1 of 13
Download to read offline








![10.[?????????]mlc v20160224](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-160224215915/85/10-mlc-v20160224-12-320.jpg)
![10.[?????????]mlc v20160224](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-160224215915/85/10-mlc-v20160224-13-320.jpg)
Ad
Recommended
radiation therapy in ca breast
radiation therapy in ca breast Isha Jaiswal
?
The document discusses the role of radiation therapy in breast cancer treatment, highlighting its ability to improve local control and overall survival rates in postoperative scenarios. It summarizes key findings from extensive trials, showing significant reductions in local recurrence and breast cancer mortality associated with radiation therapy following breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy. Additionally, it details treatment planning techniques, positioning, and dose distribution strategies crucial for effectively delivering radiation therapy to breast cancer patients.Isodose curves RADIATION ONCOLOGY
Isodose curves RADIATION ONCOLOGYPaul George
?
1. Isodose curves represent the dose distribution from radiation beams and are lines connecting points of equal percentage depth dose. They are used to depict the volumetric and planar variations in absorbed dose.
2. The parameters that affect the shape of isodose curves include beam quality, source size, SSD, SDD, field size, and beam modifiers like wedges and flattening filters. Lower beam energy results in greater lateral scatter and more bulging curves.
3. Multiple radiation fields can be combined using appropriate beam weights, sizes, angles and modifiers to deliver a more uniform dose to the tumor while sparing surrounding tissues. Parameters like setup accuracy and plan practicality are also considered.Beam modification in radiotherapy
Beam modification in radiotherapyTata Memorial Centre
?
This document discusses various methods of modifying radiation beams used in radiation therapy. It describes four main types of beam modification: shielding, compensation, wedge filtration, and flattening. Shielding is used to protect critical structures by devices like blocks, compensators help achieve uniform dose for irregular surfaces, wedge filters tilt the dose distribution, and flattening filters even out the natural beam profile. The document outlines different beam modifying devices and materials like wedges, compensators, bolus, and blocks. It discusses factors that must be considered for beam modification like scatter and attenuation. Overall, the document provides an overview of common techniques and devices used to modify radiation beams for optimal dose distribution in radiation therapy.13.[?????????]??????????????????????????????????????????????????
13.[?????????]??????????????????????????????????????????????????Samsung Medical Center
?
??????????????????????????????????????????????????12.[?????????]????????????????????????????????????????????
12.[?????????]????????????????????????????????????????????Samsung Medical Center
?
????????????????????????????????????????????10.[?????????]mlc v20160224(ch)
10.[?????????]mlc v20160224(ch)Samsung Medical Center
?
¶àҶ׼ֱÆ÷£¨³¾±ô³¦£©ÊÇÒ»ÖÖÓÃÓÚ¾«×¼ÕÕÉäÖ×Áö²¢±£»¤ÖÜΧÕý³£×éÖ¯µÄ×°Öá£Ó봫ͳÕڱοéÏà±È£¬³¾±ô³¦Äܹ»¼´Ê±µ÷ÕûÒÔÊÊÓ¦Ö×ÁöµÄÐÎ×´£¬ÏÔ×ÅËõ¶ÌÖÎÁÆ×¼±¸Ê±¼ä¡£ÈþÐÇÊ׶ûÒ½ÔºÖÊ×ÓÖÐÐÄÅ䱸ÁË×îÏȽøµÄ³¾±ô³¦¹¦ÄÜ£¬ÒÔÌá¸ßÖÎÁƾ«È·¶ÈºÍЧÂÊ¡£09.[?????????]cbct v20160224(ch)
09.[?????????]cbct v20160224(ch)Samsung Medical Center
?
°äµþ°ä°Õ£¨Ô²×¶Êø°ä°Õ£©ÊÇÒ»ÖÖÈþάӰÏñÉ豸£¬ÓÃÓÚʵʱȷÈÏÖ×ÁöµÄλÖã¬ÒÔÈ·±£ÔÚÖÊ×ÓÖÎÁÆÖÐÄÜ׼ȷÕÕÉäÖ×Áö²¿Î»¡£Í¨¹ý±È½ÏÖÎÁƼƻ®Öеİä°ÕÓëÖÎÁÆ×ËÊÆϵİäµþ°ä°Õ£¬¿É¼ì²â²¢µ÷ÕûλÖÃÆ«²î£¬´Ó¶øÌá¸ßÖÎÁƵÄ׼ȷÐÔ¡£Ê¹Óðäµþ°ä°Õ½øÐÐÈ·ÈÏ¿ÉÒÔÏÔ×ÅÔö¼ÓÖÎÁƵľ«×¼¶È¡£08.[?????????]?????????? v20160224(ch)
08.[?????????]?????????? v20160224(ch)Samsung Medical Center
?
ºôÎüͬ²½ÊÇÒ»ÖÖÖÎÁÆ·½·¨£¬Ö¼ÔÚÓ¦¶ÔÒòºôÎüµ¼ÖµÄÖ×ÁöºÍÔàÆ÷λÖñ仯¡£Í¨¹ý¼à¿ØºôÎü״̬ºÍʹÓÃËÄά³ÉÏñ¼¼Êõ£¬Äܹ»Öƶ¨¸ü¾«È·µÄ·ÅÉäÖÎÁƼƻ®£¬´Ó¶ø¼õÉÙ¶ÔÕý³£×éÖ¯µÄ·ÅÉäÏß¼ÁÁ¿¡£ÓÐЧµÄºôÎüͬ²½ÖÎÁƿɽµµÍ·ÅÉäÏßÕÕÉ䷶Χ£¬Ìá¸ßÖÎÁÆЧ¹û¡£More Related Content
More from Samsung Medical Center (20)
13.[?????????]??????????????????????????????????????????????????
13.[?????????]??????????????????????????????????????????????????Samsung Medical Center
?
??????????????????????????????????????????????????12.[?????????]????????????????????????????????????????????
12.[?????????]????????????????????????????????????????????Samsung Medical Center
?
????????????????????????????????????????????10.[?????????]mlc v20160224(ch)
10.[?????????]mlc v20160224(ch)Samsung Medical Center
?
¶àҶ׼ֱÆ÷£¨³¾±ô³¦£©ÊÇÒ»ÖÖÓÃÓÚ¾«×¼ÕÕÉäÖ×Áö²¢±£»¤ÖÜΧÕý³£×éÖ¯µÄ×°Öá£Ó봫ͳÕڱοéÏà±È£¬³¾±ô³¦Äܹ»¼´Ê±µ÷ÕûÒÔÊÊÓ¦Ö×ÁöµÄÐÎ×´£¬ÏÔ×ÅËõ¶ÌÖÎÁÆ×¼±¸Ê±¼ä¡£ÈþÐÇÊ׶ûÒ½ÔºÖÊ×ÓÖÐÐÄÅ䱸ÁË×îÏȽøµÄ³¾±ô³¦¹¦ÄÜ£¬ÒÔÌá¸ßÖÎÁƾ«È·¶ÈºÍЧÂÊ¡£09.[?????????]cbct v20160224(ch)
09.[?????????]cbct v20160224(ch)Samsung Medical Center
?
°äµþ°ä°Õ£¨Ô²×¶Êø°ä°Õ£©ÊÇÒ»ÖÖÈþάӰÏñÉ豸£¬ÓÃÓÚʵʱȷÈÏÖ×ÁöµÄλÖã¬ÒÔÈ·±£ÔÚÖÊ×ÓÖÎÁÆÖÐÄÜ׼ȷÕÕÉäÖ×Áö²¿Î»¡£Í¨¹ý±È½ÏÖÎÁƼƻ®Öеİä°ÕÓëÖÎÁÆ×ËÊÆϵİäµþ°ä°Õ£¬¿É¼ì²â²¢µ÷ÕûλÖÃÆ«²î£¬´Ó¶øÌá¸ßÖÎÁƵÄ׼ȷÐÔ¡£Ê¹Óðäµþ°ä°Õ½øÐÐÈ·ÈÏ¿ÉÒÔÏÔ×ÅÔö¼ÓÖÎÁƵľ«×¼¶È¡£08.[?????????]?????????? v20160224(ch)
08.[?????????]?????????? v20160224(ch)Samsung Medical Center
?
ºôÎüͬ²½ÊÇÒ»ÖÖÖÎÁÆ·½·¨£¬Ö¼ÔÚÓ¦¶ÔÒòºôÎüµ¼ÖµÄÖ×ÁöºÍÔàÆ÷λÖñ仯¡£Í¨¹ý¼à¿ØºôÎü״̬ºÍʹÓÃËÄά³ÉÏñ¼¼Êõ£¬Äܹ»Öƶ¨¸ü¾«È·µÄ·ÅÉäÖÎÁƼƻ®£¬´Ó¶ø¼õÉÙ¶ÔÕý³£×éÖ¯µÄ·ÅÉäÏß¼ÁÁ¿¡£ÓÐЧµÄºôÎüͬ²½ÖÎÁƿɽµµÍ·ÅÉäÏßÕÕÉ䷶Χ£¬Ìá¸ßÖÎÁÆЧ¹û¡£10.[?????????]mlc v20160224
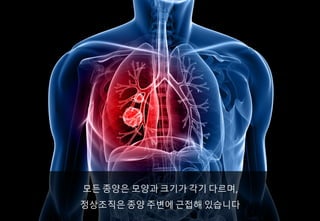
- 3. ?? ??? ??? ??? ?? ???, ????? ?? ??? ??? ????
- 4. ??, ??? ???? ??? ??? ????? ??? ?? ??? ??? ? ?????
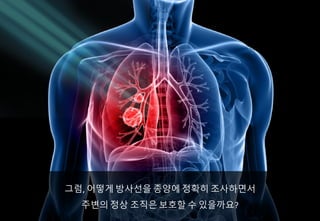
- 6. ????? ??? ??? ??? ??? ????, ?? ??? ?? ??? ??? ?????
- 7. ????, MLC? ?? ??? ????? ????? ???? ???? ? ? ????
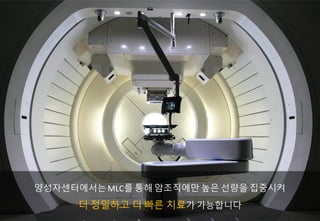
- 9. ??? ??? ????????? ??? ?, ???? ??? ??? ?? MLC???? ? ????
- 10. vs ??????? MLC(Multi-Leaf Collimator) ???? ?? ???? ????? ??? ?? ???? ??? MLC? ??? ????? ??? ?? ?? ????? ????? ??? ? ????
- 11. ????????MLC? ?? ????? ?? ??? ???? ? ???? ? ?? ??? ?????
