1 auditorium acoustics
- 1. Acoustics of Concert Halls and Rooms SOME BASICS OF ARCHITECTURAL ACOUSTICS Auditorium Acoustics Science of Sound, Chapter 23 Principles of Vibration and Sound, Chapter 11 Kimmel Center
- 2. Free field Reflections p vs r log p vs log r SOUND FIELD
- 3. Sound decay Sound decay in a 400 m3 classroom Sound pressure level as a function of time for that room
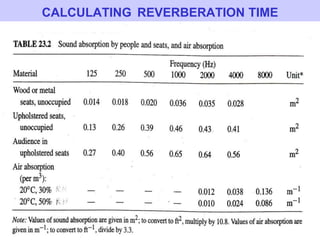
- 4. GROWTH AND DECAY OF REVERBERANT SOUND RT = K (volume / area) RT = 0.161 V/A (V in m3; A in m2 ) If room dimensions are given in feet, the formula may be written: RT= 0.049 V/A (V in ft.3 ; A in ft.2 )
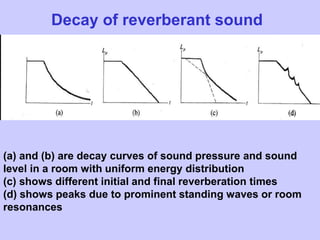
- 5. Decay of reverberant sound (a) and (b) are decay curves of sound pressure and sound level in a room with uniform energy distribution (c) shows different initial and final reverberation times (d) shows peaks due to prominent standing waves or room resonances
- 8. Desirable reverberation times for various sizes and functions Variation of reverberation time with frequency in good halls
- 12. Walt Disney Concert Hall
- 13. Disney
- 17. ?Spatial impression ?Intimacy ?Early decay time ?Clarity ?Ą°WarmthĄą Important criteria for concert halls: