1 introduction to strategy
- 1. Strategic Management An Introduction to Strategy
- 2. Learning Outline ’éó What is strategic management? ’éó Why is strategic management important? ’éó Who is involved with strategic management? ’éó Strategic management today 2
- 3. A definition of strategy ’éó Goal-directed decisions and actions in which capabilities and resources are matched with the opportunities and threats in the environment. 3
- 4. Military influences in strategy ’éó ŌĆ£StrategosŌĆØ referred to a general in command of an army ’éó The art of the general ’ü¼ By 450 B.C. it came to mean managerial skill ’ü¼ By 330 B.C. it referred to the skill of employing forces to overcome positions to create a system of global governance ’éó Carl von Clausewitz ŌĆ£tacticsŌĆ”(involve) the use of armed forces in the engagement, strategy (is) the use of engagements for the object of warŌĆØ 1838 On War 4
- 5. Academic influences in strategy ’éó 1911 Scientific management (Taylor) ŌĆō Still in place today (UPS), some consider it micromanaging ’éó HBS requires a class in Business Policy in 1912 ’éó Adam SmithŌĆÖs ŌĆ£invisible handŌĆØ (the market) gives way to Alfred Sloan (GM CEO from 1923-1946) concept of the ŌĆ£visible handŌĆØŌĆömiddle manager ’éó Chester Bernard influential book ŌĆ£The ExecutiveŌĆØ argues that managers should pay attention to ŌĆ£strategic factorsŌĆØ ’éó Ronald CoaseŌĆÖs 1937 article ŌĆ£why firms existŌĆØ (Nobel Prize in economics) and Joseph SchumpterŌĆÖs concept of ŌĆ£disruptive technologiesŌĆØ written in 1942 bring in organizational economics ’éó Max Weber warns against bureaucratic organizations but sees a shift toward this way of organizing 5
- 6. Recent influences in strategy ’éó 1960s (Strategy and structure; Corporate Strategy) ŌĆó 1963 Harvard business conference leads to SWOT analysis ŌĆó BCG founded in 1963 ŌĆ£strategy boutiqueŌĆØ ŌĆó Created the portfolio analysis ŌĆó Stars, dogs, cash cows, question marks ’éó 1980s (PorterŌĆÖs 5 forces) ’éó 1990s (Resource based view of the firm) 6
- 7. Why is strategic management important? ’éó Gives everyone a role ’éó Makes a difference in performance levels ’éó Provides systematic approach to uncertainties ’éó Coordinates and focuses employees 7
- 8. Why Strategy? ’éó To change, an organization needs ’ü¼ Burning Platform ’ü¼ Vision ’ü¼ Leadership ’ü¼ Strategic Management ’ü¼ Political Management 8
- 9. Strategy vs. Strategic Management ’éó Strategy ’éó Strategic ’ü¼A series of goal- management ’ü¼ Analyze current directed decisions and actions situation ’ü¼ Develop matching an organizationŌĆÖs appropriate strategies skills and ’ü¼ Put strategies into resources with the action opportunities and ’ü¼ Evaluate, modify, threats in its or change environment strategy 9
- 10. Strategy vs. Strategic Management ’éó Strategy involves ’éó Strategic ’ü¼ OrganizationŌĆÖs management goals ’ü¼ Planning ’ü¼ Goal-oriented ’ü¼ Organizing action ’ü¼ Related decisions ’ü¼ Implementing and actions ’ü¼ Controlling ’ü¼ Internal strengths ’ü¼ External opportunities and threats 10
- 11. Basics of Strategic Management ’éó Four aspects that set strategic management apart ’ü¼ Interdisciplinary ŌĆó Capstone of the Business degree ’ü¼ External focus ŌĆó Competition ’ü¼ Internalfocus ’ü¼ Future direction 11
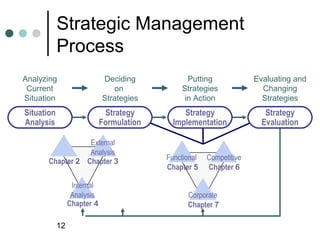
- 12. Strategic Management Process Analyzing Deciding Putting Evaluating and Current on Strategies Changing Situation Strategies in Action Strategies Situation Strategy Strategy Strategy Analysis Formulation Implementation Evaluation External Analysis Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Functional Competitive Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Internal Analysis Corporate Chapter 4 Chapter 7 12
- 13. Strategic Management Process ’éó Situation Analysis ’ü¼ Scanning & evaluating context ’ü¼ Internal and External environments ’éó Strategy formulation ’ü¼ Functional ’ü¼ Competitive ’ü¼ Corporate strategies 13
- 14. Levels of strategy Corporate What direction are we going and what business(es) are we in or do we want to be in? Competitive: How are we going to compete in our chosen business(es)? Functional What resources and capabilities do we have to support the corporate and competitive strategies? 14
- 15. Strategic Management Process ’éó Strategy implementation ’ü¼ Process of putting strategies into action ’ü¼ Consider implementation at each level ’éó Strategy evaluation ’ü¼ Was the strategy effective? ’ü¼ ŌĆ£Close the loopŌĆØ 15
- 16. Who does strategy? ’é¦ The Role of the Board of Directors ’é¦ Elected representatives of the companyŌĆÖs stockholders ’é¦ Legally obligated to represent and protect stockholderŌĆÖs ’é¦ The Role of Top Management ’é¦ Responsible for decisions and action of every employee ’é¦ Providing effective leadership ’é¦ Other Organizational Employees ’é¦ ImplementŌĆö put the strategies into action and monitor performance ’é¦ EvaluateŌĆödo the actual evaluations and take necessary actions 16
- 17. The Role of the Board of Directors ’é¦ Review and approve strategic goals and plans ’é¦ Review and approve organization's financial standards and policies ’é¦ Approve an organizational philosophy ’é¦ Monitor organizational performance and regularly review performance results ’é¦ Select, evaluate, and compensate top-level managers ’é¦ Develop management succession plans ’é¦ Monitor relations with shareholders and other key stakeholders 17
- 18. Who is on the board of directors? ’éó Chairman of the board ’ü¼ Chief Executive officer (CEO) ’éó President ’ü¼ Chief Operating officer (COO) ’éó Other CŌĆÖs ’ü¼ Chief Financial officer ’ü¼ Chief Information officer ’éó Inside board members ’éó Outside board members 18
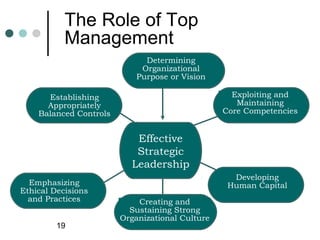
- 19. The Role of Top Management Determining Organizational Purpose or Vision Establishing Exploiting and Appropriately Maintaining Balanced Controls Core Competencies Effective Strategic Leadership Developing Emphasizing Human Capital Ethical Decisions and Practices Creating and Sustaining Strong Organizational Culture 19
- 20. Strategic Management Principle Effective strategy-making begins with a vision of where the organization needs to head! 20
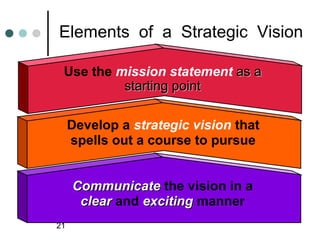
- 21. Elements of a Strategic Vision Use the mission statement as a starting point Develop a strategic vision that spells out a course to pursue Communicate the vision in a clear and exciting manner 21
- 22. Characteristics of a Mission Statement ’éó Defines current business activities ’éó Highlights boundaries of current business ’éó Conveys ’ü¼ Who we are, ’ü¼ What we do, and ’ü¼ Where we are now 22
- 23. Characteristics of a Mission Statement ’éó Company specific, not generic ŌĆöso as to give a company its own identity ’éó A companyŌĆÖs mission is not to make a profit ! ’éó The real mission is alwaysŌĆöŌĆ£What will we do to make a profit?ŌĆØ 23
- 24. Examples of Missions Microsoft Corporation Empower people through great software anytime, anyplace, and on any device. 24
- 25. Examples of Missions Otis Elevator Our mission is to provide any customer a means of moving people and things up, down, and sideways over short distances with higher reliability than any similar enterprise in the world. 25
- 26. Examples of Mission American Red Cross The mission of the American Red Cross is to improve the quality of human life; to enhance self-reliance and concern for others; and to help people avoid, prepare for, and cope with emergencies. 26
- 27. Ritz-Carlton Hotels The Ritz-Carlton Hotel is a place where the genuine care and comfort of our guests is our highest mission. We pledge to provide the finest personal service and facilities for our guests who will always enjoy a warm, relaxed yet refined ambiance. The Ritz-Carlton experience enlivens the senses, instills well-being, and fulfills even the unexpressed wishes and needs of our guests (vision) 27
- 28. Characteristics of a Strategic Vision ’éó Charts a companyŌĆÖs future strategic course ’éó Defines the business makeup for 5 years (or more) ’éó Specifies future technology- product-customer focus 28
- 29. Communicating the Vision ’éó An exciting, inspirational vision ’ü¼ Challenges and motivates workforce ’ü¼ Arouses strong sense of organizational purpose ’ü¼ Induces employee buy-in ’ü¼ Galvanizes people to live the business 29
- 30. Value of a Well-Conceived Strategic Vision and Mission ’éó Crystallizes long-term direction ’éó Reduces risk of rudderless decision-making ’éó Conveys organizational purpose and identity ’éó Keeps direction-related actions of lower- level managers on common path ’éó Helps organization prepare for the future 30
- 31. Concept of Strategic Intent A company exhibits strategic intent when it relentlessly pursues an ambitious strategic objective and concentrates its competitive actions and energies on achieving that objective! 31
- 32. Lessons about change: Built to last ’éó Understand why superior companies are better than peer companies which are better than most companies ’ü¼ $1 invested in stock market in 1926 yields ŌĆó $420 in all other companies ŌĆó $960 in peer companies ŌĆó $6360 in superior (visionary) companies 32
- 33. Who are these companies ’éó Visionary ’éó Peer companies ’ü¼ 3M ’ü¼ Norton ’ü¼ Boeing ’ü¼ McDonnell Douglass ’ü¼ GE ’ü¼ Westinghouse ’ü¼ IBM ’ü¼ Burroughs ’ü¼ Zenith ’ü¼ Motorola ’ü¼ Melville ’ü¼ Nordstrom ’ü¼ Colgate ’ü¼ P&G ’ü¼ Kenwood ’ü¼ Sony ’ü¼ Ames ’ü¼ Wal-mart 33
- 34. So what did they find? ’éó Great companies had BHAG ’ü¼Big Hairy Audacious Goals ’éó What ever your values are ŌĆ£stick with itŌĆØ ’éó Deal with the AND, not the OR ’éó Seek Alignment (internally) 34
- 35. Characteristics of Strategic Intent ’éó Indicates firmŌĆÖs intent to stake out a particular position over the long-term ’éó Involves establishing a BHAG - ŌĆØbig, hairy, audacious goalŌĆØ ’éó Signals relentless commitment to winning 35
- 36. Example of BHAG ’ü¼ General Electric ŌĆó All businesses are held to a standard of being #1 or #2 in their industries as well as achieving good business results ’ü¼ John F. Kennedy ŌĆó Put a man on the moon and return safely by the end of the decade 36
- 37. Crafting a Strategy ’éó An organizationŌĆÖs strategy deals with ’ü¼ How to make the strategic vision a reality and achieve target objectives ’ü¼ The game plan for ŌĆó Pleasing customers ŌĆó Conducting operations ŌĆó Building a sustainable competitive advantage 37
- 38. Take Aways ’éó Strategy has become more important ŌĆó Information, technology, globalization ’éó Key ideas in the strategy making process ’ü¼ Mission (who are we) ’ü¼ Vision (where do we want to go) ’ü¼ Strategic intent / BHAG (major goal) ’ü¼ Strategy (specific plan at different levels) ’ü¼ Ethics (code of conduct or values) ’éó Linkage & communication are important ’éó Avoid mission creep! 38
- 39. Take Aways ’éó Where strategy came from ’éó Strategic Management Process ’éó Who does strategy ’éó Next week ’ü¼ Read Airline Simulation Book (1-35) ’ü¼ Bring Laptop 39