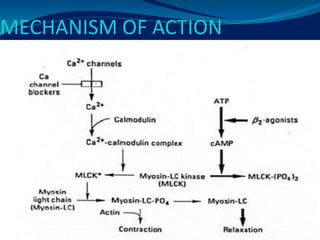
- 22. CALCIUM CHANNEL ANTAGONISTS ´éù types:- 1. Dihydropyridine (amlodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine) 2. Non-Dihydropyridine 1. Phenylalkylamine (verapamil, gallopamil) 2. Benzodiazapenes (diltiazem) 3. Non-selective (bepridil, mibefradil)
- 24. MARKETED PREPARATIONS ´éù Calaptin (PIRAMAL) ´éù Vasopten (TORRENT) ´éù Coriem XL (RANBAXY) ´éù Dicard (INTAS) ´éù Amtas (INTAS) ´éù Cadeut (PFIZER) Verapamil Diltiazem Amplodipine
- 25. Beta blocker - propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol ´éù Beta blocker inhibit the activation of heart by blocking Beta 1 receptor ´éù They reduce of work by the heart rate, contraction, cardiac output, blood pressure ´éù The reduce demand of O2 during exercise & rest ´éù All the blocker are non selective at high dose & decrease beta 2 receptor ´éù In classical angina beta blocker + Nitrates is a better response ´éù Contraindication in asthma, diabetes, brady cardia
- 26. ´üó-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONOSTS ´éù Important in prophylaxis of angina and treating unstable angina ´éù Decrease O2 consumption by the heart ´éù Effects on coronary vessels-not important ´éù Avoided in variant angina ´éù As they increase the chances of spasm ´éù Eg:- ´éù Atenolol ´éù Propranolol
- 28. MARKETED PREPARATIONS ´éù Betacard ( TORRENT) ´éù Aten (ZYDUS CADILA) ´éù Betacap (SUN PHARMA) ´éù Cardilax (INTAS)
- 29. COMBINATION THERAPY 1. Nitrates + ´üó-blockers :- in stable angina 2. Ca++ channel blockers + ´üó-blockers :-in stable angina when the treatment with nitrates and ´üó- blockers has failed. 3. Ca++ channel blockers + Nitrates :- in unstable angina 4. All 3 together:- when the combinations of 2 drugs has failed, where:- 1. Nitrates:- decrease Preload 2. Ca++ channel Blockers:- decrease Afterload 3. ´üó-blockers:- decrease heart rate and myocardial contractions
- 30. THANK YOU!!!!