1,3 dipolar cycloadditions
- 1. RECENT ADVANCES IN 1,3-DIPOLAR CYCLOADDITIONS JAYANTA SAHA IIT ROPAR 2015CHS1003
- 2. INTRODUCTION The [3 + 2] 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is a reaction where two organic compounds, a dipolarophile, and a 1,3-dipole (or ylide), combine to form a five membered heterocycle B A C R2 R1 R1 A B C R2 + R3 R4 C B AR2 R1 R4R3 ÔÉòThis reaction is often used as a key step in many natural products and pharmaceuticals synthesis ÔÉòThe asymmetric variants of this reaction using either chiral auxiliaries or chiral catalysts are relatively new research fields and have attracted a continually growing interest
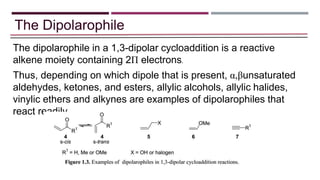
- 3. The Dipolarophile The dipolarophile in a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is a reactive alkene moiety containing 2Π electrons. Thus, depending on which dipole that is present, α,βunsaturated aldehydes, ketones, and esters, allylic alcohols, allylic halides, vinylic ethers and alkynes are examples of dipolarophiles that react readily
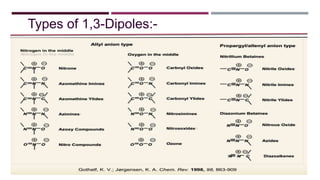
- 4. The 1,3-dipole/ylide The 1,3-dipole, also known as an ylide, bears a positive and a negative charge distributed over three atoms and has 4 Π electrons. The most common atoms incorporated in the 1,3-dipole are nitrogen, carbon, oxygen or sulfur. These are divided into two groups, the allyl anion type which has a bent structure and  the propargyl/allenyl anion type with a linear structure
- 6. Mechamisms for the 1,3-DC reaction The 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction of a 1,3-dipole with a dipolarophile involves the 4Π electrons of the dipole/ylide and the 2Π electrons of the dipolarophile. The reaction mostly proceeds in a concerted manner, which means that all bonds are created simultaneously Depending on the nature of the dipole and the dipolarophile, the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction is controlled either by a LUMO(dipolarophile)- HOMO(dipole)- or a LUMO(dipole)-HOMO(dipolarophile) interaction but insome cases both interactions is involved .
- 7. Mechamisms for the 1,3-DC reaction
- 8. The classification of the 1,3-DC reactions onthe basis of the FMOs NITRONE NITRILE OXIDE Azomethine imine Diazoalkene Nitosooxide Ozone
- 9. The change in frontier orbitals by coordination of a Lewis acid Type II
- 10. Recent Literature 1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions of azomethine ylides with aromatic dipolarophiles General reaction Examples of isoindole-containing natural products, pharmaceuticals and dyes: (+)-staurosporine 4 (indolocarbazole alkaloid), mitiglinide 5 (type 2 diabetes),46 lenalidomide 6 (anticancer, multiple myeloma), and Pigment Yellow 139 7 (dye).
- 11. 1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions of azomethine ylides with aromatic dipolarophiles Some products formed in this manner Main reaction John H. Ryan,ARKIVOC 2015 (i) 160-183
- 12. Methods for asymmetric 1,3-DC reactions of Nitrones with Alkenes Pellissier, H. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 3235-3285
- 13. N H Ph X H H exo endo Stereoselectivity Regioselectivity EDG H NPh H NPh EWG head-to-head head-to-tail N H Ph H H XN H Ph N H Ph X X N H Ph EDG N H Ph EWG General Approach to the Selectivity in 1,3-Dipolar Cycloadditions
- 14. Acylaziridines Methods for asymmetric 1,3-DC reactions of Nitrones with Alkenes
- 15. J.Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 4999 + Methods for asymmetric 1,3-DC reactions of Nitrones with Alkenes
- 16. Application of cycloaddition reaction in natural product synthesis
![INTRODUCTION
The [3 + 2] 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is a reaction where two organic
compounds, a dipolarophile, and a 1,3-dipole (or ylide), combine to
form a five membered heterocycle
B
A
C
R2
R1 R1
A
B
C
R2
+
R3
R4
C
B
AR2 R1
R4R3
ÔÉòThis reaction is often used as a key step in many natural products and
pharmaceuticals synthesis
ÔÉòThe asymmetric variants of this reaction using either chiral auxiliaries or chiral
catalysts are relatively new research fields and have attracted a continually
growing interest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-dipolarcycloadditions-160909194941/85/1-3-dipolar-cycloadditions-2-320.jpg)