10409004.ppt
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes10 views
This document discusses key concepts in sampling design and procedures. It covers reasons for sampling such as pragmatic and cost reasons. It also discusses defining the target population and sampling frame. The document contrasts probability sampling techniques like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling with non-probability techniques like convenience sampling and snowball sampling. It discusses factors to consider in determining sample size such as variance, desired confidence level and interval. Sample size formulas for estimating means and proportions are also provided.
1 of 43
Download to read offline




























Ad
Recommended
Mba2216 week 09 10 sampling
Mba2216 week 09 10 samplingStephen Ong
╠²
This document discusses research design and sampling in business research projects. It covers key concepts related to sampling such as defining the target population, sampling frame, sampling units, probability and non-probability sampling methods, and sources of error. Probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling are explained along with their advantages and disadvantages. Non-probability sampling techniques including convenience sampling, judgment sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling are also outlined.SAMPLING.pptx
SAMPLING.pptxVaagdevi College of Engineering
╠²
The document discusses various sampling techniques used in research methodology, focusing on both probability and non-probability sampling designs. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of each method, factors influencing sample size, and the importance of representative sampling for achieving accurate results. Additionally, it provides detailed explanations of different sampling methods, including simple random, systematic, stratified, cluster, and multistage sampling, along with guidelines for determining optimal sample sizes.Abdm4064 week 09 10 sampling
Abdm4064 week 09 10 samplingStephen Ong
╠²
This document discusses research design and sampling in business research. It covers key concepts related to sampling such as the target population, sampling frame, sampling units, probability and non-probability sampling methods. Probability sampling methods discussed include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. Non-probability sampling methods discussed include convenience sampling, judgment sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. The document also covers reasons for sampling, defining a valid sample size, and sources of error such as sampling error and non-sampling error.Sampling Design in Applied Marketing Research
Sampling Design in Applied Marketing ResearchKelly Page
╠²
This document discusses key concepts in sampling design, including:
1. It defines key terms like population, sample, sampling frame, sampling error, and non-sampling error.
2. It outlines the steps in developing a sampling plan, including defining the population, choosing a data collection method, identifying the sampling frame, selecting a sampling method, determining sample size, and developing operational procedures.
3. It describes different sampling methods like probability and non-probability sampling, and provides examples of methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling under probability sampling.Sampling techniques
Sampling techniquesIrfan Hussain
╠²
This document discusses sampling methods used in research. It outlines key concepts like population, sample, probability sampling, and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling and cluster sampling are explained. Non-probability methods like convenience sampling, judgment sampling, and quota sampling are also outlined. Factors to consider for determining sample size and types of errors in sampling are discussed. The advantages and disadvantages of probability and non-probability sampling are compared.Sampling 20 october 2012
Sampling 20 october 2012Nurul Ain
╠²
The document discusses research methodology and sampling techniques. It begins by outlining the sampling design process, which includes defining the target population, determining the sampling frame, selecting a sampling technique, determining sample size, and executing the sampling. It then covers various probability and non-probability sampling techniques such as simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and convenience sampling. It provides examples and definitions for each technique. The document concludes by discussing considerations for choosing between probability and non-probability sampling.Types of sampling
Types of samplingKarishma Chaudhary
╠²
Sampling is a technique used to gather data from a subset of a population. It can save time and money compared to surveying the entire population. There are different sampling techniques, including random sampling methods like simple random sampling and stratified random sampling, and non-random methods like convenience sampling. Proper sampling requires defining the sampling frame and using random selection to avoid bias. Errors can occur from using non-random samples or from issues in data collection and measurement.Sampling Design
Sampling DesignJale Nonan
╠²
The document discusses different types of sampling designs used in research, including probability and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling methods aim to give all members of the population an equal chance of being selected and include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Non-probability sampling methods do not use random selection and include convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and quota sampling. The key factors to consider in sampling design are determining the target population, parameters of interest, sampling frame, appropriate sampling method, and sample size.Marketing research ch 11_malhotra
Marketing research ch 11_malhotraJamil Ahmed AKASH
╠²
Chapter eleven outlines sampling design and procedures in marketing research, detailing the differences between sample and census methods, and types of sampling techniques. Key aspects include defining target populations, selecting sampling techniques, and determining sample size, along with a discussion of nonprobability versus probability sampling. The chapter emphasizes the importance of understanding various sampling methods to ensure the accuracy and representativeness of research findings.Business Research Method - Unit IV, AKTU, Lucknow Syllabus
Business Research Method - Unit IV, AKTU, Lucknow SyllabusKartikeya Singh
╠²
The document summarizes various sampling methods and concepts related to determining sample size. It discusses probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. It also discusses non-probability sampling methods such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, and judgmental sampling. The document provides details on each method and highlights key considerations for determining sample size such as the nature of the population, required accuracy and confidence level, and budget constraints.Mba ii rm unit-3.3 sampling methods a
Mba ii rm unit-3.3 sampling methods aRai University
╠²
This document discusses sampling methods used in research. It defines key sampling concepts like population, sample, sampling unit and frame. It also describes different probability sampling methods like simple random, stratified, systematic and cluster sampling as well as non-probability methods like convenience, judgment and snowball sampling. The document provides guidance on developing a sampling plan including defining the population, identifying the sampling method and frame, determining sample size, executing the sample, and validating the sample. It emphasizes that a well-designed sampling plan clearly defines what will be learned, how long it will take and how much it will cost.sampling techniques.pdf
sampling techniques.pdfmng2021
╠²
This document discusses various sampling methods used in business research. It defines key concepts like population, sample, sampling frame, and sampling errors. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. It also covers non-probability sampling methods such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, and judgmental sampling. The document provides examples and explanations of each sampling method.Business Research Methods Unit IV
Business Research Methods Unit IVKartikeya Singh
╠²
This document discusses various sampling methods used in business research. It covers probability sampling techniques like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. It also discusses non-probability sampling techniques such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, and judgmental sampling. The key factors in determining sample size are described as the nature of the population, desired level of accuracy, available resources, and characteristics of the sampling method. Methods to reduce sampling errors like measurement, consistency checks, and quality control are also summarized.Sampling techniques 2
Sampling techniques 2ssuser0903d3
╠²
This document discusses sampling techniques and procedures. It provides an overview of sample vs census studies, outlines the sampling design process, and classifies sampling techniques into nonprobability and probability methods. Specific techniques covered include convenience, judgmental, quota, snowball, simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. The document also discusses choosing between nonprobability and probability sampling, and provides examples of procedures for drawing probability samples.CH 3 Sampling (3).pptx.ppt
CH 3 Sampling (3).pptx.pptcaptaindeadpool495
╠²
This document discusses different sampling techniques and determining sample size. It begins by outlining the objectives of learning about sampling methods, distinguishing between probability and non-probability sampling, and calculating sample sizes using appropriate formulas. The document then defines key sampling terms and discusses the reasons for sampling, including that it is less costly, more accessible, and useful than surveying an entire population. It describes different sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified random sampling. It emphasizes that probability sampling allows results to be generalized to the overall population.Chapter5_Sampling_28.10.22 (1).ppt
Chapter5_Sampling_28.10.22 (1).pptAsmaRahmatRika
╠²
This document discusses key concepts related to sampling in marketing research. It defines important terminology like population, element, sampling unit, and sample. It explains different sampling designs like probability sampling methods (e.g. random, stratified, cluster) and non-probability methods (e.g. convenience, judgment, quota, snowball). The document emphasizes that the sample size and sampling method should be chosen based on the characteristics of the target population and research objectives. Response rates and potential sources of error are also addressed.6152935.ppt
6152935.pptPradeep513562
╠²
The document defines key concepts related to sampling, including population, sample, sampling methods, and errors. It discusses different types of sampling methods like probability sampling (simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling) and non-probability sampling (convenience sampling, judgement sampling). It also explains sampling frame, sampling frame error, random sampling error, and non-response error that can occur in sampling. The document provides steps involved in conducting a sample survey from defining the target population to selecting the sampling technique and sample size.Types of sampling designs
Types of sampling designsManoj Xavier
╠²
This document discusses different types of sampling designs used in research. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling which allow samples to be generalized back to the population. It also covers non-probability sampling techniques like convenience sampling, judgmental sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling which do not allow generalization. The document provides details on how to implement each sampling method and discusses their relative strengths and weaknesses.Sampling Meaning needs and modes by shohrab
Sampling Meaning needs and modes by shohrabshohrabagashe
╠²
This presentation discusses the concept of sampling in research methodology, defining it as a technique for selecting individual members from a population to estimate characteristics of the whole. It distinguishes between probability sampling (e.g., random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling) and non-probability sampling (e.g., convenience, judgment, quota, and snowball sampling), outlining their methods and purposes. The document emphasizes the importance of a carefully chosen sample for accurate representation of a larger population.Sampling methods
Sampling methodsSagar Gadekar
╠²
The document discusses different types of sampling designs used in research. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling and systematic sampling which allow every unit in the population to have a chance of being selected. It also covers non-probability sampling which does not assure equal chance of selection. Key factors in sampling like sample size, target population, and parameters of interest are explained.Sampling design
Sampling designBalaji P
╠²
The document discusses the principles and methods of sampling design in research, highlighting the distinction between populations and samples, as well as the importance of accuracy, precision, and the steps in designing a sample. It outlines various sampling methods, including probability and non-probability sampling techniques, and emphasizes how to determine sample size and understand related statistical concepts such as margin of error and confidence level. Examples and explanations are provided to illustrate different methods and their applications in real-world scenarios.Ch6_Sampling_and_Estimation_1665986605149647534634cf02dbcbec (1).pdf
Ch6_Sampling_and_Estimation_1665986605149647534634cf02dbcbec (1).pdfTANISHASINHA21
╠²
The document discusses key concepts of sampling and estimation, including definitions of population, sampling frame, and methods of sampling such as non-random and random techniques. It outlines various sampling methods, sample size determination, and the impact of budgetary constraints, as well as potential errors that can occur during sampling. Additionally, the text covers confidence intervals for estimating population parameters, including conditions for applying different statistical distributions based on sample size.Sampling final
Sampling finalShashankk Jain
╠²
This document discusses sampling methods used in research. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole population. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every unit has a known chance of selection, and non-probability sampling, which relies on judgment. Some key probability methods include simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Non-probability methods include convenience sampling and snowball sampling. The document outlines steps for designing a sampling procedure, including defining the population, choosing a sampling technique, and determining an appropriate sample size.Sampling Design
Sampling Designitsvineeth209
╠²
1. There are two main types of sampling designs - probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling allows you to estimate errors and make statistical inferences, while non-probability sampling does not.
2. Some common probability sampling techniques include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multi-stage sampling. These aim to select a sample that accurately represents the population.
3. When designing a sample, researchers must determine the sampling unit, sampling frame, sample size, and sampling procedure based on factors like the population, budget, and goal of reducing bias and sampling error. Probability sampling is generally preferred but non-probability techniques may also be used for small populations.Sampling design
Sampling designJayaprakash CR
╠²
1. Sampling is selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole population. It involves defining the population, specifying a sampling frame and sampling unit, choosing a sampling method, determining sample size, and selecting the sample.
2. There are two main types of sampling methods - probability sampling, where every unit has a known chance of selection, and non-probability sampling, where the probability of selection is unknown. Common probability methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. Common non-probability methods include quota sampling, snowball sampling, and convenience sampling.
3. Sources of error in sampling include sampling errors, which arise from differences between the sample and population, and non-samplingSampling methods roll no. 509
Sampling methods roll no. 509s.s saini
╠²
This document discusses various sampling methods used in research. It defines key terms like population, element, sampling unit, and sample. It describes probability sampling methods like random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. It also covers non-probability methods like convenience sampling, judgment sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. The document provides details on how to implement these various sampling techniques and discusses factors to consider for determining sample size.More Related Content
Similar to 10409004.ppt (20)
Sampling Design
Sampling DesignJale Nonan
╠²
The document discusses different types of sampling designs used in research, including probability and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling methods aim to give all members of the population an equal chance of being selected and include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Non-probability sampling methods do not use random selection and include convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and quota sampling. The key factors to consider in sampling design are determining the target population, parameters of interest, sampling frame, appropriate sampling method, and sample size.Marketing research ch 11_malhotra
Marketing research ch 11_malhotraJamil Ahmed AKASH
╠²
Chapter eleven outlines sampling design and procedures in marketing research, detailing the differences between sample and census methods, and types of sampling techniques. Key aspects include defining target populations, selecting sampling techniques, and determining sample size, along with a discussion of nonprobability versus probability sampling. The chapter emphasizes the importance of understanding various sampling methods to ensure the accuracy and representativeness of research findings.Business Research Method - Unit IV, AKTU, Lucknow Syllabus
Business Research Method - Unit IV, AKTU, Lucknow SyllabusKartikeya Singh
╠²
The document summarizes various sampling methods and concepts related to determining sample size. It discusses probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. It also discusses non-probability sampling methods such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, and judgmental sampling. The document provides details on each method and highlights key considerations for determining sample size such as the nature of the population, required accuracy and confidence level, and budget constraints.Mba ii rm unit-3.3 sampling methods a
Mba ii rm unit-3.3 sampling methods aRai University
╠²
This document discusses sampling methods used in research. It defines key sampling concepts like population, sample, sampling unit and frame. It also describes different probability sampling methods like simple random, stratified, systematic and cluster sampling as well as non-probability methods like convenience, judgment and snowball sampling. The document provides guidance on developing a sampling plan including defining the population, identifying the sampling method and frame, determining sample size, executing the sample, and validating the sample. It emphasizes that a well-designed sampling plan clearly defines what will be learned, how long it will take and how much it will cost.sampling techniques.pdf
sampling techniques.pdfmng2021
╠²
This document discusses various sampling methods used in business research. It defines key concepts like population, sample, sampling frame, and sampling errors. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. It also covers non-probability sampling methods such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, and judgmental sampling. The document provides examples and explanations of each sampling method.Business Research Methods Unit IV
Business Research Methods Unit IVKartikeya Singh
╠²
This document discusses various sampling methods used in business research. It covers probability sampling techniques like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. It also discusses non-probability sampling techniques such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, and judgmental sampling. The key factors in determining sample size are described as the nature of the population, desired level of accuracy, available resources, and characteristics of the sampling method. Methods to reduce sampling errors like measurement, consistency checks, and quality control are also summarized.Sampling techniques 2
Sampling techniques 2ssuser0903d3
╠²
This document discusses sampling techniques and procedures. It provides an overview of sample vs census studies, outlines the sampling design process, and classifies sampling techniques into nonprobability and probability methods. Specific techniques covered include convenience, judgmental, quota, snowball, simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. The document also discusses choosing between nonprobability and probability sampling, and provides examples of procedures for drawing probability samples.CH 3 Sampling (3).pptx.ppt
CH 3 Sampling (3).pptx.pptcaptaindeadpool495
╠²
This document discusses different sampling techniques and determining sample size. It begins by outlining the objectives of learning about sampling methods, distinguishing between probability and non-probability sampling, and calculating sample sizes using appropriate formulas. The document then defines key sampling terms and discusses the reasons for sampling, including that it is less costly, more accessible, and useful than surveying an entire population. It describes different sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified random sampling. It emphasizes that probability sampling allows results to be generalized to the overall population.Chapter5_Sampling_28.10.22 (1).ppt
Chapter5_Sampling_28.10.22 (1).pptAsmaRahmatRika
╠²
This document discusses key concepts related to sampling in marketing research. It defines important terminology like population, element, sampling unit, and sample. It explains different sampling designs like probability sampling methods (e.g. random, stratified, cluster) and non-probability methods (e.g. convenience, judgment, quota, snowball). The document emphasizes that the sample size and sampling method should be chosen based on the characteristics of the target population and research objectives. Response rates and potential sources of error are also addressed.6152935.ppt
6152935.pptPradeep513562
╠²
The document defines key concepts related to sampling, including population, sample, sampling methods, and errors. It discusses different types of sampling methods like probability sampling (simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling) and non-probability sampling (convenience sampling, judgement sampling). It also explains sampling frame, sampling frame error, random sampling error, and non-response error that can occur in sampling. The document provides steps involved in conducting a sample survey from defining the target population to selecting the sampling technique and sample size.Types of sampling designs
Types of sampling designsManoj Xavier
╠²
This document discusses different types of sampling designs used in research. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling which allow samples to be generalized back to the population. It also covers non-probability sampling techniques like convenience sampling, judgmental sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling which do not allow generalization. The document provides details on how to implement each sampling method and discusses their relative strengths and weaknesses.Sampling Meaning needs and modes by shohrab
Sampling Meaning needs and modes by shohrabshohrabagashe
╠²
This presentation discusses the concept of sampling in research methodology, defining it as a technique for selecting individual members from a population to estimate characteristics of the whole. It distinguishes between probability sampling (e.g., random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling) and non-probability sampling (e.g., convenience, judgment, quota, and snowball sampling), outlining their methods and purposes. The document emphasizes the importance of a carefully chosen sample for accurate representation of a larger population.Sampling methods
Sampling methodsSagar Gadekar
╠²
The document discusses different types of sampling designs used in research. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling and systematic sampling which allow every unit in the population to have a chance of being selected. It also covers non-probability sampling which does not assure equal chance of selection. Key factors in sampling like sample size, target population, and parameters of interest are explained.Sampling design
Sampling designBalaji P
╠²
The document discusses the principles and methods of sampling design in research, highlighting the distinction between populations and samples, as well as the importance of accuracy, precision, and the steps in designing a sample. It outlines various sampling methods, including probability and non-probability sampling techniques, and emphasizes how to determine sample size and understand related statistical concepts such as margin of error and confidence level. Examples and explanations are provided to illustrate different methods and their applications in real-world scenarios.Ch6_Sampling_and_Estimation_1665986605149647534634cf02dbcbec (1).pdf
Ch6_Sampling_and_Estimation_1665986605149647534634cf02dbcbec (1).pdfTANISHASINHA21
╠²
The document discusses key concepts of sampling and estimation, including definitions of population, sampling frame, and methods of sampling such as non-random and random techniques. It outlines various sampling methods, sample size determination, and the impact of budgetary constraints, as well as potential errors that can occur during sampling. Additionally, the text covers confidence intervals for estimating population parameters, including conditions for applying different statistical distributions based on sample size.Sampling final
Sampling finalShashankk Jain
╠²
This document discusses sampling methods used in research. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole population. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every unit has a known chance of selection, and non-probability sampling, which relies on judgment. Some key probability methods include simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Non-probability methods include convenience sampling and snowball sampling. The document outlines steps for designing a sampling procedure, including defining the population, choosing a sampling technique, and determining an appropriate sample size.Sampling Design
Sampling Designitsvineeth209
╠²
1. There are two main types of sampling designs - probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling allows you to estimate errors and make statistical inferences, while non-probability sampling does not.
2. Some common probability sampling techniques include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multi-stage sampling. These aim to select a sample that accurately represents the population.
3. When designing a sample, researchers must determine the sampling unit, sampling frame, sample size, and sampling procedure based on factors like the population, budget, and goal of reducing bias and sampling error. Probability sampling is generally preferred but non-probability techniques may also be used for small populations.Sampling design
Sampling designJayaprakash CR
╠²
1. Sampling is selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole population. It involves defining the population, specifying a sampling frame and sampling unit, choosing a sampling method, determining sample size, and selecting the sample.
2. There are two main types of sampling methods - probability sampling, where every unit has a known chance of selection, and non-probability sampling, where the probability of selection is unknown. Common probability methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. Common non-probability methods include quota sampling, snowball sampling, and convenience sampling.
3. Sources of error in sampling include sampling errors, which arise from differences between the sample and population, and non-samplingSampling methods roll no. 509
Sampling methods roll no. 509s.s saini
╠²
This document discusses various sampling methods used in research. It defines key terms like population, element, sampling unit, and sample. It describes probability sampling methods like random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. It also covers non-probability methods like convenience sampling, judgment sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. The document provides details on how to implement these various sampling techniques and discusses factors to consider for determining sample size.More from Praveen Kumar (20)
chap 4 Die set and press workmechancasndk.pptx
chap 4 Die set and press workmechancasndk.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document discusses die sets and press work, outlining various types of dies such as cutting, forming, compound, combination, and progressive dies based on their operations. It explains the press working process which involves applying force to sheet metal using a punch and die, detailing operations like blanking, piercing, and bending. Additionally, it categorizes presses by power source, number of slides, and other factors important for selecting the appropriate press for efficient metal forming operations.UNIT1-Castingprocess.mechanjcalalrning ppt
UNIT1-Castingprocess.mechanjcalalrning pptPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document outlines the discipline of mechanical engineering, focusing on manufacturing, particularly the casting process, which involves pouring molten metal into molds to create solidified objects. It details the various types of casting processes, pattern making, materials used for patterns, and factors influencing pattern selection, along with advantages and disadvantages of casting. Additionally, it discusses different types of molding sands and methods for producing castings, emphasizing the evolution of manufacturing and casting techniques through history.chap 5 Forging PPTmechancalengn (1).pptx
chap 5 Forging PPTmechancalengn (1).pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document discusses metal forging, a historical deformation process where work is compressed between two dies to form high-strength components for various industries. It outlines different forging processes, including open-die, impression-die, and flashless forging, explaining their mechanics, advantages, and applications. Additionally, it highlights the properties and challenges of forging, as well as specific examples and calculations related to this manufacturing technique.chap 4 Die set and press workmechanical.pptx
chap 4 Die set and press workmechanical.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document discusses die sets and press work, defining dies and their various types, including cutting, forming, compound, combination, and progressive dies. It explains the presswork process, where force is applied to sheet metal to cut or form it, detailing different types of presses such as manual, mechanical, hydraulic, and pneumatic presses based on their operation and characteristics. The selection of presses is emphasized, highlighting factors like size, force, energy, and speed requirements to ensure efficient production.chap 3 Fundamentals of Metal Forming (1).ppt
chap 3 Fundamentals of Metal Forming (1).pptPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of metal forming processes, emphasizing plastic deformation utilized to shape metal workpieces. It details the types of stresses involved, the impact of temperature on material properties, and various metal forming methods like rolling, forging, extrusion, and drawing. Additionally, the document discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different working temperatures and processes, as well as specific calculations regarding flow stress and extrusion ratios.chap 1 introduction to manufacturing (1).pptx
chap 1 introduction to manufacturing (1).pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
Manufacturing is defined as the process of transforming raw materials into valuable products through various technological procedures. It involves both processing operations, which change the form or properties of materials, and assembly operations, which join components to create new entities. Factors influencing manufacturing processes include shape and size requirements, material properties, production quantity, quality expectations, surface finish, and cost.Basic Mechanical Engineering bcm-MID-I.pptx
Basic Mechanical Engineering bcm-MID-I.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document outlines a mechanical engineering course focused on manufacturing processes, thermal engineering, and robotics applications. It covers various manufacturing techniques including casting, forming, machining, and modern technologies like CNC and 3D printing, along with their principles, advantages, and applications. Additionally, it discusses different joining processes, welding techniques, and the evolution of these methods over time.Unit-5 Thin & Thick Cylindermechanical.pptx
Unit-5 Thin & Thick Cylindermechanical.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document discusses the mechanics of thin and thick cylinders, including their applications in engineering for transporting and storing fluids. It covers the derivation of formulas for various stresses (hoop, longitudinal), strains, and the behavior of cylindrical and spherical shells under pressure. Important concepts include the definition of thin vs. thick cylinders based on wall thickness relative to diameter and the application of Lame's equation for thick cylinders.Presentation_ICTmechanical engineering.pptx
Presentation_ICTmechanical engineering.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document outlines the Washington Accord and its role in the accreditation of undergraduate engineering programs globally, emphasizing mutual recognition of qualifications among signatory countries. It discusses the concept of Outcome-Based Education (OBE) as a student-centered approach aimed at achieving specific learning outcomes, highlighting benefits for students and faculty. Additionally, it details various educational outcomes including Program Educational Objectives (PEOs), Program Outcomes (POs), and Course Outcomes (COs) while integrating Bloom's taxonomy for assessment purposes.Columns_Buckling_and_Stabilitymecha.pptx
Columns_Buckling_and_Stabilitymecha.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document provides an overview of columns, buckling phenomena, and stability in structural engineering. It outlines critical concepts such as the maximum load before buckling, different support conditions, and formulas for calculating critical loads. Additionally, it discusses the limitations of Euler's formula and introduces Rankine's formula, which combines material strength with Euler's theory.Columns_Buckling_Stability_Lecture_Notes.pptx
Columns_Buckling_Stability_Lecture_Notes.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document discusses buckling and stability of structural columns under axial compression, emphasizing the importance of preventing structural failures in engineering. It details Euler's theory of buckling, critical load formulas based on different support conditions, and limitations of EulerŌĆÖs formula for short columns. Additionally, it introduces Rankine's formula for combining elastic and inelastic buckling and lists practical applications in engineering design.3unit-200715014624.bending stress sherarpptx
3unit-200715014624.bending stress sherarpptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document discusses the theory of flexural stresses, including the derivation of bending equations and the determination of stresses in various beam sections. It explains the concepts of bending and shear stresses, moment of resistance, and the flexure formula, which describes the relationship between bending stresses and the geometry of the beam. Additionally, it covers shear stress distribution in different beam sections and the implications of applied moments and forces on beam stability and failure.BME I-Unitmechancialnacc datafiles PPT.pptx
BME I-Unitmechancialnacc datafiles PPT.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document outlines the role of mechanical engineers, emphasizing their contributions to various sectors such as design and innovation, energy efficiency, and healthcare. It details the manufacturing process, highlighting the importance of quality control, and the integration of emerging technologies like robotics, IoT, and smart materials. Furthermore, it discusses materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, composites, and ceramics, illustrating their properties and applications in various industries.Product Specificationsmechaicalen234.pptx
Product Specificationsmechaicalen234.pptxPraveen Kumar
╠²
The document outlines the product development process, emphasizing the importance of establishing and refining product specifications based on customer needs and competitive benchmarks. It includes steps for setting target specifications and final specifications, highlighting the necessity of trade-offs and modeling to ensure feasibility and market success. Overall, the goal is to create a detailed method that integrates marketing, design, and manufacturing functions in product development.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Cadastral Maps
Cadastral MapsGoogle
╠²
Preparation of cadastral maps based by Engineer Dungo Tizazu from Dire Dawa University Introduction to Natural Language Processing - Stages in NLP Pipeline, Challen...
Introduction to Natural Language Processing - Stages in NLP Pipeline, Challen...resming1
╠²
Lecture delivered in 2021. This gives an introduction to Natural Language Processing. It describes the use cases of NLP in daily life. It discusses the stages in NLP Pipeline. It highlights the challenges involved covering the different levels of ambiguity that could arise. It also gives a brief note on the present scenario with the latest language models, tools and frameworks/libraries for NLP.Deep Learning for Image Processing on 16 June 2025 MITS.pptx
Deep Learning for Image Processing on 16 June 2025 MITS.pptxresming1
╠²
This covers how image processing or the field of computer vision has advanced with the advent of neural network architectures ranging from LeNet to Vision transformers. It covers how deep neural network architectures have developed step-by-step from the popular CNNs to ViTs. CNNs and its variants along with their features are described. Vision transformers are introduced and compared with CNNs. It also shows how an image is processed to be given as input to the vision transformer. It give the applications of computer vision.Modern multi-proposer consensus implementations
Modern multi-proposer consensus implementationsFran├¦ois Garillot
╠²
Multi-proposer consensus protocols let multiple validators propose blocks in parallel, breaking the single-leader throughput bottleneck of classic designs. Yet the modern multi-proposer consensus implementation has grown a lot since HotStuff. THisworkshop will explore the implementation details of recent advances ŌĆō DAG-based approaches like Narwhal and SuiŌĆÖs Mysticeti ŌĆō and reveal how implementation details translate to real-world performance gains. We focus on the nitty-gritty: how network communication patterns and data handling affect throughput and latency. New techniques such as Turbine-like block propagation (inspired by SolanaŌĆÖs erasure-coded broadcast) and lazy push gossip broadcasting dramatically cut communication overhead. These optimizations arenŌĆÖt just theoretical ŌĆō they enable modern blockchains to process over 100,000 transactions per second with finality in mere millisecondsŌĆŗ redefining what is possible in decentralized systems.
(Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment/Delivery) is a fundamental ...
(Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment/Delivery) is a fundamental ...ketan09101
╠²
(Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment/Delivery) is a fundamental practice in DevOps that streamlines software development and deployment.Learning ŌĆō Types of Machine Learning ŌĆō Supervised Learning ŌĆō Unsupervised UNI...
Learning ŌĆō Types of Machine Learning ŌĆō Supervised Learning ŌĆō Unsupervised UNI...23Q95A6706
╠²
Learning ŌĆō Types of Machine Learning ŌĆō Supervised Learning ŌĆō Unsupervised Learning- semi supervised learning - The Brain and the Neuron ŌĆō Design a Learning System ŌĆō Perspectives and Issues in Machine Learning ŌĆō Concept Learning Task ŌĆō Concept Learning as Search ŌĆō Finding a Maximally Specific Hypothesis ŌĆō Version Spaces and the Candidate Elimination Algorithm
Machine Learning - Classification Algorithms
Machine Learning - Classification Algorithmsresming1
╠²
This covers traditional machine learning algorithms for classification. It includes Support vector machines, decision trees, Naive Bayes classifier , neural networks, etc.
It also discusses about model evaluation and selection. It discusses ID3 and C4.5 algorithms. It also describes k-nearest neighbor classifer.Rapid Prototyping for XR: Lecture 6 - AI for Prototyping and Research Directi...
Rapid Prototyping for XR: Lecture 6 - AI for Prototyping and Research Directi...Mark Billinghurst
╠²
This is lecture 6 in the course on Rapid Prototyping for XR, taught on June 13th, 2025 by Mark Billinghurst. This lecture was about using AI for Prototyping and Research Directions. Abraham Silberschatz-Operating System Concepts (9th,2012.12).pdf
Abraham Silberschatz-Operating System Concepts (9th,2012.12).pdfShabista Imam
╠²
Complete book of operating system edition 9Ad
10409004.ppt
- 1. viewords.wordpress.com Sampling Design and Procedu Lecture & Seminar
- 2. If you decide whether or not you want to see a new movie or television program on the basis of the ŌĆ£coming attractionsŌĆØ or television commercial previews, are you using a sampling technique? A scientific sampling technique?
- 4. Why Sample? ’ā╝Pragmatic Reasons ’ā╝Accurate and Reliable Results ’ā╝Destruction of Test Units www.mktginc.com
- 5. Stages in the Selection of a Sample 16ŌĆō5
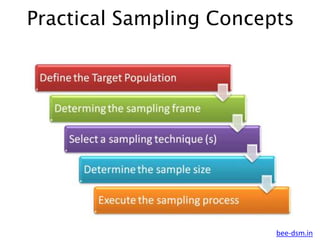
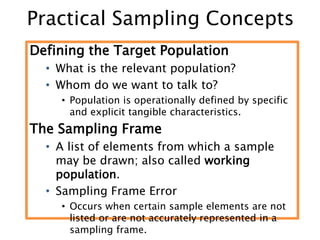
- 7. Practical Sampling Concepts Defining the Target Population ŌĆó What is the relevant population? ŌĆó Whom do we want to talk to? ŌĆó Population is operationally defined by specific and explicit tangible characteristics. The Sampling Frame ŌĆó A list of elements from which a sample may be drawn; also called working population. ŌĆó Sampling Frame Error ŌĆó Occurs when certain sample elements are not listed or are not accurately represented in a sampling frame.
- 8. 16ŌĆō8 Sampling Units Sampling Unit A single element or group of elements subject to selection in the sample. 1. Primary Sampling Unit (PSU) 2. Secondary Sampling Unit 3. Tertiary Sampling Unit
- 9. 16ŌĆō9 Random Sampling and Non-sampling Errors Random Sampling Error ŌĆó The difference between the sample result and the result of a census conducted using identical procedures. ŌĆó A statistical fluctuation that occurs because of chance variations in the elements selected for a sample. Non-Sampling (Systematic Sampling) Error ŌĆó Systematic (nonsampling) error results from nonsampling factors, primarily the nature of a studyŌĆÖs design and the correctness of execution.
- 10. 16ŌĆō10 ŌĆó Less than Perfectly Representative Samples ŌĆō Random sampling errors and systematic errors associated with the sampling process may combine to yield a sample that is less than perfectly representative of the population. Random Sampling and Nonsampling Errors (contŌĆÖd)
- 11. Errors Associated with Sampling 16ŌĆō11
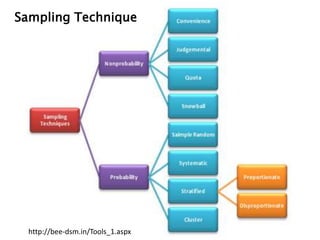
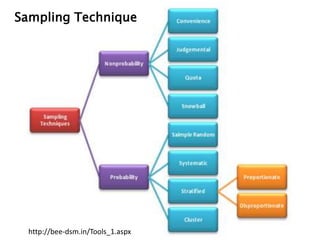
- 13. 16ŌĆō13 Probability Sampling A sampling technique in which every member of the population has a known, nonzero probability of selection. Nonprobability Sampling ŌĆō A sampling technique in which units of the sample are selected on the basis of personal judgment or convenience. ŌĆō The probability of any particular member of the population being chosen is unknown. Probability versus Nonprobability Sampling
- 15. http://lc.gcumedia.com/hlt362v/the-visual-learner/convenience-sampling.html Nonprobability Sampling: Convenience Sampling Obtaining those people or units that are most conveniently available
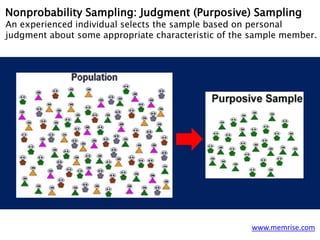
- 16. www.memrise.com Nonprobability Sampling: Judgment (Purposive) Sampling An experienced individual selects the sample based on personal judgment about some appropriate characteristic of the sample member.
- 17. Nonprobability Sampling: Quota Sampling Ensures that various subgroups of a population will be represented on pertinent characteristics to the exact extent that the investigator desires. BUYERS RESPONDENT QUOTA (SAMPLE SIZE= 200) MEN 40% 80 WOMEN 60% 120
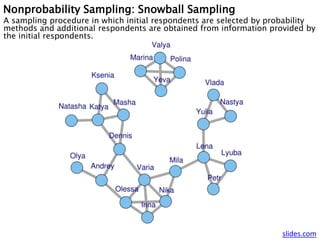
- 18. Nonprobability Sampling: Snowball Sampling A sampling procedure in which initial respondents are selected by probability methods and additional respondents are obtained from information provided by the initial respondents. slides.com
- 19. 16ŌĆō19 Probability Sampling ŌĆó Simple Random Sampling ŌĆō Assures each element in the population of an equal chance of being included in the sample. ŌĆó Systematic Sampling ŌĆō A starting point is selected by a random process and then every nth number on the list is selected. ŌĆó Stratified Sampling ŌĆō Simple random subsamples that are more or less equal on some characteristic are drawn from within each stratum of the population.
- 20. www.nedarc.org Probability Sampling: Simple Random Sampling Assures each element in the population of an equal chance of being included in the sample
- 21. Probability Sampling : Systematic Sampling A starting point is selected by a random process and then every nth number on the list is selected http://lc.gcumedia.com/hlt362v/the-visual-learner/systematic-sample.html
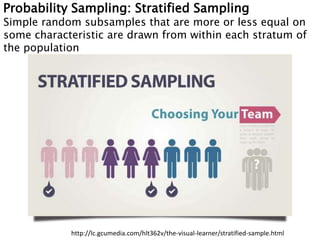
- 22. Probability Sampling: Stratified Sampling Simple random subsamples that are more or less equal on some characteristic are drawn from within each stratum of the population http://lc.gcumedia.com/hlt362v/the-visual-learner/stratified-sample.html
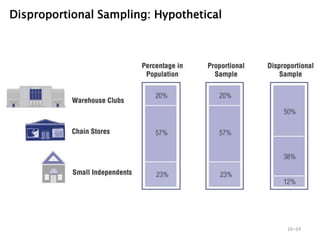
- 23. 16ŌĆō23 ŌĆó Proportional Stratified Sample ŌĆō The number of sampling units drawn from each stratum is in proportion to the population size of that stratum. ŌĆó Disproportional Stratified Sample ŌĆō The sample size for each stratum is allocated according to analytical considerations. Proportional versus Disproportional Sampling
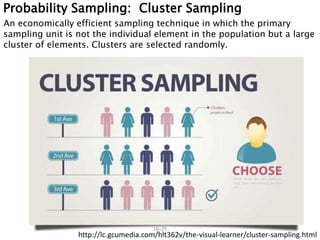
- 25. 16ŌĆō25 Probability Sampling: Cluster Sampling An economically efficient sampling technique in which the primary sampling unit is not the individual element in the population but a large cluster of elements. Clusters are selected randomly. http://lc.gcumedia.com/hlt362v/the-visual-learner/cluster-sampling.html
- 26. 16ŌĆō26 Multistage Area Sampling Involves using a combination of two or more probability sampling techniques. ŌĆó Typically, geographic areas are randomly selected in progressively smaller (lower-population) units. ŌĆó Researchers may take as many steps as necessary to achieve a representative sample. ŌĆó Progressively smaller geographic areas are chosen until a single housing unit is selected for interviewing.
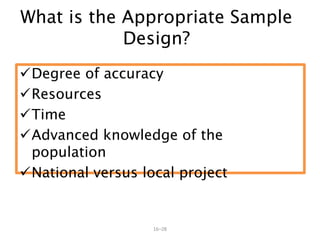
- 28. 16ŌĆō28 What is the Appropriate Sample Design? ’ā╝Degree of accuracy ’ā╝Resources ’ā╝Time ’ā╝Advanced knowledge of the population ’ā╝National versus local project
- 29. 16ŌĆō29 Internet Sampling is Unique ŌĆó Website Visitors ŌĆō Internet surveys use unrestricted samples. ŌĆō May not be representative. ŌĆó Panel Samples ŌĆó Recruited Ad Hoc Samples
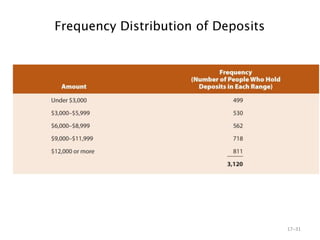
- 31. Frequency Distribution of Deposits 17ŌĆō31
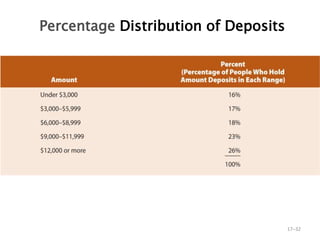
- 32. Percentage Distribution of Deposits 17ŌĆō32
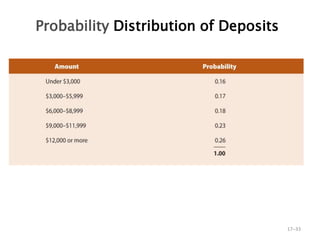
- 33. Probability Distribution of Deposits 17ŌĆō33
- 34. 17ŌĆō34 Factors of Concern in Choosing Sample Size 1. Variance (or Heterogeneity) ŌĆó A heterogeneous population has more variance (a larger standard deviation) which will require a larger sample. ŌĆó A homogeneous population has less variance (a smaller standard deviation) which permits a smaller sample. 2. Magnitude of Error (Confidence Interval) ŌĆó How precise must the estimate be? 3. Confidence Level ŌĆó How much error will be tolerated?
- 35. 17ŌĆō35 ŌĆó Sequential Sampling ŌĆō Conducting a pilot study to estimate the population parameters so that another, larger sample of the appropriate sample size may be drawn. ŌĆó Estimating sample size: Estimating Sample Size for Questions Involving Means
- 36. 17ŌĆō36 Sample Size Example Suppose a survey researcher, studying expenditures on lipstick, wishes to have a 95 percent confident level (Z) and a range of error (E) of less than $2.00. The estimate of the standard deviation is $29.00. What is the calculated sample size?
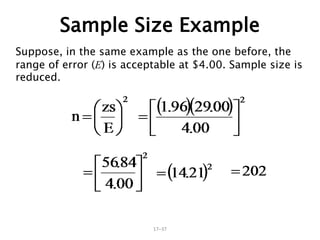
- 37. 17ŌĆō37 Sample Size Example Suppose, in the same example as the one before, the range of error (E) is acceptable at $4.00. Sample size is reduced.
- 38. Calculating Sample Size at the 99 Percent Confidence Level 17-38
- 39. Determining Sample Size for Proportions 17-39
- 40. Determining Sample Size for Proportions (contŌĆÖd) 17-40
- 41. 753 = 001225 . 922 . = 001225 ) 24 )(. 8416 . 3 ( = ) 035 ( . ) 4 )(. 6 (. ) 96 1. ( n 4 . q 6 . p 2 2 = = = Calculating Example Sample Size at the 95 Percent Confidence Level 17-41
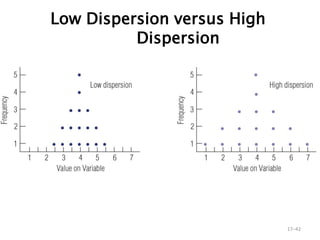
- 42. Low Dispersion versus High Dispersion 17ŌĆō42
- 43. LOs 1. Explain reasons for taking a sample rather than a complete census 2. Describe the process of identifying a target population and selecting a sampling frame 3. Compare random sampling and systematic (nonsampling) errors 4. Identify the types of nonprobability sampling, including their advantages and disadvantages 5. Discuss how to choose an appropriate sample design