Polynomials
- 2. P O LY N O M I A L V O C A B U L A R Y Term â a number or a product of a number and variables raised to powers Coefficient â numerical factor of a term Constant â term which is only a number Polynomial is a sum of terms involving variables raised to a whole number exponent, with no variables appearing in any denominator.
- 3. P O LY N O M I A L V O C A B U L A R Y In the polynomial 7x5 + x2y2 â 4xy + 7 There are 4 terms: 7x5, x2y2, -4xy and 7. The coefficient of term 7x5 is 7, of term x2y2 is 1, of term â4xy is â4 and of term 7 is 7. 7 is a constant term.
- 4. T Y P E S O F P O LY N O M I A L S Monomial is a polynomial with 1 term. Binomial is a polynomial with 2 terms. Trinomial is a polynomial with 3 terms. Multinomial is a polynomial with 4 or more terms.
- 5. DEGREES Degree of a term To find the degree, take the sum of the exponents on the variables contained in the term. Degree of a constant is 0. Degree of the term 5a4b3c is 8 (remember that c can be written as c1). Degree of a polynomial To find the degree, take the largest degree of any term of the polynomial. Degree of 9x3 â 4x2 + 7 is 3.
- 6. E VA L U AT I N G P O LY N O M I A L S Evaluating a polynomial for a particular value involves replacing the value for the variable(s) involved. Example Find the value of 2x3 â 3x + 4 when x = 2. 2x3 â 3x + 4 = 2( 2)3 â 3( 2) + 4 = 2( 8) + 6 + 4 = 6
- 7. COMBINING LIKE TERMS Like terms are terms that contain exactly the same variables raised to exactly the same powers. Warning! Only like terms can be combined through addition and subtraction. Example Combine like terms to simplify. x2y + xy â y + 10x2y â 2y + xy = x2y + 10x2y + xy + xy â y â 2y (Like terms are grouped together) = (1 + 10)x2y + (1 + 1)xy + (â 1 â 2)y = 11x2y + 2xy â 3y
- 8. ADDING AND SUBTRACTING POLYNOMIALS Letâs Add and Subtract!
- 9. ADDING AND SUBTRACTING POLYNOMIALS Adding Polynomials Combine all the like terms. Subtracting Polynomials Change the signs of the terms of the polynomial being subtracted, and then combine all the like terms.
- 10. ADDING AND SUBTRACTING POLYNOMIALS Example Add or subtract each of the following, as indicated. 1) (3x â 8) + (4x2 â 3x +3) = 3x â 8 + 4x2 â 3x + 3 = 4x2 + 3x â 3x â 8 + 3 = 4x2 â 5 2) 4 â (â y â 4) = 4 + y + 4 = y + 4 + 4 = y + 8 3) (â a2 + 1) â (a2 â 3) + (5a2 â 6a + 7) = â a2 + 1 â a2 + 3 + 5a2 â 6a + 7 = â a2 â a2 + 5a2 â 6a + 1 + 3 + 7 = 3a2 â 6a + 11
- 11. ADDING AND SUBTRACTING POLYNOMIALS In the previous examples, after discarding the parentheses, we would rearrange the terms so that like terms were next to each other in the expression. You can also use a vertical format in arranging your problem, so that like terms are aligned with each other vertically.
- 12. MULTIPLYING POLYNOMIALS Letâs Multiply!
- 13. M U LT I P LY I N G P O LY N O M I A L S Multiplying polynomials âĒ If all of the polynomials are monomials, use the associative and commutative properties. âĒ If any of the polynomials are not monomials, use the distributive property before the associative and commutative properties. Then combine like terms.
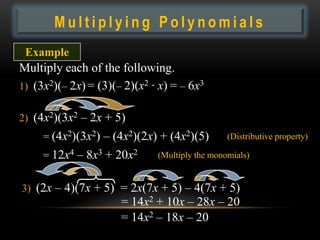
- 14. Multiplying Polynomials Example Multiply each of the following. 1) (3x2)(â 2x) = (3)(â 2)(x2 · x) = â 6x3 2) (4x2)(3x2 â 2x + 5) = (4x2)(3x2) â (4x2)(2x) + (4x2)(5) (Distributive property) = 12x4 â 8x3 + 20x2 (Multiply the monomials) 3) (2x â 4)(7x + 5) = 2x(7x + 5) â 4(7x + 5) = 14x2 + 10x â 28x â 20 = 14x2 â 18x â 20
- 15. Multiplying Polynomials Example Multiply (3x + 4)2 Remember that a2 = a · a, so (3x + 4)2 = (3x + 4)(3x + 4). (3x + 4)2 = (3x + 4)(3x + 4) = (3x)(3x + 4) + 4(3x + 4) = 9x2 + 12x + 12x + 16 = 9x2 + 24x + 16
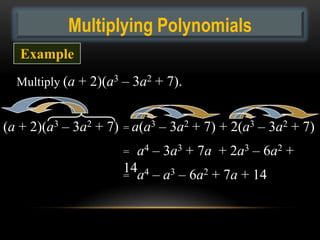
- 16. Multiplying Polynomials Example Multiply (a + 2)(a3 â 3a2 + 7). (a + 2)(a3 â 3a2 + 7) = a(a3 â 3a2 + 7) + 2(a3 â 3a2 + 7) = a4 â 3a3 + 7a + 2a3 â 6a2 + 14a4 â a3 â 6a2 + 7a + 14 =
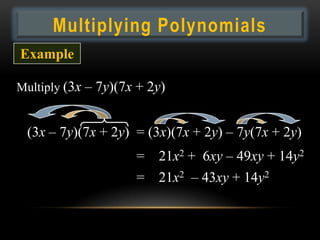
- 17. Multiplying Polynomials Example Multiply (3x â 7y)(7x + 2y) (3x â 7y)(7x + 2y) = (3x)(7x + 2y) â 7y(7x + 2y) = 21x2 + 6xy â 49xy + 14y2 = 21x2 â 43xy + 14y2
- 18. Multiplying Polynomials Example Multiply (5x â 2z)2 (5x â 2z)2 = (5x â 2z)(5x â 2z) = (5x)(5x â 2z) â 2z(5x â 2z) = 25x2 â 10xz â 10xz + 4z2 = 25x2 â 20xz + 4z2
- 19. Multiplying Polynomials Example Multiply (2x2 + x â 1)(x2 + 3x + 4) (2x2 + x â 1)(x2 + 3x + 4) = (2x2)(x2 + 3x + 4) + x(x2 + 3x + 4) â 1(x2 + 3x + 4) = 2x4 + 6x3 + 8x2 + x3 + 3x2 + 4x â x2 â 3x â 4 = 2x4 + 7x3 + 10x2 + x â 4
- 20. SPECIAL PRODUCTS Letâs multiply!
- 21. THE FOIL METHOD When multiplying 2 binomials, the distributive property can be easily remembered as the FOIL method. F â product of First terms O â product of Outside terms I â product of Inside terms L â product of Last terms
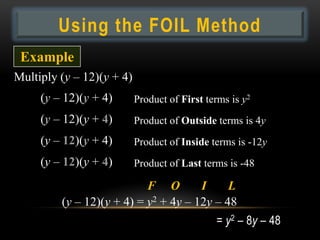
- 22. Using the FOIL Method Example Multiply (y â 12)(y + 4) (y â 12)(y + 4) Product of First terms is y2 (y â 12)(y + 4) Product of Outside terms is 4y (y â 12)(y + 4) Product of Inside terms is -12y (y â 12)(y + 4) Product of Last terms is -48 F O I L (y â 12)(y + 4) = y2 + 4y â 12y â 48 = y2 â 8y â 48
- 23. Using the FOIL Method Example Multiply (2x â 4)(7x + 5) F L F O I L (2x â 4)(7x + 5) = 2x(7x) + 2x(5) â 4(7x) â 4(5) I O = 14x2 + 10x â 28x â 20 = 14x2 â 18x â 20 We multiplied these same two binomials together in the previous section, using a different technique, but arrived at the same product.
- 24. Special Products In the process of using the FOIL method on products of certain types of binomials, we see specific patterns that lead to special products. Squaring a Binomial (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 (a â b)2 = a2 â 2ab + b2 Multiplying the Sum and Difference of Two Terms (a + b)(a â b) = a2 â b2
- 25. Special Products Although you will arrive at the same results for the special products by using the techniques of this section or last section, memorizing these products can save you some time in multiplying polynomials.
- 26. DIVIDING POLYNOMIALS Letâs divide!
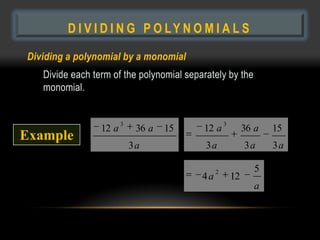
- 27. D I V I D I N G P O LY N O M I A L S Dividing a polynomial by a monomial Divide each term of the polynomial separately by the monomial. 3 3 12 a 36 a 15 12 a 36 a 15 Example 3a 3a 3a 3a 2 5 4a 12 a
- 28. DIVIDING POLYNOMIALS D I V I D I N G P O LY N O M I A L S Dividing a polynomial by a polynomial other than a monomial uses a âlong divisionâ technique that is similar to the process known as long division in dividing two numbers, which is reviewed on the next slide.
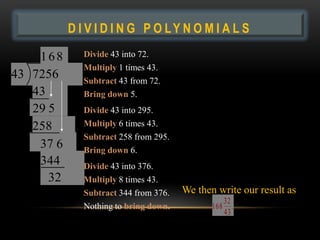
- 29. DIVIDING POLYNOMIALS D I V I D I N G P O LY N O M I A L S 168 Divide 43 into 72. Multiply 1 times 43. 43 7256 Subtract 43 from 72. 43 Bring down 5. 29 5 Divide 43 into 295. 258 Multiply 6 times 43. Subtract 258 from 295. 37 6 Bring down 6. 344 Divide 43 into 376. 32 Multiply 8 times 43. Subtract 344 from 376. We then write our result as 32 Nothing to bring down. 168 . 43
- 30. Dividing P O L Y N O M I A L S DIVIDING Polynomials As you can see from the previous example, there is a pattern in the long division technique. Divide Multiply Subtract Bring down Then repeat these steps until you canât bring down or divide any longer. We will incorporate this same repeated technique with dividing polynomials.
- 31. DIVIDING POLYNOMIALS D I V I D I N G P O LY N O M I A L S 4x 5 Divide 7x into 28x2. Multiply 4x times 7x+3. 2 7x 3 28 x 23 x 15 Subtract 28x2 + 12x from 28x2 â 23x. 2 Bring down â 15. 28 x 12 x Divide 7x into â35x. 35 x 15 Multiply â 5 times 7x+3. Subtract â35xâ15 from â35xâ15. 35 x 15 Nothing to bring down. So our answer is 4x â 5.
- 32. Dividing P O L Y N O M I A L S DIVIDING Polynomials 2 x 10 Divide 2x into 4x2. 2 Multiply 2x times 2x+7. 2 x 7 4x 6x 8 Subtract 4x2 + 14x from 4x2 â 6x. 2 4 x 14 x Bring down 8. 20 x 8 Divide 2x into â20x. 20 x 70 Multiply -10 times 2x+7. Subtract â20xâ70 from â20x+8. 78 Nothing to bring down. We write our final answer as 2 x 10 78 ( 2 x 7)