1 f arson explosives
- 1. Forensic Arson andForensic Arson and Explosive InvestigationsExplosive Investigations
- 2. Forensic Arson and ExplosiveForensic Arson and Explosive InvestigationsInvestigations Two Main Areas of Interest: âĒ isolation and analysis of flammable residues âĒ collection and analysis of explosive material Any flammable liquid or substance used to start and/or maintain a fire is known as an accelerant Not all flammable or explosive material will burn in a fire â accelerants always get trapped in pores in material and will not burn
- 3. The Chemistry of FireThe Chemistry of Fire Fire is the product of combustion - the rapid combination of oxygen with another substance accompanied by the production of light and heat Two Important Points: âĒ Most combustion reactions will not happen by themselves (they are not spontaneous)âĶ.they need help getting started âĒThe energy released comes from the breaking and reforming of the bonds that hold the compounds together
- 4. Accelerants and ExplosivesAccelerants and Explosives Accelerants and explosives are almost always organic in nature (wood, gasoline, kerosene, paper, etc) If an organic molecule burns completely, the products are always carbon dioxide and water. Smoke, ash, carbon monoxide result from incomplete combustion. Explosive materials are often compounds that are chemically unstable â they want to react and form more stable molecules
- 5. Investigating Arson or BombingsInvestigating Arson or Bombings Steps to Follow: 1. Begin collecting evidence as soon as possible. 2. Collect totally burned, partially burned, and unburned samples from the scene for comparison 3. Back in the forensic lab, isolate and concentrate the accelerant material - there are four common methods used to isolate and concentrate this material 4. Analyze the material to determine its composition
- 6. Investigating Arson or BombingsInvestigating Arson or Bombings Steps to Follow: 1. Begin collecting evidence as soon as possible. 2. Collect totally burned, partially burned, and unburned samples from the scene for comparison 3. Back in the forensic lab, isolate and concentrate the accelerant material - there are four common methods used to isolate and concentrate this material 4. Analyze the material to determine its composition
- 7. Methods for Isolating and ConcentratingMethods for Isolating and Concentrating AccelerantsAccelerants a. Steam Distillation b. Solvent Extraction c. Head Space Analysis d. Vapor Concentration on Charcoal e. Solid Phase Extraction
- 8. Methods for Isolating and ConcentratingMethods for Isolating and Concentrating AccelerantsAccelerants a. Steam Distillation b. Solvent Extraction c. Head Space Analysis d. Vapor Concentration on Charcoal e. Solid Phase Extraction
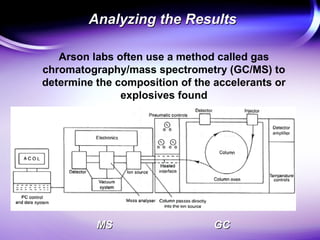
- 9. Analyzing the ResultsAnalyzing the Results Arson labs often use a method called gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) to determine the composition of the accelerants or explosives found GCGCMSMS
- 10. Analyzing the ResultsAnalyzing the Results Important Parts of a Gas Chromatograph: âĒ injection port and vaporization chamber âĒ column â usually inside coated with non-polar material âĒ a âcarrier gasâ to push accelerant molecules through the column âĒ a detector (usually this is the mass spectrometer)
- 11. Analyzing the ResultsAnalyzing the Results Important Parts of a Mass Spectrometer: âĒ ionizing chamber âĒ analyzer tube âĒ detector
- 12. Analyzing the ResultsAnalyzing the Results
- 13. Analyzing the ResultsAnalyzing the Results
- 14. Analyzing the ResultsAnalyzing the Results Ion Mobility Spectrometer âĒ vaporize with heat âĒ ionize the sample with electrons âĒ detect by how fast they move in an electric field